
Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are currently 485 species in this family, divided among 9 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.

A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions often have a centre of necrosis or cell death. Symptoms can overlap across causal agents, however differing signs and symptoms of certain pathogens can lead to the diagnosis of the type of leaf spot disease. Prolonged wet and humid conditions promote leaf spot disease and most pathogens are spread by wind, splashing rain or irrigation that carry the disease to other leaves.

Plum pox, also known as sharka, is the most devastating viral disease of stone fruit from the genus Prunus. The disease is caused by the plum pox virus (PPV), and the different strains may infect a variety of stone fruit species including peaches, apricots, plums, nectarine, almonds, and sweet and tart cherries. Wild and ornamental species of Prunus may also become infected by some strains of the virus.

Potato leafroll virus (PLRV) is a member of the genus Polerovirus and family Luteoviridae. The phloem limited positive sense RNA virus infects potatoes and other members of the family Solanaceae. PLRV was first described by Quanjer et al. in 1916. PLRV is transmitted by aphids, primarily the green peach aphid, Myzus persicae. PLRV is one of the most important potato viruses worldwide but particularly devastating in countries with limited resources and management. It can be responsible for individual plant yield losses of over 50%. One estimate suggests that PLRV is responsible for an annual global yield loss of 20 million tons. Symptoms include chlorosis, necrosis and leaf curling.
Citrus tristeza virus (CTV) is a viral species of the genus Closterovirus that causes the most economically damaging disease to its namesake plant genus, Citrus. The disease has led to the death of millions of Citrus trees all over the world and has rendered millions of others useless for production. Farmers in Brazil and other South American countries gave it the name "tristeza", meaning sadness in Portuguese and Spanish, referring to the devastation produced by the disease in the 1930s. The virus is transmitted most efficiently by the brown citrus aphid.
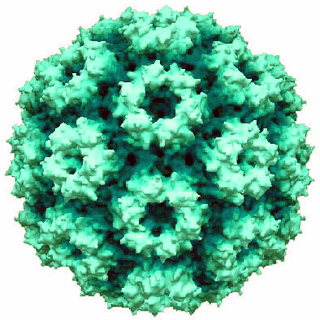
Cowpea chlorotic mottle virus, known by the abbreviation CCMV, is a virus that specifically infects the cowpea plant, or black-eyed pea. The leaves of infected plants develop yellow spots, hence the name "chlorotic". Similar to its "brother" virus, Cowpea mosaic virus (CPMV), CCMV is produced in high yield in plants. In the natural host, viral particles can be produced at 1–2 mg per gram of infected leaf tissue. Belonging to the bromovirus genus, cowpea chlorotic mottle virus (CCMV) is a small spherical plant virus. Other members of this genus include the brome mosaic virus (BMV) and the broad bean mottle virus (BBMV).

Podosphaera leucotricha is a plant pathogen that can cause powdery mildew of apples and pears.

Apple mosaic virus (ApMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Bromoviridae. It is named after its symptoms that were first present on apples. ApMV is a positive sense RNA based virus. The disease itself has several synonyms including Mild Apple Mosaic Virus, Hop Virus, Rose Mosaic Virus, and European Plum Line Patten Virus. It causes a severe yield reduction and decreased life-expectancy of fruit trees.
Cherry mottle leaf virus (CMLV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing leaf rot. It is closely related to the peach mosaic virus.

Cymbidium mosaic virus (CymMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Alphaflexiviridae.
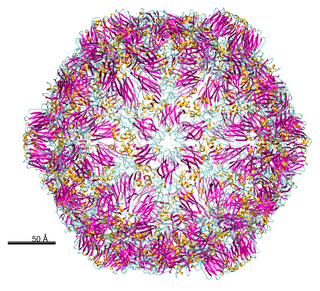
Grapevine fanleaf virus (GFLV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Secoviridae. It infects grapevines, causing chlorosis of the leaves and lowering the fruit quality. Because of its effect on grape yield, GFLV is a pathogen of commercial importance. It is transmitted via a nematode vector, Xiphinema index. This nematode acquires the virus through feeding on roots of an infected plant, and passes it on in the same manner.
Groundnut rosette virus (GRV) is a peanut pathogenic virus found in Sub-Saharan Africa. It is transmitted between plants by insect vectors such as the groundnut aphid.
Maize Dwarf Mosaic Virus (MDMV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the family Potyviridae. Depending on the corn plant’s growth stage, the virus can have severe implications to the corn plant’s development which can also result in economic consequences to the producer of the crop.

Prunus necrotic ringspot virus (PNRSV) is a plant pathogenic virus causing ring spot diseases affecting species of the genus Prunus, as well as other species such as rose and hops. PNRSV is found worldwide due to easy transmission through plant propagation methods and infected seed. The virus is in the family Bromoviridae and genus Ilarvirus. Synonyms of PNRSV include European plum line pattern virus, hop B virus, hop C virus, plum line pattern virus, sour cherry necrotic ringspot virus, and peach ringspot virus.
Tobacco ringspot virus is a plant pathogenic virus in the plant virus family Secoviridae. It is the type species of the genus Nepovirus. Nepoviruses are transmitted between plants by nematodes, varroa mites and honeybees. TRSV is also easily transmitted by sap inoculation and transmission in seeds has been reported. In recent cases it has also been shown to appear in bees.

Orthotospovirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses, in the family Tospoviridae of the order Bunyavirales, which infects plants. Tospoviruses take their name from the type species tomato spotted wilt orthotospovirus (TSWV) which was discovered in Australia in 1919. The type species remained the only member of the family until the early 1990s when genetic characterisation of plant viruses became more common. There are now at least twenty species in the genus with more being discovered on a regular basis. Member viruses infect over eight hundred plant species from 82 different families.

Trichovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically angiosperms such as pome fruits, citrus, and pear, serve as natural hosts for this plant pathogen. There are currently seven species in this genus including the type species Apple chlorotic leaf spot virus.
Grapevine leafroll-associated virus (GLRaV) is a name for a group of viruses infecting grapevine in the genus Closterovirus.
Badnavirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caulimoviridae order Ortervirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 59 species in this genus including the type species Commelina yellow mottle virus. Diseases associated with this genus include: CSSV: leaf chlorosis, root necrosis, red vein banding in young leaves, small mottled pods, and stem/root swelling followed by die-back. Infection decreases yield by 25% within one year, 50% within two years and usually kills trees within 3–4 years.
Cocoa necrosis virus (CNV) is a plant pathogenic virus of the genus nepovirus that infects Theobroma cacao en natura causing cacao necrosis disease. CNV is considered synonymous with Strain S of cacao swollen shoot virus. Unlike Cacao swollen shoot virus, it is not transmitted by mealybugs nor vectored by aphids, beetles, or leafhoppers that also commonly infest cacao. It is serologically, distantly related to Tomato black ring virus and very distantly related to Grapevine chrome mosaic virus.













