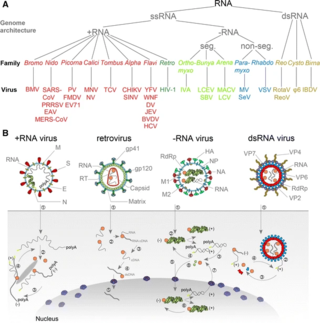
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.
Order is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families.
Flexiviridae was a family of viruses named after being filamentous and highly flexible. Members of the family infect plants. In 2009, the family was dissolved and replaced with four families, each of which still contain the name flexiviridae:

Tymoviridae is a family of single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 42 species in this family, assigned to three genera, with two species unassigned to a genus.

The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV) authorizes and organizes the taxonomic classification of and the nomenclatures for viruses. The ICTV has developed a universal taxonomic scheme for viruses, and thus has the means to appropriately describe, name, and classify every virus that affects living organisms. The members of the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses are considered expert virologists. The ICTV was formed from and is governed by the Virology Division of the International Union of Microbiological Societies. Detailed work, such as delimiting the boundaries of species within a family, typically is performed by study groups of experts in the families.

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Trichovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically angiosperms such as pome fruits, citrus, and pear, serve as natural hosts for this plant pathogen. There are seven species in this genus.

Picornavirales is an order of viruses with vertebrate, invertebrate, protist and plant hosts. The name has a dual etymology. First, picorna- is an acronym for poliovirus, insensitivity to ether, coxsackievirus, orphan virus, rhinovirus, and ribonucleic acid. Secondly, pico-, meaning extremely small, combines with RNA to describe these very small RNA viruses. The order comprises viruses that historically are referred to as picorna-like viruses.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Betaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 108 species in this family, assigned to 13 genera in two subfamilies. Diseases associated with this family include mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Vitivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 15 species in this genus.
Lolavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically ryegrass, serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Lolium latent virus.
Capillovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, pome fruits, citrus, and pear serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: abnormal graft union, possibly black necrotic leaf spot disease.
Foveavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are eight species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Maculavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Grapevine fleck virus.
Marafivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this genus.

Tymovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Tymoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 28 species in this genus.
Citrivirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Citrus leaf blotch virus.
Tepovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants as well as some other root and tuber crops in the andes serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus.
Alsuviricetes is a class of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. The name of the group is a syllabic abbreviation of "alpha supergroup" with the suffix -viricetes indicating a virus class.