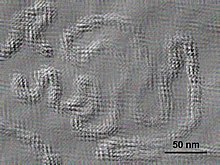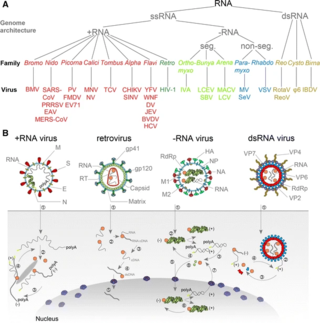
An RNA virus is a virus characterized by a ribonucleic acid (RNA) based genome. The genome can be single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) or double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include influenza, SARS, MERS, COVID-19, Dengue virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.

Potyviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses that encompasses more than 30% of known plant viruses, many of which are of great agricultural significance. The family has 12 genera and 235 species, three of which are unassigned to a genus.
Closterovirus, also known as beet yellows viral group, is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 17 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem. This genus has a probably worldwide distribution and includes among other viral species the Beet yellows virus and Citrus tristeza virus, rather economically important plant diseases. At least some species require vectors such as aphids or mealybugs for their transmission from plant to plant.

Crinivirus, formerly the lettuce infectious yellows virus group, is a genus of viruses, in the family Closteroviridae. They are linear, single-stranded positive sense RNA viruses. There are 14 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.

Dependoparvovirus is a genus in the subfamily Parvovirinae of the virus family Parvoviridae; they are Group II viruses according to the Baltimore classification.

Alfalfa mosaic virus (AMV), also known as Lucerne mosaic virus or Potato calico virus, is a worldwide distributed phytopathogen that can lead to necrosis and yellow mosaics on a large variety of plant species, including commercially important crops. It is the only Alfamovirus of the family Bromoviridae. In 1931 Weimer J.L. was the first to report AMV in alfalfa. Transmission of the virus occurs mainly by some aphids, by seeds or by pollen to the seed.
Strawberry mottle virus (SMV) is a pathogenic plant virus in Secoviridae, a family of plant-infecting picornaviruses. It is not yet assigned to a genus. Virions are isometric, approximately 28 nm in diameter, and contain two RNA strands (RNA1 and RNA2) equal to about 12,600 nucleotides in length. The polyprotein of RNA1 contains regions identified as helicase, protease, RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and a viral genome-linked protein while RNA2 shows similarities to the large coat protein domain of the Satsuma dwarf virus.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.

Benyvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Benyviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: BNYVV: rhizomania.
Sadwavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Picornavirales, in the family Secoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are three subgenera and five species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: satsuma dwarf virus disease which causes spoon-shaped leaves on citrus tree. Symptoms are enations, multiple flushing, stunting or dwarfing, reduction in number and size of leaves and fruits. The name of this genus comes from one of its species: Satsuma dwarf virus.

Sobemovirus is a genus of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 21 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaics and mottles.
Umbravirus is a genus of plant viruses assigned to the family Tombusviridae. The genus has 11 species.

Potexvirus is a genus of pathogenic viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Alphaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 48 species in this genus, three of which are assigned to a subgenus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms. The genus name comes from POTato virus X).

Carlavirus, formerly known as the "Carnation latent virus group", is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 53 species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.

Trichovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Tymovirales, in the family Betaflexiviridae. Plants, specifically angiosperms such as pome fruits, citrus, and pear, serve as natural hosts for this plant pathogen. There are seven species in this genus.
Picobirnavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only genus in the family Picobirnaviridae. Although amniotes, especially mammals, were thought to serve as hosts, it has been recently suggested that these viruses might infect bacteria and possibly some other invertebrates. If they do infect bacteria, then they are Bacteriophages. There are three species in this genus. Associated symptoms include gastroenteritis in animals and humans, though the disease association is unclear.
Lagovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Caliciviridae. Lagomorphs serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: necrotizing hepatitis leading to fatal hemorrhages.
Gammaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus in the family, Mycoflexivirus, which has one species: Botrytis virus F.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.

The Blueberry mosaic associated ophiovirus (B1MaV) is a plant virus which infects blueberry plants, causing a discoloration of the leaves of the plants in a mosaic-like pattern. The disease is found in blueberry plants in many regions of North America, as well as South America, Europe, New Zealand, and South Africa. Within these regions the virus is most often found in high blueberry-yielding areas, but can be spread to other locations. Blueberry mosaic associatedophiovirus is one of seven species in the genus Ophiovirus. It is a member of the Aspiviridae family, in the Serpentovirales order, and in the Milnevircetes class. The Ophioviridae viruses are characterized by a flexible and elongated nucleocapsid that is composed mostly of filamentous structures and is helically symmetrical. It also has a non-enveloped protein capsid that is capable of coiling around itself allowing for a super-coiled structure and the helical symmetry. The virus has the potential to be symptomatic or asymptomatic within plants causing the display of symptoms in only a few plants, but the ability to transmit the virus unknowingly in many plants. B1MaV often remains asymptomatic for long periods of time after initial infection allowing for blind transmission.