
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: Duplodnaviria and Varidnaviria, and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm Monodnaviria, which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom Pararnavirae in the realm Riboviria.

Geminiviridae is a family of plant viruses that encode their genetic information on a circular genome of single-stranded (ss) DNA. There are 520 species in this family, assigned to 14 genera. Diseases associated with this family include: bright yellow mosaic, yellow mosaic, yellow mottle, leaf curling, stunting, streaks, reduced yields. They have single-stranded circular DNA genomes encoding genes that diverge in both directions from a virion strand origin of replication. According to the Baltimore classification they are considered class II viruses. It is the largest known family of single stranded DNA viruses.
Pseudoviridae is a family of viruses, which includes three genera.
Baltimore classification is a system used to classify viruses based on their manner of messenger RNA (mRNA) synthesis. By organizing viruses based on their manner of mRNA production, it is possible to study viruses that behave similarly as a distinct group. Seven Baltimore groups are described that take into consideration whether the viral genome is made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) or ribonucleic acid (RNA), whether the genome is single- or double-stranded, and whether the sense of a single-stranded RNA genome is positive or negative.
Yingchengvirus is a genus of double stranded DNA viruses that infect haloarchaea. The genus was previously named Betasphaerolipovirus.

Positive-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have positive-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. The positive-sense genome can act as messenger RNA (mRNA) and can be directly translated into viral proteins by the host cell's ribosomes. Positive-strand RNA viruses encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp) which is used during replication of the genome to synthesize a negative-sense antigenome that is then used as a template to create a new positive-sense viral genome.
Polintons are large DNA transposons which contain genes with homology to viral proteins and which are often found in eukaryotic genomes. They were first discovered in the mid-2000s and are the largest and most complex known DNA transposons. Polintons encode up to 10 individual proteins and derive their name from two key proteins, a DNA polymerase and a retroviral-like integrase.

Genomoviridae is a family of single stranded DNA viruses that mainly infect fungi. The genomes of this family are small. The genomes are circular single-stranded DNA and encode rolling-circle replication initiation proteins (Rep) and unique capsid proteins. In Rep-based phylogenies, genomoviruses form a sister clade to plant viruses of the family Geminiviridae. Ten genera are recognized in this family.
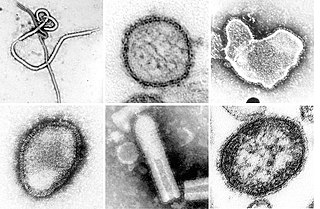
Negative-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA). They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented.
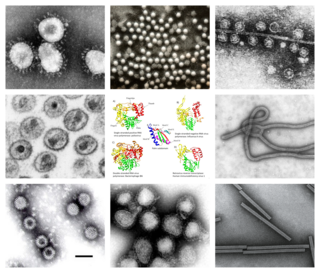
Riboviria is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, as well as reverse-transcribing viruses that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins.
In virology, realm is the highest taxonomic rank established for viruses by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), which oversees virus taxonomy. Six virus realms are recognized and united by specific highly conserved traits:

Redondoviruses are a family of human-associated DNA viruses. Their name derives from the inferred circular structure of the viral genome . Redondoviruses have been identified in DNA sequence based surveys of samples from humans, primarily samples from the oral cavity and upper airway.

Smacoviridae is a family of single-stranded DNA viruses. The genomes of this family are small. The name Smacoviridae stands for 'small circular genome virus'. The genomes are circular single-stranded DNA and encode rolling-circle replication initiation proteins (Rep) and unique capsid proteins. As of 2021, 12 genera and 84 species are recognized in this family. The viruses in this taxon were isolated from faecal samples from insects and vertebrates by metagenomic methods. Little is known about their biology.

Monodnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all single-stranded DNA viruses that encode an endonuclease of the HUH superfamily that initiates rolling circle replication of the circular viral genome. Viruses descended from such viruses are also included in the realm, including certain linear single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses and circular double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses. These atypical members typically replicate through means other than rolling circle replication.

Varidnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes all DNA viruses that encode major capsid proteins that contain a vertical jelly roll fold. The major capsid proteins (MCP) form into pseudohexameric subunits of the viral capsid, which stores the viral deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA), and are perpendicular, or vertical, to the surface of the capsid. Apart from this, viruses in the realm also share many other characteristics, such as minor capsid proteins (mCP) with the vertical jelly roll fold, an ATPase that packages viral DNA into the capsid, and a DNA polymerase that replicates the viral genome.

Bacilladnaviridae is a family of single-stranded DNA viruses that primarily infect diatoms.

Orthornavirae is a kingdom of viruses that have genomes made of ribonucleic acid (RNA), including genes which encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). The RdRp is used to transcribe the viral RNA genome into messenger RNA (mRNA) and to replicate the genome. Viruses in this kingdom share a number of characteristics which promote rapid evolution, including high rates of genetic mutation, recombination, and reassortment.
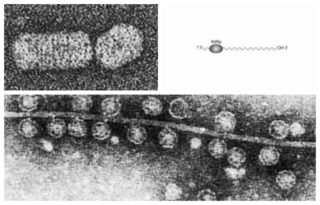
Lenarviricota is a phylum of RNA viruses that includes all positive-strand RNA viruses that infect prokaryotes. Some members also infect eukaryotes. Most of these viruses do not have capsids, except for the genus Ourmiavirus. The name of the group is a syllabic abbreviation of the names of founding member families "Leviviridae and Narnaviridae" with the suffix -viricota, denoting a virus phylum.

An archaeal virus is a virus that infects and replicates in archaea, a domain of unicellular, prokaryotic organisms. Archaeal viruses, like their hosts, are found worldwide, including in extreme environments inhospitable to most life such as acidic hot springs, highly saline bodies of water, and at the bottom of the ocean. They have been also found in the human body. The first known archaeal virus was described in 1974 and since then, a large diversity of archaeal viruses have been discovered, many possessing unique characteristics not found in other viruses. Little is known about their biological processes, such as how they replicate, but they are believed to have many independent origins, some of which likely predate the last archaeal common ancestor (LACA).
Virosphere was coined to refer to all those places in which viruses are found or which are affected by viruses. However, more recently virosphere has also been used to refer to the pool of viruses that occurs in all hosts and all environments, as well as viruses associated with specific types of hosts, type of genome or ecological niche.














