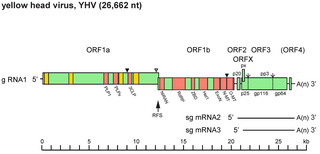
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Barnaviridae is a family of non-enveloped, positive-strand RNA viruses. Cultivated mushrooms serve as natural hosts. The family has one genus, Barnavirus, which contains one species: Mushroom bacilliform virus. Diseases associated with this family includes La France disease.
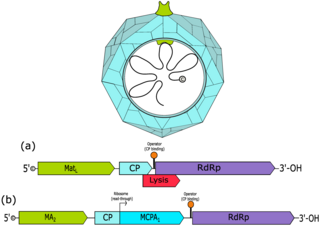
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Ilarvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 22 species in this genus.

Ourmiavirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses. Cucurbits, cherry, and cassava serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: OuMV: yellowing and chlorotic spot symptoms.

Alphaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Plants and fungi serve as natural hosts. There are 65 species in this family, assigned to six genera. Diseases associated with this family include: mosaic and ringspot symptoms.
Gammaflexiviridae is a family of viruses in the order Tymovirales. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There is only one genus in the family, Mycoflexivirus, which has one species: Botrytis virus F.
Yatapoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Monkeys and baboons serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: histiocytomas, tumor-like mass of mononuclear cells.

Virgaviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. The name of the family is derived from the Latin word virga (rod), as all viruses in this family are rod-shaped. There are currently 59 species in this family, divided among seven genera.

Qubevirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family Fiersviridae. Enterobacteria serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. In 2020, the genus was renamed from Allolevivirus to its current name.

Alphanodavirus is a genus of non-enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Nodaviridae. Insects, mammals, and fishes serve as natural hosts. Diseases associated with this genus include: Nodamura virus paralysis in infected wax moth larvae. Member viruses can also provoke paralysis and death to suckling mice and suckling hamsters. There are five species in this genus.
Alphatetraviridae is a family of viruses. Moths and butterflies serve as natural hosts. There are two genera in the family. Infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.
Cervidpoxvirus is a genus of viruses in the family Poxviridae in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Deer serve as natural hosts. Only one species is in this genus: Mule deerpox virus.
Leporipoxvirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Poxviridae, in the subfamily Chordopoxvirinae. Lagomorphs and squirrels serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus. Diseases associated with this genus include: myxomatosis.
Emesvirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family Fiersviridae. Enterobacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus. In 2020, the genus was renamed from Levivirus to its current name.
Mitovirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses, in the family Mitoviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are five species in the genus.
Narnavirus is a genus of positive-strand RNA viruses in the family Narnaviridae. Fungi serve as natural hosts. There are two species in this genus. Member viruses have been shown to be required for sexual reproduction of Rhizopus microsporus. Narnaviruses have a naked RNA genome without a virion and derive their name from this feature.

Carmotetraviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses. There is only one genus in this family, Alphacarmotetravirus, which has one species: Providence virus. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts.
Permutotetraviridae is a family of viruses. Lepidopteran insects serve as natural hosts. The family contains one genus that has two species. Diseases associated with this family include: infection outcome varies from unapparent to lethal.

Quadriviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with a single genus Quadrivirus. The fungi Rosellinia necatrix serves as a natural host. The name of the group derives from the quadripartite genome of its members where in Latin quad means four. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix quadrivirus 1.












