Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.
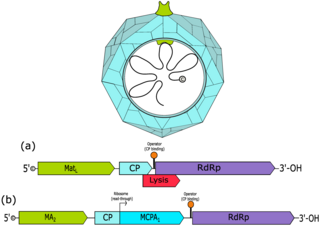
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Lipothrixviridae is a family of viruses in the order Ligamenvirales. Thermophilic archaea in the phylum Thermoproteota serve as natural hosts. There are 11 species in this family, assigned to 4 genera. The genus

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.

Schizotequatrovirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Myoviridae, in the subfamily Tevenvirinae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There are three species in this genus.
Rosenblumvirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Rountreeviridae, in the subfamily Rakietenvirinae. Gram positive bacteria serve as natural hosts, with transmission achieved through passive diffusion. There are 12 species in this genus.
Spbetavirus is a genus of viruses in the order Caudovirales, in the family Siphoviridae. Bacteria serve as natural hosts. There is only one species in this genus: Bacillus virus SPbeta.
Semotivirus is the only genus of viruses in the family Belpaoviridae. Species exist as retrotransposons in a eukaryotic host's genome. BEL/pao transposons are only found in animals.
Riboviria is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, as well as reverse-transcribing viruses that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins.
Tectiliviricetes is a class of viruses.

Ribozyviria is a realm of satellite nucleic acids. Established in ICTV TaxoProp 2020.012D, the realm is named after the presence of genomic and antigenomic ribozymes of the Deltavirus type. Additional common features include a rod-like structure, a RNA-binding "delta antigen" encoded in the genome, and animal hosts. Furthermore, the size range of the genomes of these viruses is between around 1547–1735nt, they encode a hammerhead ribozyme or a hepatitis delta virus ribozyme, and their coding capacity only involves one conserved protein. Most lineages of this realm are poorly understood, the notable exception being members of the genus Deltavirus, the causal agents of Hepatitis D in humans.

Adnaviria is a realm of viruses that includes archaeal viruses that have a filamentous virion and a linear, double-stranded DNA genome. The genome exists in A-form (A-DNA) and encodes a dimeric major capsid protein (MCP) that contains the SIRV2 fold, a type of alpha-helix bundle containing four helices. The virion consists of the genome encased in capsid proteins to form a helical nucleoprotein complex. For some viruses, this helix is surrounded by a lipid membrane called an envelope. Some contain an additional protein layer between the nucleoprotein helix and the envelope. Complete virions are long and thin and may be flexible or a stiff like a rod.
Leviviricetes is a class of viruses, which infect prokaryotes. Most of these bacteriophages were discovered by metagenomics.
Norzivirales is an order of viruses, which infect prokaryotes. Most of these bacteriophages were discovered by metagenomics.
Atkinsviridae is a family of RNA viruses, which infect prokaryotes.
Solspiviridae is a family of RNA viruses, which infect prokaryotes.
Steitzviridae is a family of RNA viruses, which infect prokaryotes.
Blumeviridae is a family of RNA viruses, which infect prokaryotes.
Duinviridae is a family of RNA viruses, which infect prokaryotes.
Bacteriophage φCb5 is a bacteriophage that infects Caulobacter bacteria and other caulobacteria. The bacteriophage was discovered in 1970, it belongs to the genus Cebevirus of the Steitzviridae family and is the type species of the family. The bacteriophage is widely distributed in the soil, freshwater lakes, streams and seawater, places where caulobacteria inhabit and can be sensitive to salinity.





