| Ortervirales | |
|---|---|
 | |
| HI-virión | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Riboviria |
| Kingdom: | Pararnavirae |
| Phylum: | Artverviricota |
| Class: | Revtraviricetes |
| Order: | Ortervirales |
| Families | |
Ortervirales is an order that contains all accepted species of single-stranded RNA viruses that replicate through a DNA intermediate (Group VI) and all accepted species of double-stranded DNA viruses (except Hepadnaviridae ) that replicate through an RNA intermediate (Group VII). [1] [2] The name is derived from the reverse of retro. [3]
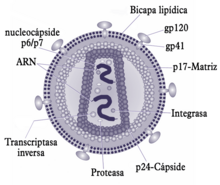
All reverse-transcribing viruses possess significant similarities to each other. Their reverse transcriptase proteins share a common origin. Moreover, belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses, and retroviruses have other features in common. Their polymerase proteins are similar in structure and include aspartic protease (retroviral aspartyl protease) and an integrase belonging to the DDE recombinase superfamily (see Recombination-activating gene [structure]). They also share similar capsid and nucleocapsid proteins/domains. [4] Caulimoviruses also share some features with belpaoviruses, metaviruses, pseudoviruses, and retroviruses such as a homologous aspartate protease. On the other hand, Hepadnaviridae family is part of a sister order of Ortervirales called Blubervirales . [1]