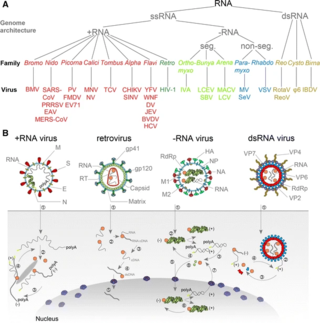
An RNA virus is a virus—other than a retrovirus—that has ribonucleic acid (RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA viruses include the common cold, influenza, SARS, MERS, Covid-19, Dengue Virus, hepatitis C, hepatitis E, West Nile fever, Ebola virus disease, rabies, polio, mumps, and measles.
Virus classification is the process of naming viruses and placing them into a taxonomic system similar to the classification systems used for cellular organisms.

Bunyavirales is an order of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses with mainly tripartite genomes. Member viruses infect arthropods, plants, protozoans, and vertebrates. It is the only order in the class Ellioviricetes. The name Bunyavirales derives from Bunyamwera, where the original type species Bunyamwera orthobunyavirus was first discovered. Ellioviricetes is named in honor of late virologist Richard M. Elliott for his early work on bunyaviruses.

An arenavirus is a bi- or trisegmented ambisense RNA virus that is a member of the family Arenaviridae. These viruses infect rodents and occasionally humans. A class of novel, highly divergent arenaviruses, properly known as reptarenaviruses, have also been discovered which infect snakes to produce inclusion body disease. At least eight arenaviruses are known to cause human disease. The diseases derived from arenaviruses range in severity. Aseptic meningitis, a severe human disease that causes inflammation covering the brain and spinal cord, can arise from the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Hemorrhagic fever syndromes, including Lassa fever, are derived from infections such as Guanarito virus, Junin virus, Lassa virus, Lujo virus, Machupo virus, Sabia virus, or Whitewater Arroyo virus. Because of the epidemiological association with rodents, some arenaviruses and bunyaviruses are designated as roboviruses.

Portunus trituberculatus, the gazami crab, South Korea's blue crab or horse crab, is the most widely fished species of crab in the world. It is found off the coasts of East Asia and is closely related to Portunus armatus.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.
Dabie bandavirus, also called SFTS virus, is a tick-borne virus in the genus Bandavirus in the family Phenuiviridae, order Bunyavirales. The clinical condition it caused is known as severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome (SFTS). SFTS is an emerging infectious disease that was first described in northeast and central China 2009 and now has also been discovered in Japan, South Korea, Vietnam and Taiwan in 2015. SFTS has a fatality rate of 12% and as high as over 30% in some areas. The major clinical symptoms of SFTS are fever, vomiting, diarrhea, multiple organ failure, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and elevated liver enzyme levels. Another outbreak occurred in East China in the early half of 2020.
Amur virus (AMRV) is a zoonotic negative-sense single-stranded RNA virus. It may be a member of the genus Orthohantavirus, but it has not be definitively classified as a species and may only be a strain. It has been identified as a causative agent of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome.
The Pacific spadenose shark is a species of requiem shark, in the family Carcharhinidae. It was once regarded as conspecific to the spadenose shark.
Serang virus(SERV) is a single-stranded, negative-sense, enveloped, novel RNA orthohantavirus.

Quaranjavirus is a genus of enveloped RNA viruses, one of seven genera in the virus family Orthomyxoviridae. The genome is single-stranded, negative-sense segmented RNA, generally with six segments. The genus contains two species: Johnston Atoll virus and Quaranfil virus; it has been proposed to contain species or strains including Cygnet River virus, Lake Chad virus, Tyulek virus and Wellfleet Bay virus. Quaranjaviruses predominantly infect arthropods and birds; As of March 2015, Quaranfil quaranjavirus is the only member of the genus to have been shown to infect humans. The Quaranfil and Johnston Atoll viruses are transmitted between vertebrates by ticks, resembling members of Thogotovirus, another genus of Orthomyxoviridae.

Phenuiviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Ruminants, camels, humans, and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Member genus Phlebovirus is the only genus of the family that has viruses that cause disease in humans except Dabie bandavirus.
Negative-strand RNA viruses are a group of related viruses that have negative-sense, single-stranded genomes made of ribonucleic acid. They have genomes that act as complementary strands from which messenger RNA (mRNA) is synthesized by the viral enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp). During replication of the viral genome, RdRp synthesizes a positive-sense antigenome that it uses as a template to create genomic negative-sense RNA. Negative-strand RNA viruses also share a number of other characteristics: most contain a viral envelope that surrounds the capsid, which encases the viral genome, −ssRNA virus genomes are usually linear, and it is common for their genome to be segmented.
Mivirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect arthropods. Member viruses have nonsegmented and bisegmented genomes. There are nine species in the genus.
Yingvirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect invertebrates. Member viruses have bisegmented genomes. It is the only genus in the family Qinviridae, which is the only family in Muvirales, which is the only order in Chunqiuviricetes. There are eight species in the genus.

Monjiviricetes is a class of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect fungi, plants, invertebrates, and vertebrates. The name is a portmanteau of the two orders within the class, Mononegavirales and Jingchuvirales and the suffix for a virus class -viricetes.
Riboviria is a realm of viruses that includes all viruses that use a homologous RNA-dependent polymerase for replication. It includes RNA viruses that encode an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, as well as reverse-transcribing viruses that encode an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), also called RNA replicase, produces RNA from RNA. RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (RdDp), also called reverse transcriptase (RT), produces DNA from RNA. These enzymes are essential for replicating the viral genome and transcribing viral genes into messenger RNA (mRNA) for translation of viral proteins.
Pisoniviricetes is a class of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. A characteristic of the group is a conserved 3C-like protease from the PA clan of proteases for processing the translated polyprotein. The name of the group is a portmanteau of member orders "picornavirales, sobelivirales, nidovirales" and -viricetes which is the suffix for a virus class.

Sobelivirales is an order of RNA viruses which infect eukaryotes. Member viruses have a positive-sense single-stranded RNA genome. The name of the group is a portmanteau of member orders "sobemovirus-like" and -virales which is the suffix for a virus order.

Ribozyviria is a realm of satellite nucleic acids. Established in ICTV TaxoProp 2020.012D, the realm is named after the presence of genomic and antigenomic ribozymes of the Deltavirus type. Additional common features include a rod-like structure, a RNA-binding "delta antigen" encoded in the genome, and animal hosts. Furthermore, the size range of the genomes of these viruses is between around 1547–1735nt, they encode a hammerhead ribozyme or a hepatitis delta virus ribozyme, and their coding capacity only involves one conserved protein. Most lineages of this realm are poorly understood, the notable exception being members of the genus Deltavirus, the causal agents of Hepatitis D in humans.














