
Nanoviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are currently 12 species in this family, divided among 2 genera and one unassigned species. Diseases associated with this family include: stunting. Their name is derived from the Greek word νᾶνος, because of their small genome and their stunting effect on infected plants.
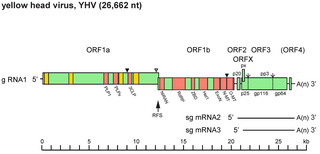
Okavirus is a genus of enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses which infect crustaceans. Host organisms are mostly shrimp. It is the only genus in the family Roniviridae. Viruses associated with the genus include: gill-associated virus (GAV) which causes reddening, biofouling with exoparasites, emaciation, and massive mortality; and yellow head virus (YHV) which causes yellow head, arrest of feeding, and massive mortality. The name is derived from the 'Oka' or lymphoid organ in which the viruses are commonly detected and in which pathology occurs during acute infections. Lymphoid organs are anatomical structures common to penaeid shrimp. There are three species in this genus.

Closteroviridae is a family of viruses. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four genera and 59 species in this family, seven of which are unassigned to a genus. Diseases associated with this family include: yellowing and necrosis, particularly affecting the phloem.
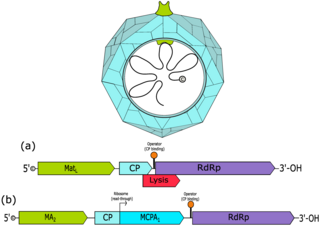
Fiersviridae is a family of positive-strand RNA viruses which infect prokaryotes. Bacteria serve as the natural host. They are small viruses with linear, positive-sense, single-stranded RNA genomes that encode four proteins. All phages of this family require bacterial pili to attach to and infect cells. The family has 185 genera, most discovered by metagenomics. In 2020, the family was renamed from Leviviridae to its current name.

Alphachrysovirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is one of two genera in the family Chrysoviridae. They infect fungi, in particular Penicillium. Their name is derived from the Greek word chrysos which means yellow-green. There are 20 species in this genus.

Partitiviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses. Plants, fungi, and protozoa serve as natural hosts. It has been suggested that they can also infect bacteria. The name comes from the Latin partitius, which means divided, and refers to the segmented genome of partitiviruses. There are five genera and 60 species in the family, 15 of which are unassigned to a genus.

Cucumovirus is a genus of viruses, in the family Bromoviridae. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this genus.

Globuloviridae is a family of hyperthermophilic archaeal viruses. Crenarchaea of the genera Pyrobaculum and Thermoproteus serve as natural hosts. There are four species in this family, assigned to a single genus, Alphaglobulovirus.
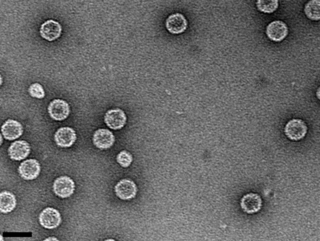
Picobirnavirus is a genus of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only genus in the family Picobirnaviridae. Although amniotes, especially mammals, were thought to serve as hosts, it has been recently suggested that these viruses might infect bacteria and possibly some other invertebrates. There are three species in this genus. Associated symptoms include gastroenteritis in animals and humans, though the disease association is unclear.

Iflaviridae is a family of positive sense RNA viruses insect-infecting viruses. Some of the insects commonly infected by iflaviruses include aphids, leafhoppers, flies, bees, ants, silkworms and wasps. The name "Ifla" is derived from the name "Infectious flacherie virus", a member species. There is one genus (Iflavirus) and 16 species in this family.

Aspiviridae, formerly Ophioviridae, is a family of segmented negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. Member viruses are characterized by an elongated and highly filamentous and flexible nucleocapsid with helical symmetry. It is a monotypic taxon containing only one genus, Ophiovirus. Aspiviridae is also the only family in the order Serpentovirales, which in turn is the only order in the class Milneviricetes.

Secoviridae is a family of viruses in the order Picornavirales. Plants serve as natural hosts. There are 8 genera and 86 species in this family, one of which is unassigned to a genus. The family was created in 2009 with the grouping of families Sequiviridae, now dissolved, and Comoviridae, now subfamily Comovirinae, along with the then unassigned genera Cheravirus, Sadwavirus, and Torradovirus.

Ampullaviridae is a family of viruses that infect archaea of the genus Acidianus. Only one genus in this family has been described, Bottigliavirus, which contains three species. The name of the family and genus is derived from the Latin word for bottle, ampulla, due to the virions having the shape of a bottle. The family was first described during an investigation of the microbial flora of hot springs in Italy.

Emaravirus is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses which infect plants. The plant virus group is the sole genus in the family Fimoviridae. The genus has 21 species.
Entomobirnavirus is a genus of viruses in the family Birnaviridae. Its natural host is the fly Drosophila melanogaster. There are two species in this genus.

Alvernaviridae is a family of non-enveloped positive-strand RNA viruses. Dinoflagellates serve as natural hosts. There is one genus in this family, Dinornavirus, which contains one species: Heterocapsa circularisquama RNA virus 01. Diseases associated with this family include host population control, possibly through lysis of the host cell.
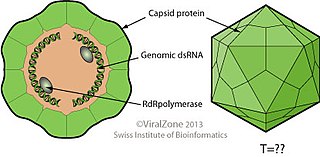
Megabirnaviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with one genus Megabirnavirus which infects fungi. The group name derives from member's bipartite dsRNA genome and mega that is greater genome size than families Birnaviridae and Picobirnaviridae. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix megabirnavirus 1. Diseases associated with this family include: reduced host virulence.

Quadriviridae is a family of double-stranded RNA viruses with a single genus Quadrivirus. The fungi Rosellinia necatrix serves as a natural host. The name of the group derives from the quadripartite genome of its members where in Latin quad means four. There is only one species in this family: Rosellinia necatrix quadrivirus 1.

Phenuiviridae is a family of negative-strand RNA viruses in the order Bunyavirales. Ruminants, camels, humans, and mosquitoes serve as natural hosts. Member genus Phlebovirus is the only genus of the family that has viruses that cause disease in humans except Dabie bandavirus.

Ghabrivirales is an order of double-stranded RNA viruses. It is the only order in the class Chrysmotiviricetes. The name of the class is a portmanteau of member families: chrysoviridae, megabirnaviridae, and totiviridae; and -viricetes which is the suffix for a virus class. The name of the order derives from Said Ghabrial, a pioneering researcher who studied viruses in this order, and -virales which is the suffix for a virus order.





















