
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It documents the story of human culture from its beginnings to the present. The British Museum was the first public national museum in the world.

A torc, also spelled torq or torque, is a large rigid or stiff neck ring in metal, made either as a single piece or from strands twisted together. The great majority are open at the front, although some had hook and ring closures and a few had mortice and tenon locking catches to close them. Many seem designed for near-permanent wear and would have been difficult to remove. Torcs are found in the Scythian, Illyrian, Thracian, Celtic, and other cultures of the European Iron Age from around the 8th century BC to the 3rd century AD. For the Iron Age Celts, the gold torc seems to have been a key object. It identifies the wearer as a person of high rank, and many of the finest works of ancient Celtic art are torcs. The Celtic torc disappears in the Migration Period, but during the Viking Age torc-style metal necklaces, now mainly in silver, came back into fashion. Torc styles of neck-ring are found as part of the jewellery styles of various other cultures and periods.

A hoard or "wealth deposit" is an archaeological term for a collection of valuable objects or artifacts, sometimes purposely buried in the ground, in which case it is sometimes also known as a cache. This would usually be with the intention of later recovery by the hoarder; hoarders sometimes died or were unable to return for other reasons before retrieving the hoard, and these surviving hoards might then be uncovered much later by metal detector hobbyists, members of the public, and archaeologists.

The Ulster Museum, located in the Botanic Gardens in Belfast, has around 8,000 square metres of public display space, featuring material from the collections of fine art and applied art, archaeology, ethnography, treasures from the Spanish Armada, local history, numismatics, industrial archaeology, botany, zoology and geology. It is the largest museum in Northern Ireland, and one of the components of National Museums Northern Ireland.
Senuna was a Celtic goddess worshipped in Roman Britain. She was unknown until a cache of 26 votive offerings to her were discovered in 2002 in an undisclosed field at Ashwell End in Hertfordshire by metal detectorist Alan Meek. Her imagery shows evidence of syncretism between a pre-Roman goddess with the Roman Minerva.

Zsujta is a village in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Hungary. A large Bronze Age hoard of weapons and cart fittings, was discovered at the village in the late 19th century. The hoard is now in the collections of the British Museum, London.

The Broighter Gold or more correctly, the Broighter Hoard, is a hoard of gold artefacts from the Iron Age of the 1st century BC that were found in 1896 by Tom Nicholl and James Morrow on farmland near Limavady, in the north of Ireland. The hoard includes a 7-inch-long (18 cm) gold boat, a gold torc and bowl and some other jewellery.

Forró is a village in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén County in northeastern Hungary. As of 2008, the village had a population of 2,459. A large Bronze Age hoard was discovered at the village in the 19th century. The treasure is now in the collections of the British Museum, London.
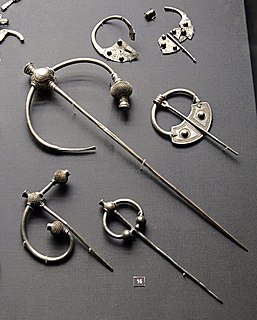
The Penrith Hoard is a dispersed hoard of 10th century silver penannular brooches found at Flusco Pike, Newbiggin Moor, near Penrith in Cumbria, and now in the British Museum in London. The largest "thistle brooch" was discovered in 1785 and another in 1830, with the bulk of items being recovered in two groups close to each other by archaeologists in 1989. Whether all the finds made close to each other were originally deposited at the same time remains uncertain, but it is thought likely that at least the brooches were. The brooches are thought to have been deposited in about 930.

The Meyrick Helmet is an Iron Age bronze peaked helmet, with La Tène style decoration, that is held at the British Museum in London. It is one of only four Iron Age helmets to have been discovered in Britain, the other three being the more famous Waterloo Helmet, the Canterbury Helmet and the North Bersted Warrior helmet. Unlike the Waterloo Helmet, which bears two cone-shaped horns, the Meyrick Helmet is hornless and appears to be based on a Roman model. Vincent Megaw, emeritus professor of archaeology at the University of Leicester, has conjectured that the helmet may have belonged to a British auxiliary fighting in the Roman army during the campaigns against the Brigantes in AD 71–74.

Castle Rings is a univallate hill fort in the parish of Donhead St Mary in Wiltshire in England. The fort is a Scheduled Ancient Monument, with a list entry identification number of 1005698. Castle Rings has been dated to the Iron Age and is situated at an altitude of 228 metres (748 ft) upon Upper Greensand sandstone beds. The main bulk of the fort enclosure lies within the boundaries of Donhead St Mary parish but some of the outlying earthworks are situated in the neighbouring Sedgehill and Semley parish. In the mid-1980s a metal detectorist unearthed a hoard of stater coins of the Durotriges tribe within the hill fort.

The Cordoba Treasure, or Tesoro de Córdoba in Spanish, is the name of a major Iron Age silver hoard found on the outskirts of the city of Córdoba, Spain in 1915. The entire treasure was purchased by the British Museum in 1932, where it has been on public display ever since.

The Lampsacus Treasure or Lapseki Treasure is the name of an important early Byzantine silver hoard found near the town of Lapseki in modern-day Turkey. Most of the hoard is now in the British Museum's collection, although a few items can be found in museums in Paris and Istanbul too.

The Great Torc from Snettisham or Snettisham Great Torc is a large Iron Age torc or neck ring in electrum, from the 1st century BC. It is one of the finest pieces of early Celtic art in a distinctly British Celtic style. It is the most spectacular object in the Snettisham Hoard of torcs and other metalwork found in 1950 near the village of Snettisham in Norfolk, East Anglia. The perfectly intact torc is outstanding for its high level of craftsmanship and superb artistry. Soon after its discovery it was acquired by the British Museum.
Broighter is a townland in west County Londonderry, Northern Ireland. It lies 4.4 miles (7 km) northwest of Limavady and 2.5 miles (4 km) northeast of Ballykelly. Broighter is part of Causeway Coast and Glens district.

The Rogart Brooch is a large penannular brooch of Pictish origin, dated to the eighth century. Characteristic of contemporary Pictish brooches, it contains three-dimensional bird-head inserts formed with glass.














