
Hormizd-Ardashir, better known by his dynastic name of Hormizd I, was the third Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran, who ruled from May 270 to June 271. He was the third-born son of Shapur I, under whom he was governor-king of Armenia, and also took part in his father's wars against the Roman Empire. Hormizd I's brief time as ruler of Iran was largely uneventful. He built the city of Hormizd-Ardashir, which remains a major city today in Iran. He promoted the Zoroastrian priest Kartir to the rank of chief priest (mowbed) and gave the Manichaean prophet Mani permission to continue his preaching.

Hormizd II was king (shah) of the Sasanian Empire. He ruled for six years and five months, from 303 to 309. He was a son and successor of Narseh.

Bahram I was the fourth Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 271 to 274. He was the eldest son of Shapur I and succeeded his brother Hormizd I, who had reigned for a year.

Bahram II was the fifth Sasanian King of Kings (shahanshah) of Iran, from 274 to 293. He was the son and successor of Bahram I. Bahram II, while still in his teens, ascended the throne with the aid of the powerful Zoroastrian priest Kartir, just like his father had done.

Shapur I was the second Sasanian King of Kings of Iran. The precise dating of his reign is disputed, but it is generally agreed that he ruled from 240 to 270, with his father Ardashir I as co-regent until the death of the latter in 242. During his co-regency, he helped his father with the conquest and destruction of the city of Hatra, whose fall was facilitated, according to Islamic tradition, by the actions of his future wife al-Nadirah. Shapur also consolidated and expanded the empire of Ardashir I, waged war against the Roman Empire, and seized its cities of Nisibis and Carrhae while he was advancing as far as Roman Syria. Although he was defeated at the Battle of Resaena in 243 by Roman emperor Gordian III, he was the following year able to win the Battle of Misiche and force the new Roman emperor Philip the Arab to sign a favorable peace treaty that was regarded by the Romans as "a most shameful treaty".

Ardashir II, was the Sasanian King of Kings of Iran from 379 to 383. He was the brother of his predecessor, Shapur II, under whom he had served as vassal king of Adiabene, where he fought alongside his brother against the Romans. Ardashir II was appointed as his brother's successor to rule interimly till the latter's son Shapur III reached adulthood. Ardashir II's short reign was largely uneventful, with the Sasanians unsuccessfully trying to maintain rule over Armenia.
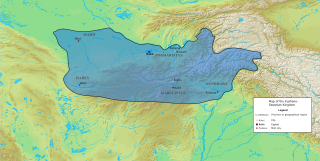
The Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom was a polity established by the Sasanian Empire in Bactria during the 3rd and 4th centuries. The Sasanian Empire captured the provinces of Sogdia, Bactria and Gandhara from the declining Kushan Empire following a series of wars in 225 CE. The local Sasanian governors then went on to take the title of Kushanshah or "King of the Kushans", and to mint coins. They are sometimes considered as forming a "sub-kingdom" inside the Sasanian Empire.

Pabag was an Iranian prince who ruled Istakhr, the capital of Pars, from 205 or 206 until his death sometime between 207 and 210. He was the father, stepfather, grandfather, or father-in-law of Ardashir I, the founder of the Sasanian Empire. He was succeeded by his eldest son, Shapur.

Kushanshah was the title of the rulers of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom, the parts of the former Kushan Empire in the areas of Sogdiana, Bactria and Gandhara, named Kushanshahr and held by the Sasanian Empire, during the 3rd and 4th centuries CE. They are collectively known as Kushano-Sasanians, or Indo-Sasanians.

Peroz I Kushanshah was Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 245 to 275. He was the successor of Ardashir I Kushanshah. He was an energetic ruler, who minted coins in Balkh, Herat, and Gandhara. Under him, the Kushano-Sasanians further expanded their domains into the west, pushing the weakened Kushan Empire to Mathura in North India.

Hormizd I Kushanshah was Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 275 to 300. His reign was marked by his rebellion against his brother and suzerain the Sasanian King of Kings Bahram II.

BahramKushanshah, was the last Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 330 to 365. He was the successor of Peroz II Kushanshah.

Peroz II Kushanshah was the penultimate Kushanshah of the Kushano-Sasanian Kingdom from 303 to 330. He was the successor of Hormizd II Kushanshah.

Peroz, was according to modern scholarship an early Kidarite ruler in Gandhara, right after the end of Kushano-Sasanians.

Shapur was an Iranian prince, who was the penultimate King of Persis from 207–210 to 211/2. He was succeeded by his younger brother Ardashir I, who founded the Sasanian Empire.

The Kings of Persis, also known as the Darayanids, were a series of Iranian kings, who ruled the region of Persis in southwestern Iran, from the 2nd century BCE to 224 CE. They ruled as vassal kings of the Parthian Empire, until they toppled them and established the Sasanian Empire. They effectively formed some Persian dynastic continuity between the Achaemenid Empire and the Sasanian Empire.

Ardakhshir I was a dynast (frataraka) of Persis in the late 3rd-century BC, ruling sometime after 220 to c. 205 BC.
Hind was the name of a southeastern Sasanian province lying near the Indus River in modern-day southern Pakistan. The boundaries of the province are obscure. The Austrian historian and numismatist Nikolaus Schindel has suggested that the province may have corresponded to the Sindh region, where the Sasanians notably minted unique gold coins of themselves. According to the modern historian C. J. Brunner, the province possibly included—whenever jurisdiction was established—the areas of the Indus River, including the southern part of Punjab.
The Sasanian–Kushan Wars were a series of wars between the newly established Persian Sasanian empire, under Ardashir I and later his successor Shapur I, against the declining Kushan empire. These wars resulted in the eastward expansion of the Sasanians who conquered much of the Kushan territory including Bactria, Gandhara and Sogdia. The Sassanids, shortly after victory over the declining Parthian empire, extended their dominion to most of former Parthian lands, including Bactria, during the reign of Ardashir I around 230 CE, then they further expanded to the eastern parts of their empire in what is now western Pakistan, at the expense of warring against the declining Kushan empire, during the reign of his son Shapur I (240–270). Thus the Kushans lost their western territory to the rule of Sassanid nobles, who eventually established their own states and were collectively referred to as Kushanshahs or "Kings of the Kushans". At their greatest extent, these Kushano-Sasanians also seem to have expanded eastwards all the way to Gandhara, however do not seem to have crossed the Indus River, since almost none of their coinage has been found in the city of Taxila, just beyond the Indus.


















