Natural language generation (NLG) is a software process that produces natural language output. A widely-cited survey of NLG methods describes NLG as "the subfield of artificial intelligence and computational linguistics that is concerned with the construction of computer systems than can produce understandable texts in English or other human languages from some underlying non-linguistic representation of information".
Question answering (QA) is a computer science discipline within the fields of information retrieval and natural language processing (NLP) that is concerned with building systems that automatically answer questions that are posed by humans in a natural language.

A dialogue system, or conversational agent (CA), is a computer system intended to converse with a human. Dialogue systems employed one or more of text, speech, graphics, haptics, gestures, and other modes for communication on both the input and output channel.

The Macaulay Institute, formally the Macaulay Land Use Research Institute and sometimes referred to simply as The Macaulay, was a research institute based at Aberdeen in Scotland, which is now part of the James Hutton Institute. Its work covered aspects such as landscape, soil and water conservation and climate change.
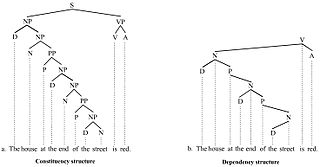
In linguistics, a treebank is a parsed text corpus that annotates syntactic or semantic sentence structure. The construction of parsed corpora in the early 1990s revolutionized computational linguistics, which benefitted from large-scale empirical data.
What you see is what you meant (WYSIWYM) is a text editing interaction technique that emerged from two projects at University of Brighton. It allows users to create abstract knowledge representations such as those required by the Semantic Web using a natural language interface. Natural language understanding (NLU) technology is not employed. Instead, natural language generation (NLG) is used in a highly interactive manner.
In linguistics, realization is the process by which some kind of surface representation is derived from its underlying representation; that is, the way in which some abstract object of linguistic analysis comes to be produced in actual language. Phonemes are often said to be realized by speech sounds. The different sounds that can realize a particular phoneme are called its allophones.
Referring expression generation (REG) is the subtask of natural language generation (NLG) that received most scholarly attention. While NLG is concerned with the conversion of non-linguistic information into natural language, REG focuses only on the creation of referring expressions that identify specific entities called targets.
Lexical choice is the subtask of Natural language generation that involves choosing the content words in a generated text. Function words are usually chosen during realisation.
In linguistics, aggregation is a subtask of natural language generation, which involves merging syntactic constituents together. Sometimes aggregation can be done at a conceptual level.
Document Structuring is a subtask of Natural language generation, which involves deciding the order and grouping of sentences in a generated text. It is closely related to the Content determination NLG task.
Content determination is the subtask of natural language generation (NLG) that involves deciding on the information to be communicated in a generated text. It is closely related to the task of document structuring.
LEPOR is an automatic language independent machine translation evaluation metric with tunable parameters and reinforced factors.
Andrew John Smith Greig was a Scottish footballer who played as a goalkeeper in the Scottish Football League for Aberdeen and in the Football League for Darlington either side of the First World War. He also played for Mugiemoss, Raith Rovers, Shildon, Peterhead and Montrose. He was deaf.
![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Narrative Science</span> American [[natural language]] generation company](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8a/Narrative_Science_Office.jpg/320px-Narrative_Science_Office.jpg)
Narrative Science was a natural language generation company based in Chicago, Illinois, that specialized in data storytelling. As of December 17, 2021, Narrative Science was acquired by Salesforce and has been integrated into Salesforce's Tableau Software.

Automated Insights (AI) is an American-based technology company that specializes in natural language generation (NLG) software that turns big data into readable narratives.
Yseop is a French software company, specializing in no code intelligent report automation, using natural language generation (NLG). Established in 2000 with offices in Paris, New York, Lyon and Bogota. Yseop was a pioneer in NLG which laid the groundwork for Chat GPT and Generative AI. Yseop's original founding team sold their stake in the company to Next Stage, a French Private Equity Company.
Sir Robert Blyth Greig was a Scottish agriculturalist. He served as Chairman of the Scottish Board of Agriculture from 1921 to 1928 and was Secretary to the Department of Agriculture for all Great Britain from 1928 to 1934.
Verena Rieser is a German computer scientist specialising in natural-language generation, including conversational modelling as well as studies of how gender cues in synthetic language can trigger biases in the people who interact with them. She is a professor in the School of Mathematical and Computer Sciences at Heriot-Watt University in Edinburgh, where she directs the Natural Language Processing Laboratory.
Abstract Wikipedia is an in-development project of the Wikimedia Foundation. It aims to use Wikifunctions to create a language-independent version of Wikipedia using its structured data. First conceived in 2020, Abstract Wikipedia has been under active development ever since, with the related project of Wikifunctions launched successfully in 2023. Nevertheless, the project has proved controversial. As envisioned, Abstract Wikipedia would consist of "Constructors", "Content", and "Renderers".



![<span class="mw-page-title-main">Narrative Science</span> American [[natural language]] generation company](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/8/8a/Narrative_Science_Office.jpg/320px-Narrative_Science_Office.jpg)
