Related Research Articles

An endosymbiont or endobiont is an organism that lives within the body or cells of another organism. Typically the two organisms are in a mutualistic relationship. Examples are nitrogen-fixing bacteria, which live in the root nodules of legumes, single-cell algae inside reef-building corals, and bacterial endosymbionts that provide essential nutrients to insects.

Trypanosomatida is a group of kinetoplastid unicellular organisms distinguished by having only a single flagellum. The name is derived from the Greek trypano (borer) and soma (body) because of the corkscrew-like motion of some trypanosomatid species. All members are exclusively parasitic, found primarily in insects. A few genera have life-cycles involving a secondary host, which may be a vertebrate, invertebrate or plant. These include several species that cause major diseases in humans. Some trypanosomatida are intracellular parasites, with the important exception of Trypanosoma brucei.

Wolbachia is a genus of gram-negative bacteria infecting many species of arthropods and filarial nematodes. The symbiotic relationship ranges from parasitism to obligate mutualism. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes of arthropods, and is possibly the most widespread reproductive parasite bacterium in the biosphere. Its interactions with hosts are complex and highly diverse across different host species. Some host species cannot reproduce, or even survive, without Wolbachia colonisation. One study concluded that more than 16% of neotropical insect species carry bacteria of this genus, and as many as 25 to 70% of all insect species are estimated to be potential hosts.

Francisella is a genus of Gram-negative bacteria. They are small coccobacillary or rod-shaped, nonmotile organisms, which are also facultative intracellular parasites of macrophages. Strict aerobes, Francisella colonies bear a morphological resemblance to those of the genus Brucella. Some Francisella species are pathogenic bacteria but some others are endosymbionts of ticks. Ticks do not use any other food source than vertebrate blood and therefore ingest high levels of protein, iron and salt, but few vitamins. To overcome these nutritional deficiencies, ticks have evolved obligate interactions with nutritional endosymbionts, including Francisella endosymbionts. Their experimental elimination typically results in decreased tick survival, molting, fecundity and egg viability, as well as in physical abnormalities, which all are fully restored with an oral supplement of B vitamins. The genome sequencing of Francisella endosymbionts confirmed that they consistently produce three B vitamin types, biotin (vitamin B7), riboflavin (B2) and folate (B9). Francisella endosymbionts are often misidentified as Francisella tularensis; however, Francisella endosymbionts lack virulence genes and cannot infect humans.
In prokaryote nomenclature, Candidatus is used to name prokaryotic taxa that are well characterized but yet-uncultured. Contemporary sequencing approaches, such as 16S ribosomal RNA sequencing or metagenomics, provide much information about the analyzed organisms and thus allow identification and characterization of individual species. However, the majority of prokaryotic species remain uncultivable and hence inaccessible for further characterization in in vitro study. The recent discoveries of a multitude of candidate taxa has led to candidate phyla radiation expanding the tree of life through the new insights in bacterial diversity.
Horizontal transmission is the transmission of organisms between biotic and/or abiotic members of an ecosystem that are not in a parent-progeny relationship. Because the evolutionary fate of the agent is not tied to reproductive success of the host, horizontal transmission tends to evolve virulence. It is therefore a critical concept for evolutionary medicine.
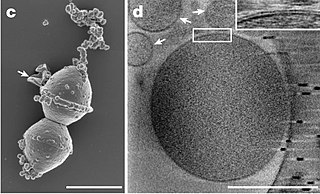
"Candidatus Carsonella ruddii" is an obligate endosymbiotic Gammaproteobacterium with one of the smallest genomes of any characterised bacteria.

Trichonympha is a genus of single-celled, anaerobic parabasalids of the order Hypermastigia that is found exclusively in the hindgut of lower termites and wood roaches. Trichonympha’s bell shape and thousands of flagella make it an easily recognizable cell. The symbiosis between lower termites/wood roaches and Trichonympha is highly beneficial to both parties: Trichonympha helps its host digest cellulose and in return receives a constant supply of food and shelter. Trichonympha also has a variety of bacterial symbionts that are involved in sugar metabolism and nitrogen fixation.
"Candidatus Midichloria" is a candidatus genus of Gram-negative, non-endospore-forming bacteria, with a bacillus shape around 0.45 μm in diameter and 1.2 μm in length. First described in 2004 with the temporary name IricES1, "Candidatus Midichloria" species are symbionts of several species of hard ticks. They live in the cells of the ovary of the females of this tick species. These bacteria have been observed in the mitochondria of the host cells, a trait that has never been described in any other symbiont of animals.

Angomonas deanei is a flagellated trypanosomatid protozoan. As an obligate parasite, it infects the gastrointestinal tract of insects, and is in turn a host to symbiotic bacteria. The bacterial endosymbiont Ca. "Kinetoplastibacterium crithidii" maintains a permanent mutualistic relationship with the protozoan such that it is no longer able to reproduce and survive on its own. The symbiosis, subsequently also discovered in varying degrees in other protists such as Strigomonas culicis, Novymonas esmeraldas, Diplonema japonicumand Diplonema aggregatum are considered as good models for the understanding of the evolution of eukaryotes from prokaryotes, and on the origin of cell organelles.
Arsenophonus nasoniae is a species of bacterium which was previously isolated from Nasonia vitripennis, a species of parasitoid wasp. These wasps are generalists which afflict the larvae of parasitic carrion flies such as blowflies, houseflies and flesh flies. A. nasoniae belongs to the phylum Pseudomonadota and family Morganellaceae. The genus Arsenophonus, has a close relationship to the Proteus (bacterium) rather than to that of Salmonella and Escherichia. The genus is composed of gammaproteobacterial, secondary-endosymbionts which are gram-negative. Cells are non-flagellated, non-motile, non-spore forming and form long to highly filamentous rods. Cellular division is exhibited through septation. The name 'Arsenophonus nasoniae gen. nov., sp. nov.' was therefore proposed for the discovered bacterium due to its characteristics and its microbial interaction with N. vitripennis. The type strain of A. nasoniae is Strain SKI4.
Arsenophonus is a genus of Morganellaceae, of the Gammaproteobacteria. Members of the Arsenophonus genus are increasingly discovered bacterial symbionts of arthropods that are estimated to infect over 5% of arthropod species globally and form a variety of relationships with hosts across the mutualism parasitism continuum. Arsenophonus bacteria have been identified in a diversity of insect taxa, including economically important species such as the Western honey bee and the rice pest Nilaparvata lugens.
Sodalis is a genus of bacteria within the family Pectobacteriaceae. This genus contains several insect endosymbionts and also a free-living group. It is studied due to its potential use in the biological control of the tsetse fly. Sodalis is an important model for evolutionary biologists because of its nascent endosymbiosis with insects.
Candidatus Caballeronia kirkii is a Gram-negative, non-fermenting bacterium from the genus Caballeronia and the family Burkholderiaceae. Ca. C. kirkii is an endosymbiont of the plant Psychotria kirkii, also known as Rubiaceae, and exists inside leaf and stem nodules.

Blochmannia is a genus of symbiotic bacteria found in carpenter ants and their allies in the tribe Camponotini. As of 2014, Blochmannia has been discovered in the guts of over 60 species across 6 genera within the Camponotini, and is predicted to be pervasive throughout the tribe. Blochmannia was first discovered by zoologist Friedrich Blochmann in 1887, who described "bacteria-like structures" in the ovaries and midgut of Camponotus ligniperdus in 1887. In 2000, Candidatus Blochmannia was proposed as its own genus.
"Candidatus Karelsulcia muelleri" is an aerobic, gram-negative, bacillus bacterium that is a part of the phylum Bacteroidota. "Ca. K. muelleri" is an obligate and mutualistic symbiotic microbe commonly found occupying specialized cell compartments of sap-feeding insects called bacteriocytes. A majority of the research done on "Ca. K. muelleri" has detailed its relationship with the host Homalodisca vitripennis. Other studies have documented the nature of its residency in other insects like the maize leafhopper (Cicadulina) or the spittlebug (Cercopoidea). "Ca. K. muelleri" is noted for its exceptionally minimal genome and it is currently identified as having the smallest known sequenced Bacteroidota genome at only 245 kilobases.

The Morganellaceae are a family of Gram-negative bacteria that include some important human pathogens formerly classified as Enterobacteriaceae. This family is a member of the order Enterobacterales in the class Gammaproteobacteria of the phylum Pseudomonadota. Genera in this family include the type genus Morganella, along with Arsenophonus, Cosenzaea, Moellerella, Photorhabdus, Proteus, Providencia and Xenorhabdus.
Thiodictyon is a genus of gram-negative bacterium classified within purple sulfur bacteria (PSB).
Novymonas esmeraldas is a protist and member of flagellated trypanosomatids. It is an obligate parasite in the gastrointestinal tract of a bug, and is in turn a host to symbiotic bacteria. It maintains strict mutualistic relationship with the bacteria as a sort of cell organelle (endosymbiont) so that it cannot lead an independent life without the bacteria. Its discovery in 2016 suggests that it is a good model in the evolution of prokaryotes into eukaryotes by symbiogenesis. The endosymbiotic bacterium was identified as member of the genus Pandoraea.
Candidatus "Glomeribacter gigasporarum" is a gram-negative β-proteobacteria. The bacterium is rod-shaped, and has a obligate endosymbiotic relationship with the arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi Gigaspora margarita. Sequencing of the16S rRNA gene places Ca. "G. gigasporarum" within the Burkholderia genus. Ca. "G. gigasporarum is unculturable as of yet, but can stay alive in enrichment for up to 4 weeks. The candidate bacteria is considered "the smallest beta-proteobacterium" with a genome size of 1.4 Mb. The chromosome is 750 kb long and a plasmid is 600 to 650 kb. The genome size was determined using gel-electrophoresis.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Dale, Colin; Beeton, Michael; Harbison, Christopher; Jones, Tait; Pontes, Mauricio (2006-04-01). "Isolation, Pure Culture, and Characterization of "Candidatus Arsenophonus arthropodicus," an Intracellular Secondary Endosymbiont from the Hippoboscid Louse Fly Pseudolynchia canariensis". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 72 (4): 2997–3004. Bibcode:2006ApEnM..72.2997D. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.4.2997-3004.2006 . ISSN 0099-2240. PMC 1449044 . PMID 16598007.
- ↑ Mouton, Laurence; Thierry, Magali; Henri, Hélène; Baudin, Rémy; Gnankine, Olivier; Reynaud, Bernard; Zchori-Fein, Einat; Becker, Nathalie; Fleury, Frédéric; Delatte, Hélène (2012-01-18). "Evidence of diversity and recombination in Arsenophonus symbionts of the Bemisia tabacispecies complex". BMC Microbiology. 12 (1): S10. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-S1-S10 . ISSN 1471-2180. PMC 3287507 . PMID 22375811.
- ↑ Darby, A. C.; Choi, J.-H.; Wilkes, T.; Hughes, M. A.; Werren, J. H.; Hurst, G. D. D.; Colbourne, J. K. (2010). "Characteristics of the genome of Arsenophonus nasoniae, son-killer bacterium of the wasp Nasonia". Insect Molecular Biology. 19 (s1): 75–89. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2583.2009.00950.x. ISSN 1365-2583. PMID 20167019. S2CID 44987264.
- ↑ "Species: Arsenophonus arthropodicus". lpsn.dsmz.de. Archived from the original on 2020-04-20. Retrieved 2020-11-02.
- ↑ Nováková, Eva; Hypša, Václav; Moran, Nancy A (2009-07-20). "Arsenophonus, an emerging clade of intracellular symbionts with a broad host distribution". BMC Microbiology. 9: 143. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-143 . ISSN 1471-2180. PMC 2724383 . PMID 19619300.