Related Research Articles

The Bronx is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the U.S. state of New York, the third-most-densely populated county in the United States. It is south of Westchester County; northeast and east of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of Queens, across the East River. The Bronx has a land area of 42 square miles (109 km2) and a population of 1,418,207 in 2019. Of the five boroughs, it has the fourth-largest area, fourth-highest population, and third-highest population density. It is the only borough predominantly on the U.S. mainland. If each borough were its own city, the Bronx would rank as the eighth-most-populous in the United States.

The Robert F. Kennedy Bridge, formerly known and still commonly referred to as the Triborough Bridge, is a complex of bridges and elevated expressway viaducts in New York City. The bridges link the boroughs of Manhattan, Queens, and the Bronx. The viaducts cross Randalls and Wards Islands, which were previously two islands but are now joined by landfill.
Interstate 278 (I-278) is an auxiliary Interstate Highway in New Jersey and New York in the United States. The road runs 35.62 miles (57.32 km) from U.S. Route 1/9 (US 1/9) in Linden, New Jersey, to the Bruckner Interchange in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The majority of I-278 is in New York City, where it serves as a partial beltway and passes through all five of the city's boroughs. I-278 follows several freeways, including the Union Freeway in Union County, New Jersey; the Staten Island Expressway (SIE) across Staten Island; the Gowanus Expressway in southern Brooklyn; the Brooklyn–Queens Expressway (BQE) across northern Brooklyn and Queens; a small part of the Grand Central Parkway in Queens; and a part of the Bruckner Expressway in the Bronx. I-278 also crosses multiple bridges, including the Goethals, Verrazzano-Narrows, Kosciuszko, and Triborough Bridges.
The Cross Island Parkway is a parkway in New York City; which is a part of the Belt System running along the perimeter of the boroughs of Queens and Brooklyn. The Cross Island Parkway runs 10.6 miles (17.1 km) from the Whitestone Expressway in Whitestone past the Throgs Neck Bridge, along and across the border of Queens and Nassau County to meet up with the Southern State Parkway. The road is designated as New York State Route 907A (NY 907A), an unsigned reference route, and bears the honorary name 100th Infantry Division Parkway.

The Cross Bronx Expressway is a major freeway in the New York City borough of the Bronx. It is mainly designated as part of Interstate 95 (I-95), but also includes portions of I-295 and U.S. Route 1 (US 1). The Cross Bronx begins at the Alexander Hamilton Bridge over the Harlem River, where the Trans-Manhattan Expressway continues west across Upper Manhattan to the George Washington Bridge. While I-95 leaves at the Bruckner Interchange in Throgs Neck, following the Bruckner Expressway and New England Thruway to Connecticut, the Cross Bronx Expressway continues east, carrying I-295 to the merge with the Throgs Neck Expressway near the Throgs Neck Bridge. Though the road goes primarily northwest-to-southeast, the nominal directions of all route numbers west of the Bruckner Interchange are aligned with the northbound route number going southeast, and the southbound route number going northwest.
The Bruckner Expressway is a freeway in the borough of the Bronx in New York City. It carries Interstate 278 (I-278) and I-95 from the Triborough Bridge to the south end of the New England Thruway at the Pelham Parkway interchange. The highway follows a mostly northeast–southwest alignment through the southern portion of the borough, loosely paralleling the course of the East River. It connects to several major freeways including the Bronx River Parkway, and at the Bruckner Interchange, it connects to the Cross Bronx Expressway, the Whitestone Expressway, and the Hutchinson River Parkway.
Interstate 678 (I-678) is a north–south auxiliary Interstate Highway that extends for 14 miles (23 km) through two boroughs of New York City. The route begins at John F. Kennedy International Airport on Jamaica Bay and travels north through Queens and across the East River to the Bruckner Interchange in the Bronx, where I-678 ends and the Hutchinson River Parkway begins.
New York State Route 895 is a short boulevard in the New York City borough of the Bronx. Its south end is at a merging with the Bruckner Expressway (I-278) in the Hunts Point neighborhood, and its north end is at the Cross Bronx Expressway (I-95), with a short continuation connecting with local West Farms streets. NY 895 is locally known as Sheridan Boulevard or simply The Sheridan.
The IRT Pelham Line, also called the Southern Boulevard–Pelham Bay Park Line, is a rapid transit line on the New York City Subway, operated as part of the A Division and served by the 6 and <6> trains. It was built as part of the Dual Contracts expansion and opened between 1918 and 1920. It is both elevated and underground with Whitlock Avenue being the southernmost elevated station. It has three tracks from the beginning to just south of the Pelham Bay Park terminal. The Pelham Line also has a connection to Westchester Yard, where 6 trains are stored, just north of Westchester Square–East Tremont Avenue. As of 2013, it has a daily ridership of 205,590.

The Alexander Hamilton Bridge is an eight-lane steel arch bridge that carries traffic over the Harlem River between the boroughs of Manhattan and the Bronx in New York City. It connects the Trans-Manhattan Expressway in the Washington Heights section of Manhattan and the Cross-Bronx Expressway, as part of Interstate 95 and U.S. 1. The bridge opened to traffic on January 15, 1963, the same day that the Cross-Bronx Expressway was completed. For 2011, the New York City Department of Transportation, which operates and maintains the bridge, reported an average daily traffic volume in both directions of 182,174; having reached a peak ADT of 192,848 in 1990.

The Bruckner Interchange is a complex interchange in the New York City borough of The Bronx in the United States. The junction connects four highways: the Bruckner, Cross Bronx, and Hutchinson River Expressways, and the Hutchinson River Parkway. It was constructed in the 1960s; however, elements of the junction date as far back as the 1940s. The interchange includes connections to several interstate routes, including I-278, I-678, I-295 and I-95.
Interstate 95 (I-95) is a part of the Interstate Highway System that runs from Miami, Florida, to the Canada–United States border near Houlton, Maine. In the U.S. state of New York, I-95 extends 23.50 miles (37.82 km) from the George Washington Bridge in New York City to the Connecticut state line at Port Chester. From the George Washington Bridge, which carries I-95 across the Hudson River from New Jersey into New York City, it runs across upper Manhattan on the Trans-Manhattan Expressway and continues east across the Harlem River on the Alexander Hamilton Bridge and onto the Cross Bronx Expressway. In the Bronx, I-95 leaves the Cross Bronx at the Bruckner Interchange, joining the Bruckner Expressway to its end. North of the interchange with Pelham Parkway, it then continues northeast via the New England Thruway out of New York City into Westchester County and to the Connecticut state line, where I-95 continues on the Connecticut Turnpike.

Henry Bruckner was an American politician from New York.

Jerome Avenue is one of the longest thoroughfares in the New York City borough of the Bronx, New York, United States. The road is 5.6 miles (9.0 km) long and stretches from Concourse to Woodlawn. Both of these termini are with the Major Deegan Expressway which runs parallel to the west. Most of the elevated IRT Jerome Avenue Line runs along Jerome Avenue. The Cross Bronx Expressway interchanges with Jerome and the Deegan. Though it runs through what is now the West Bronx neighborhood, Jerome Avenue is the dividing avenue between nominal and some named "West" and "East" streets in the Bronx; Fifth Avenue, and to a lesser extent, Broadway, also splits Manhattan into nominal "West" and "East" streets.

Robert Lawrence Moran, was a Bronx politician who served as President of the Board of Aldermen of New York City from 1918 to 1920, filling a vacancy after Alfred E. Smith was elected Governor of New York. Nominated by the Democratic Party to succeed himself as board president, Moran faced Republican Representative Fiorello H. La Guardia in the election of 1919, losing by a plurality of 1,363 votes. Moran has the distinction of being the only citizen of The Bronx to ever exercise the authority of mayor of New York City, even though this honor came to him only in his capacity as acting mayor during Mayor Hylan's absences from the city.

Starlight Park is a public park located along the Bronx River in the Bronx in New York City. Starlight Park stands on the site of an amusement park of the same name that operated in the first half of the 20th century.

The 178th and 179th Street Tunnels are two disused vehicular tunnels in Upper Manhattan in New York City. Originally conceived and constructed under the auspices of Robert Moses, the twin tunnels have been superseded by the Trans-Manhattan Expressway in Washington Heights, which itself runs through a cut with high-rise apartments built over it in places.

Michael John Garvin, also known as Michael J. Garvin and M. J. Garvin (1861–1918), was an American architect from The Bronx, New York. A graduate of Manhattan College, he served as the first Building Commissioner of the borough (1897–1903) and its first Under Sheriff. With the placement of the influential IRT Third Avenue Elevated train, Garvin was immersed in designing many surrounding structures during the borough's increasing growth at the turn of the 20th century. Of his architectural contributions the Haffen Building; the Fire House, Hook and Ladder 17; and the Bronx Borough Courthouse have all become New York City landmarks while the latter a US National Historic Place.
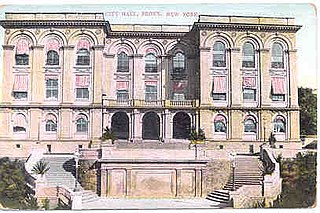
The Bronx Municipal Building, later known as Bronx Borough Hall and eventually as Old Bronx Borough Hall (1897–1969), was the original administrative headquarters of the Bronx Borough President and other local civic leaders. It was located in the Tremont neighborhood of the Bronx, New York City.
References
- ↑ NYSSPE Past Presidents, archived from the original on 26 August 2013, retrieved 26 August 2013
- ↑ About NSPE: Leadership: Past Presidents , retrieved 26 August 2013
- ↑ Sheridan Expressway , retrieved 26 August 2013
- ↑ Starlight Park , retrieved 26 August 2013
- ↑ Arthur V. Sheridan Scholarship (Manhattan College) , retrieved 26 August 2013