The Cushitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They are spoken primarily in the Horn of Africa, with minorities speaking Cushitic languages to the north in Egypt and Sudan, and to the south in Kenya and Tanzania. As of 2012, the Cushitic languages with over one million speakers were Oromo, Somali, Beja, Afar, Hadiyya, Kambaata, and Sidama.
Afar is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken by the Afar people inhabiting Djibouti, Eritrea and Ethiopia.
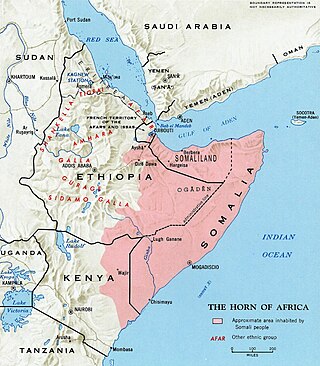
Somali is an Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic branch. It is spoken primarily in Greater Somalia, and by the Somali diaspora as a mother tongue. Somali is an official language in both Somalia and Ethiopia, and serves as a national language in Djibouti, it is also a recognised minority language in Kenya. The Somali language is officially written with the Latin alphabet although the Arabic script and several Somali scripts like Osmanya, Kaddare and the Borama script are informally used.

The Songhay, Songhai or Ayneha languages are a group of closely related languages/dialects centred on the middle stretches of the Niger River in the West African countries of Mali, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso and Nigeria. In particular, they are spoken in the cities of Timbuktu, Djenné, Niamey, Gao, Tillaberi, Dosso, Parakou, Kandi, Natitingou, Djougou, Malanville, Gorom-Gorom, In-Gall and Tabelbala. They have been widely used as a lingua franca in that region ever since the era of the Songhai Empire. In Mali, the government has officially adopted the dialect of Gao as the dialect to be used as a medium of primary education.
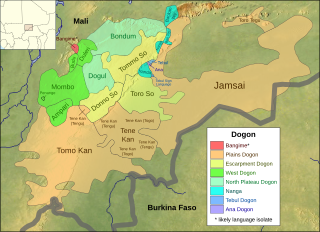
The Dogon languages are a small closely related language family that is spoken by the Dogon people of Mali and may belong to the proposed Niger–Congo family. There are about 600,000 speakers of its dozen languages. They are tonal languages, and most, like Dogul, have two tones, but some, like Donno So, have three. Their basic word order is subject–object–verb.
Khmu is the language of the Khmu people of the northern Laos region. It is also spoken in adjacent areas of Vietnam, Thailand and China. Khmu lends its name to the Khmuic branch of the Austroasiatic language family, the latter of which also includes Khmer and Vietnamese. Within Austroasiatic, Khmu is often cited as being most closely related to the Palaungic and Khasic languages. The name "Khmu" can also be seen romanized as Kmhmu, Khmu', Kammu, or Khamuk in various publications or alternatively referred to by the name of a local dialect.
Day is an Adamawa language of southern Chad, spoken by 50,000 or so people southeast of Sarh. Ethnologue reports that its dialects are mutually intelligible, but Blench (2004) lists Ndanga, Njira, Yani, Takawa as apparently separate languages.

The Garre are a prominent Somali clan that traces its lineage back to Samaale, who is believed to have originated from the Arabian Peninsula through Aqiil Abu Talib. The Garre clan is considered to be a sub-clan of the Digil-Rahanweyn clan family, which is part of the larger Rahanweyn clan. However, genealogically, they are descended from Gardheere Samaale. The Garre are also categorized as southern Hawiye as well.

The endoglossic language of Somalia has always been Somali, although throughout Somalia's history various exoglossic languages have also been used at a national level.
Boon or Af-Boon is a nearly extinct Cushitic language spoken by 59 people in Jilib District, Middle Jubba Region of southern Somalia. In recent decades they have shifted to the Maay dialect of Jilib. All speakers were reported in the 1980s to be older than 60. Their traditional occupations are as hunters, leatherworkers and, more recently, shoemakers.

Mai-Mai, commonly spelled Maay Maay, is one of the Somali languages. It is mainly spoken in Somalia and adjacent parts of Ethiopia and Kenya. In Somalia, it is spoken in South West state, Jubaland state, and Banadir.
The Somali languages form a group that are part of the Afro-Asiatic language family. They are spoken as a mother tongue by ethnic Somalis in Horn of Africa and the Somali diaspora. Even with linguistic differences, Somalis collectively view themselves as speaking dialects of a common language.
Garre is a Somali language spoken by the Garre who reside in southern Somalia, Ethiopia and northern Kenya. It belongs to the family's Cushitic branch, and had an estimated 50,000 speakers in Somalia in 1992, 57,500 in 2006 and 86,000 in 2020. The total number of speakers in Kenya and Somalia was estimated at 685,600 in 2019. Garre is in the Digil classification of Somali dialects. Garre language is readily intelligible to Digil speakers, as it has some affinity with Af-Maay and Af-Boon.
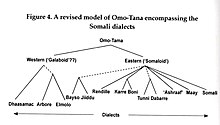
The Omo–Tana languages are a branch of the Cushitic family and are spoken in Ethiopia, Djibouti, Somalia and Kenya. The largest member is Somali. There is some debate as to whether the Omo–Tana languages form a single group, or whether they are individual branches of Lowland East Cushitic. Blench (2006) restricts the name to the Western Omo–Tana languages, and calls the others Macro-Somali.

Italian Somalis are Somali-born citizens who are fully or partially of Italian descent, whose ancestors were Italians who emigrated to Somalia during the Italian diaspora, or Italian-born people in Somalia. Most of the Italians moved to Somalia during the Italian colonial period.
Benadiri Somali, also referred to as "Coastal Somali", is a dialect of the Somali language. It is primarily spoken by the Benadiri people, who inhabit the southern Banaadir coast of Somalia and into Kenya.
The Zigula or Zigua language, Chizigua, is a Bantu language of Tanzania and Somalia, where the Mushunguli dialect is spoken.
The Macro-Somali or Somaloid languages, or Sam languages, are a branch of the Lowland East Cushitic languages. They are spoken in Somalia, Djibouti, eastern Ethiopia, and northern Kenya. The most widely spoken member is Somali.
Northern Somali is a dialect of the Somali language and forms the basis for Standard Somali. It is spoken by more than 70% of the entire Somali population, with its speech area stretching from Djibouti, Somaliland and the Somali Region of Ethiopia to the Northern Frontier District in Kenya. This widespread modern distribution is a result of a long series of southward population movements over the past ten centuries from the Gulf of Aden littoral.
Girirra also called Gariire is a Cushitic language of Ethiopia. It has extensive borrowing from Somali. Although not mutually intelligible with Somali, it is estimated that around 70% of the Garirra language is made up of Somali loan words. There has not been many studies on the language itself and is often grouped into a small umbrella of the Macro-Somali language family including relatives like: Rendille, Boni, Bayso, and the two dialects of Somali, being Af-Maay, and Af-Maxaa.