Related Research Articles

In computer networking, multicast is group communication where data transmission is addressed to a group of destination computers simultaneously. Multicast can be one-to-many or many-to-many distribution. Multicast should not be confused with physical layer point-to-multipoint communication.
The Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP) is a network protocol for delivering audio and video over IP networks. RTP is used in communication and entertainment systems that involve streaming media, such as telephony, video teleconference applications including WebRTC, television services and web-based push-to-talk features.
Helix DNA is a project to produce computer software that can play audio and video media in various formats, aid in producing such media, and serve them over a network. It is intended as a largely free and open-source digital media framework that runs on numerous operating systems and processors and was started by RealNetworks which contributed much of the code. The Helix Community is an open collaborative effort to develop and extend the Helix DNA platform.

Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) is a set of international open standards for digital television. DVB standards are maintained by the DVB Project, an international industry consortium, and are published by a Joint Technical Committee (JTC) of the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC) and European Broadcasting Union (EBU).
Digital Video Broadcasting – Satellite (DVB-S) is the original DVB standard for Satellite Television and dates from 1995, in its first release, while development lasted from 1993 to 1997. The first commercial applications was by Star TV in Asia and Galaxy in Australia, enabling digitally broadcast, satellite-delivered Television to the public.
DVB-T, short for Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial, is the DVB European-based consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital terrestrial television that was first published in 1997 and first broadcast in Singapore in February, 1998. This system transmits compressed digital audio, digital video and other data in an MPEG transport stream, using coded orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing modulation. It is also the format widely used worldwide for Electronic News Gathering for transmission of video and audio from a mobile newsgathering vehicle to a central receive point. It is also used in the US by Amateur television operators.
DVB-C stands for "Digital Video Broadcasting - Cable" and it is the DVB European consortium standard for the broadcast transmission of digital television over cable. This system transmits an MPEG-2 or MPEG-4 family digital audio/digital video stream, using a QAM modulation with channel coding. The standard was first published by the ETSI in 1994, and subsequently became the most widely used transmission system for digital cable television in Europe, Asia and South America. It is deployed worldwide in systems ranging from the larger cable television networks (CATV) down to smaller satellite master antenna TV (SMATV) systems.
Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) standards are an American set of standards for digital television transmission over terrestrial, cable and satellite networks. It is largely a replacement for the analog NTSC standard and, like that standard, is used mostly in the United States, Mexico, Canada, and South Korea. Several former NTSC users, in particular Japan, have not used ATSC during their digital television transition, because they adopted their own system called ISDB.

VLC media player is a free and open-source, portable, cross-platform media player software, and streaming media server developed by the VideoLAN project. VLC is available for desktop operating systems, and mobile platforms, such as Android, iOS, iPadOS, Tizen, Windows 10 Mobile, and Windows Phone. VLC is also available on digital distribution platforms such as Apple's App Store, Google Play, and Microsoft Store.
MPEG transport stream or simply transport stream (TS) is a standard digital container format for transmission and storage of audio, video, and Program and System Information Protocol (PSIP) data. It is used in broadcast systems such as DVB, ATSC and IPTV.
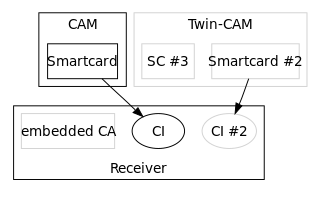
In Digital Video Broadcasting, the Common Interface is a technology which allows decryption of pay TV channels. Pay TV stations want to choose which encryption method to use. The Common Interface allows TV manufacturers to support many different pay TV stations, by allowing to plug in exchangeable conditional-access modules (CAM) for various encryption schemes.
Program-specific information (PSI) is metadata about a program (channel) and part of an MPEG transport stream.
Packetized Elementary Stream (PES) is a specification in the MPEG-2 Part 1 (Systems) and ITU-T H.222.0 that defines carrying of elementary streams in packets within MPEG program streams and MPEG transport streams. The elementary stream is packetized by encapsulating sequential data bytes from the elementary stream inside PES packet headers.
ATSC-M/H is a U.S. standard for mobile digital TV that allows TV broadcasts to be received by mobile devices.
High-definition television (HD) describes a television system providing an image resolution of substantially higher resolution than the previous generation of technologies. The term has been used since 1936, but in modern times refers to the generation following standard-definition television (SDTV), often abbreviated to HDTV or HD-TV. It is the current de facto standard video format used in most broadcasts: terrestrial broadcast television, cable television, satellite television, and Blu-ray Discs.

GPAC Project on Advanced Content is an implementation of the MPEG-4 Systems standard written in ANSI C. GPAC provides tools for media playback, vector graphics and 3D rendering, MPEG-4 authoring and distribution.
HTTP Live Streaming is an HTTP-based adaptive bitrate streaming communications protocol developed by Apple Inc. and released in 2009. Support for the protocol is widespread in media players, web browsers, mobile devices, and streaming media servers. As of 2019, an annual video industry survey has consistently found it to be the most popular streaming format.
The Helix Universal Media Server was a product developed by RealNetworks and originates from the first streaming media server originally developed by Progressive Networks in 1994. It supported a variety of streaming media delivery transports including MPEG-DASH RTMP (flash), RTSP (standard), HTTP Live Streaming (HLS), Microsoft Silverlight and HTTP Progressive Download enabling mobile phone OS and PC OS media client delivery.
Unreal Media Server is a streaming server software created by Unreal Streaming Technologies.

A TV gateway is a television headend to a network UPnP router that receives live digital video broadcast (DVB) MPEG transport streams (channels) from terrestrial aerials, satellite dishes, or cable feeds and converts them into IP streams for distribution over an IP network.