
The Lord's Resistance Army insurgency is an ongoing conflict between the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), a Ugandan militant religious extremist group, against the government of Uganda. Following the Ugandan Civil War, militant Joseph Kony formed the Lord's Resistance Army and launched an insurgency against the newly installed President Yoweri Museveni. The stated goal was to establish a Christian state based on the Ten Commandments. Currently, there is low-level LRA activity in eastern areas of the Democratic Republic of the Congo and the Central African Republic. Kony proclaims himself the 'spokesperson' of God and a spirit medium.
Joseph Rao Kony is a Ugandan militant and warlord who founded the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), designated as a terrorist group by the United Nations Peacekeepers, the European Union, and various other governments including the United Kingdom and United States of America.
The start of the period 1994 to 2002 of the Lord's Resistance Army insurgency in northern Uganda saw the conflict intensifying due to Sudanese support to the rebels. There was a peak of bloodshed in the mid-1990s and then a gradual subsiding of the conflict. Violence was renewed beginning with the offensive by the Uganda People's Defence Force in 2002.
The period from 2000 to 2006 of the Lord's Resistance Army insurgency in northern Uganda begins with the assault of the Uganda People's Defence Force (UPDF) upon LRA strongholds in South Sudan. This in turn led to a series of retaliatory attacks by the Lord's Resistance Army of an intensity not seen to since the mid-1990s. International awareness of the conflict gradually grew and in September 2005, the International Criminal Court issues warrants for the arrest of senior LRA commanders, including Joseph Kony.
Vincent Otti was a Ugandan militant who served as deputy-leader of the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), a rebel guerrilla army operating mainly in northern Uganda and southern Sudan. He was one of the five persons for whom the International Criminal Court (ICC) issued its first arrest warrants on 8 July 2005 in its investigation in Uganda. Rumours of his death began to circulate in October 2007 and strengthened in January 2008. On 17 November 2023, the ICC terminated proceedings against him.
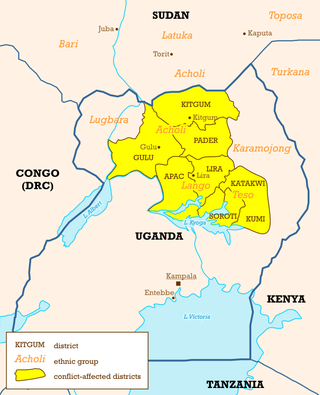
The Aboke abductions were the kidnapping of 139 secondary school female students from St. Mary's College Secondary school by rebels of the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) on 10 October 1996, in Aboke, Kole District, Uganda. The deputy head mistress of the college, Sister Rachele Fassera of Italy, pursued the rebels and successfully negotiated the release of 109 of the girls. The Aboke abductions and Fassera's dramatic actions drew international attention, unprecedented at that time, to the insurgency in northern Uganda. A book titled "Aboke Girls" was written by Els De Temmerman about the abductions and effects of the abductions.
Aboke is a town in the Kole District of the Northern Region of Uganda. It was the location of the Aboke abductions in October 1996.

The Juba talks were a series of negotiations between the government of Uganda and the Lord's Resistance Army rebel group over the terms of a ceasefire and possible peace agreement. The talks, held in Juba, the capital of autonomous Southern Sudan, began in July 2006 and were mediated by Riek Machar, the Vice President of Southern Sudan. The talks, which had resulted in a ceasefire by September 2006, were described as the best chance ever for a negotiated settlement to the 20-year-old war. However, LRA leader Joseph Kony refused to sign the peace agreement in April 2008. Two months later, the LRA carried out an attack on a Southern Sudanese town, prompting the Government of Southern Sudan to officially withdraw from their mediation role.

Atiak is a town in the Northern Region of Uganda on the Gulu-Nimule Road, the primary trade route between Uganda and South Sudan.

The Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) is a Christian extremist organization operating in Central Africa and East Africa. Its origins were in the Ugandan insurgency (1986–1994) against President Yoweri Museveni, during which Joseph Kony founded the LRA in 1987.
The 2008–2009 Garamba offensive started on 14 December 2008, when joint Ugandan, DR Congolese and Southern Sudanese forces launched a botched military attack against the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) in the Garamba region of DR Congo.

Machine Gun Preacher is a 2011 American biographical action drama film directed by Marc Forster and starring Gerard Butler, Michelle Monaghan, and Michael Shannon. It tells the story of Sam Childers, a former gang biker turned preacher, and his efforts to protect, in collaboration with the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA), the children of South Sudan from the atrocities of Joseph Kony's Lord's Resistance Army (LRA). The screenplay by Jason Keller was adapted from Childers' book Another Man's War and Ian Urbina's Vanity Fair article "Get Kony".

Invisible Children, Inc., founded in 2004, is an organization to increase awareness of the activities of the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA) in Central Africa, and its leader, Joseph Kony. Specifically, the group seeks to put an end to the practices of the LRA, which include abductions and abuse of children, and forcing them to serve as soldiers. To this end, Invisible Children urges the United States government to take military action in the central region of Africa. Invisible Children also operates as a charitable organization, soliciting donations and selling merchandise to raise money for its cause. The organization promotes its cause by dispensing films on the internet and presenting in high schools and colleges around the United States.
South Sudan and Uganda are neighboring states with strong cultural economic and political ties. The South Sudan and the neighbouring state of Uganda enjoy relatively strong cultural, political, and economic ties. As South Sudan neared independence, both states begun to take advantage of increased opportunities for trade, development and educational exchanges. The rebel group Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), however, continues to operate in the border areas between South Sudan, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Uganda.

The International Criminal Court investigation in Uganda or the situation in Uganda is an ongoing investigation by the International Criminal Court (ICC) into the Lord's Resistance Army insurgency which has been taking place in northern Uganda and neighbouring regions since 1987. The Lord's Resistance Army is a Christian-based group led by Joseph Kony that is accused of numerous human rights violations and war crimes including massacres, the abduction of civilians, the use of child soldiers, sexual enslavement, torture, and pillaging. After the government of Uganda referred the matter to the ICC in December 2003, warrants of arrest were issued in 2005 for Joseph Kony, Raska Lukwiya, Okot Odhiambo, Dominic Ongwen, and Vincent Otti, who became the first people to be indicted by the Court.

Kony 2012 is a 2012 American short documentary film produced by Invisible Children, Inc. The film's purpose was to make Ugandan cult leader, war criminal, and ICC fugitive Joseph Kony globally known so as to have him arrested by the end of 2012. The film was released on March 5, 2012, and spread virally, and the campaign was initially supported by various celebrities.
Grace Akallo is a Ugandan woman who was abducted in 1996 to be used as a child soldier in the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA), a rebel military group led by Joseph Kony. At the time of her abduction, Akallo was 15 years old and attending St. Mary's College, a Catholic boarding school in Aboke, Uganda. She remained in the LRA for seven months before escaping. After escaping the army, Akallo returned to St. Mary's College to finish her high school education. She began her college education at the Uganda Christian University, but finished her undergraduate degree at Gordon College after receiving a scholarship. Akallo then went on to receive her master's degree from Clark University. Upon her escape from the LRA, Akallo began working as an advocate for peace and for the rights of African women and children. She has been using both her experiences as a child soldier and the information she has gained in her higher education to advocate against violence and the use of child soldiers, as well as to help counsel other escaped child soldiers like herself.
The Regional Cooperation Initiative for the elimination of the LRA (RCI-LRA) with its military arm, the African Union Regional Task Force was a multi-national operation to counter the Lord's Resistance Army (LRA). On 22 November 2011 the AU Peace and Security Council authorized the RCI-LRA with the mandate to "strengthen the operational capabilities of the countries affected by the atrocities of the LRA, create an environment conducive to the stabilization of the affected areas, free of LRA atrocities, and facilitate the delivery of humanitarian aid to affected areas." The United Nations provided logistical support, the European Union and African Union contributed additional funding, and the United States provided non-combat military and strategic support.

Major General Richard Otto is a senior military officer in the Uganda People's Defence Forces (UPDF). Since 13 May 2024, he has been the Commander of the UPDF Mountain Division and also Commander of "Operation Shujaa", a joint undertaking by the UPDF and the Armed Forces of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC) to neutralize the Allied Democratic Front (ADF) terrorist organization in the Eastern DR Congo. Immediately prior to his current assignment, Richard Otto was the chairman of the "South Sudan Peace Mechanism", an IGAD-sponsored observer mechanism, to ensure adherence to the peace treaties by the protagonists.

From 1986 to 1994, a variety of rebel groups waged a civil war against the Ugandan government of President Yoweri Museveni. Most of the fighting took place in the country's north and east, although the western and central regions were also affected. The most important insurgent factions were the Uganda People's Democratic Army (UPDA), the Uganda People's Army (UPA), Alice Auma's Holy Spirit Movement (HSM), and Joseph Kony's army. Several smaller rebel factions and splinter groups of the larger movements waged their own campaigns; the rebels often clashed with each other. All belligerents, including the government, targeted civilians and committed human rights violations. In course of fighting that involved tens of thousands of troops, the Ugandan government was able to gradually defeat or contain most rebel factions. The operations in the north and east caused great destruction and resulted in high civilian casualties.











