
An oil platform, offshore platform, or offshore drilling rig is a large structure with facilities for well drilling to explore, extract, store, and process petroleum and natural gas that lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Many oil platforms will also contain facilities to accommodate their workforce. Most commonly, oil platforms engage in activities on the continental shelf, though they can also be used in lakes, inshore waters, and inland seas. Depending on the circumstances, the platform may be fixed to the ocean floor, consist of an artificial island, or float. Remote subsea wells may also be connected to a platform by flow lines and by umbilical connections. These sub-sea solutions may consist of one or more subsea wells or of one or more manifold centres for multiple wells.

A semi-submersible platform is a specialised marine vessel used in offshore roles including as offshore drilling rigs, safety vessels, oil production platforms, and heavy lift cranes. They have good ship stability and seakeeping, better than drillships.

Transocean Ltd. is the world's largest offshore drilling contractor based on revenue and is based in Vernier, Switzerland. The company has offices in 20 countries, including Canada, the United States, Norway, Scotland, India, Brazil, Singapore, Indonesia, and Malaysia.
Sonat, Inc., headquartered in Birmingham, Alabama, was a large Fortune 500 American energy holding company. The company was founded in 1928 and was listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol "SNT". Sonat was primarily involved in transmission and marketing natural gas and oil and gas exploration and production. The company was also involved in contract offshore drilling until 1995 when the offshore business became Transocean. In 1999 Sonat merged with El Paso Corporation. The company was headquartered in the AmSouth-Sonat Tower in downtown Birmingham.
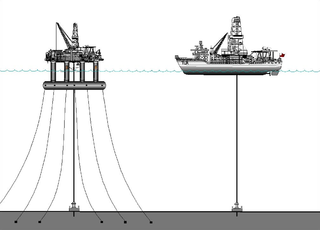
A drillship is a merchant vessel designed for use in exploratory offshore drilling of new oil and gas wells or for scientific drilling purposes. In most recent years the vessels are used in deepwater and ultra-deepwater applications, equipped with the latest and most advanced dynamic positioning systems.

Valaris plc is an offshore drilling contractor headquartered in Houston, Texas, and incorporated in the UK. It is the largest offshore drilling and well drilling company in the world, and owns 74 rigs, including 50 offshore jackup rigs, 16 drillships, and 8 semi-submersible platform drilling rigs.

Diamond Offshore Drilling, Inc. is an offshore drilling contractor. The company is headquartered in Katy, Texas, United States, and has major offices in Australia, Brazil, Mexico, Scotland, Singapore, and Norway.

Seadrill is a deepwater drilling contractor for the petroleum industry. It is incorporated in Bermuda for tax purposes and managed from London And Houston The company operates semi-submersible platforms, jackup rigs and drillships.

Offshore drilling is a mechanical process where a wellbore is drilled below the seabed. It is typically carried out in order to explore for and subsequently extract petroleum which lies in rock formations beneath the seabed. Most commonly, the term is used to describe drilling activities on the continental shelf, though the term can also be applied to drilling in lakes, inshore waters and inland seas.
Ocean Rig UDW Inc. was an operator of semi-submersible oil platforms and underwater drillships and was based in Athens. In 2018, the company was acquired by Transocean.

Deepwater Horizon was an ultra-deepwater (35,000 ft [11,000 m]), dynamically positioned, semi-submersible offshore drilling rig owned by Transocean. Built in 2001 in South Korea by Hyundai Heavy Industries, the rig was commissioned by R&B Falcon, registered in Majuro, and leased to BP from 2001 until September 2013. In September 2009, the rig drilled the deepest oil well in history at a vertical depth of 35,050 ft (10,683 m) and measured depth of 35,055 ft (10,685 m) in the Tiber Oil Field at Keathley Canyon block 102, approximately 250 miles (400 km) southeast of Houston, in 4,132 feet (1,259 m) of water.

Noble Corporation plc is an offshore drilling contractor organized in London, United Kingdom. Its affiliate, Noble Corporation, is organized in the Cayman Islands. It is the corporate successor of Noble Drilling Corporation.

A jackup rig or a self-elevating unit is a type of mobile platform that consists of a buoyant hull fitted with a number of movable legs, capable of raising its hull over the surface of the sea. The buoyant hull enables transportation of the unit and all attached machinery to a desired location. Once on location the hull is raised to the required elevation above the sea surface supported by the sea bed. The legs of such units may be designed to penetrate the sea bed, may be fitted with enlarged sections or footings, or may be attached to a bottom mat. Generally jackup rigs are not self-propelled and rely on tugs or heavy lift ships for transportation.
Deepwater drilling, or Deep well drilling, is the process of creating holes by drilling rig for oil mining in deep sea. There are approximately 3400 deepwater wells in the Gulf of Mexico with depths greater than 150 meters.

Pride International, Inc. was an offshore oil drilling company headquartered in Houston, Texas. As of February 2011, it operated 26 drilling rigs. In May 2011, it was acquired by Ensco.

Helix Energy Solutions Inc., known as Cal Dive International prior to 2006, is an American oil and gas services company headquartered in Houston, Texas. The company is a global provider of offshore services in well intervention and ROV operations of new and existing oil and gas fields.

Cameron International Corporation though now operating under Schlumberger, is a global provider of pressure control, production, processing, and flow control systems as well as project management and aftermarket services for the oil and gas and process industries. Cameron was acquired by Schlumberger (SLB) in 2016, and now operates as 'Cameron, a Schlumberger Company.' At the start of the SLB acquisition in 2015, Cameron employed approximately 23,000 people and delivered $9.8 billion in revenue.
Yavuz, ex Deepsea Metro I, is a Turkey-flagged ultra deepwater drillship owned and operated by the state-owned Turkish Petroleum Corporation (TPAO). She is Turkey's second drillship.

Kanuni is a Turkey-flagged sixth-generation ultra deepwater drillship owned and operated by the Turkish Petroleum Corporation. She is Turkey's third drillship.

SpaceX's floating launch platforms are modified oil rigs now under construction to use in the 2020s to provide a sea launch option for their second-generation launch vehicle: the heavy-lift Starship system, consisting of the Super Heavy booster and Starship second stage.














