
The Union Jack, or Union Flag, is the national flag of the United Kingdom. The flag also has a semi-official status in Canada, by parliamentary resolution, where it is known as the Royal Union Flag. Additionally, it is used as an official flag in some of the smaller British overseas territories. The Union Flag also appears in the canton of the flags of several nations and territories that are former British possessions or dominions, as well as the state flag of Hawaii.

The current state flag of Tasmania was officially adopted following a proclamation by Tasmanian colonial Governor Sir Frederick Weld on 25 September 1876, and was first published in the Tasmanian Gazette the same day. The governor's proclamation here were three official flags, they being the Governor's flag, the Tasmania Government vessel flag, and a Tasmania merchant flag. Up until 1856 when Tasmania was granted responsible self-government, the Union flag and the British ensign were primarily used on state occasions.

The current state flag of South Australia, was officially adopted by the government of South Australia in 1904.

In British maritime law and custom, an ensign is the identifying flag flown to designate a British ship, either military or civilian. Such flags display the United Kingdom Union Flag in the canton, with either a red, white or blue field, dependent on whether the vessel is civilian, naval, or in a special category. These are known as the red, white, and blue ensigns respectively.

The flag of New Zealand, also known as the New Zealand Ensign, is a defaced Blue Ensign: a blue field with the Union Flag in the canton, and four red stars with white borders to the right. The stars' pattern represents the asterism within the constellation of Crux, the Southern Cross.

The flag of the British Virgin Islands was adopted by Royal Warrant on 15 November 1960 after the islands were made into a separate British colony. Previously, the territory was administered as part of the British Leeward Islands.
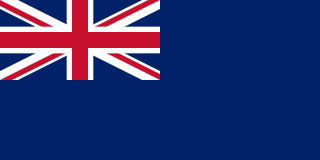
The Blue Ensign is a flag, one of several British ensigns, used by certain organisations or territories associated with the United Kingdom. It is used either plain, or defaced with a badge or other emblem.

A maritime flag is a flag designated for use on ships, boats, and other watercraft. Naval flags are considered important at sea and the rules and regulations for the flying of flags are strictly enforced. The flag flown is related to the country of registration: so much so that the word "flag" is often used symbolically as a synonym for "country of registration".

The flag of Victoria, symbolising the state of Victoria in Australia, is a British Blue Ensign defaced by the state badge of Victoria in the fly. The badge is the Southern Cross topped by an imperial crown, which is currently the St Edward's Crown. The stars of the Southern Cross are white and range from five to eight points with each star having one point pointing to the top of the flag. The flag dates from 1870, with minor variations, the last of which was in 1953. It is the only Australian state flag not to feature the state badge on a round disk.

The current state flag of New South Wales was officially adopted by the government of New South Wales in 1876.

The Australian White Ensign is a naval ensign used by ships of the Royal Australian Navy (RAN) from 1967 onwards. From the formation of the RAN until 1967, Australian warships used the British White Ensign as their ensign. However, this led to situations where Australian vessels were mistaken for British ships, and when Australia became involved in the Vietnam War, the RAN was effectively fighting under the flag of another, uninvolved nation. Proposals were made in 1965 for a unique Australian ensign, which was approved in 1966, and entered use in 1967.

The Australian Red Ensign resulted from the Commonwealth Government's 1901 Federal Flag Design Competition which required two entries: a flag for official Commonwealth Government use and another for the merchant navy. The winning design was based on the traditional British Red Ensign and featured the Southern Cross and Commonwealth Star.

The ensign of the United States is the flag of the United States when worn as an ensign. International maritime law—see International Treaty on Law of the Sea, articles 91 and 92—provides that vessels have a "national character" and thus should display a flag (ensign) that corresponds to this national character, especially when in international or foreign waters. Vessels that are formally documented under the federal vessel documentation act, vessels owned by government bodies in the United States, and vessels in the U.S. military unquestionably have U.S. national character, and thus properly hoist a U.S. ensign to show their national character. Vessels that are numbered by the states and small, non-registered craft owned by U.S. citizens and not registered in other countries may also hoist a U.S. ensign to show their national character.

The Royal Air Force Ensign is the official flag which is used to represent the British Royal Air Force. The ensign has a field of air force blue with the United Kingdom's flag in the canton and the Royal Air Force's roundel in the middle of the fly.
This article is a vexillological summary of all flags and symbols in current use by the island nation of Malta. More information on the history of the various flags and emblems, as well as on their equivalents which are no longer in use, is found on the specific articles, linked to in the subtitle headings.
The three branches of the Australian Defence Force are each represented by flags, among other emblems and insignia. Within each service various symbols fly on individual ships, at bases, camps, the Australian Defence Force Academy and colleges. These include flags, standards, guidons and banners and that denote rank, appointment, corps, formations, regiments, training units and sub units.




























