
The Tasman Sea is a marginal sea of the South Pacific Ocean, situated between Australia and New Zealand. It measures about 2,000 km (1,200 mi) across and about 2,800 km (1,700 mi) from north to south. The sea was named after the Dutch explorer Abel Janszoon Tasman, who in 1642 was the first known person to cross it. British explorer Lieutenant James Cook later extensively navigated the Tasman Sea in the 1770s during his three voyages of exploration.

Admiral of the Fleet Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe,, was a British naval officer. After serving throughout the War of the Austrian Succession, he gained a reputation for his role in amphibious operations against the French coast as part of Britain's policy of naval descents during the Seven Years' War. He also took part, as a naval captain, in the decisive British naval victory at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November 1759.

The flag of the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands was adopted in July 1, 1985 by the Second Northern Marianas Constitution. The NMI flag was originally designed during the year 1985. Later during that year, they finalized the draft of the flag in the last CNMI constitutional convention.

Lord Howe Island is an irregularly crescent-shaped volcanic remnant in the Tasman Sea between Australia and New Zealand, part of the Australian state of New South Wales. It lies 600 km (320 nmi) directly east of mainland Port Macquarie, 780 km (420 nmi) northeast of Sydney, and about 900 km (490 nmi) southwest of Norfolk Island. It is about 10 km (6.2 mi) long and between 0.3 and 2.0 km wide with an area of 14.55 km2, though just 3.98 km2 of that comprise the low-lying developed part of the island.

Ball's Pyramid is an uninhabited islet in the Pacific Ocean located 20 kilometres (12 mi) southeast of Lord Howe Island. The steep rocky basalt outcrop is the eroded plug of a shield volcano and caldera that formed 6.4 million years ago. It is 572 metres (1,877 ft) high, while measuring 1,100 metres (3,609 ft) in length and only 300 metres (984 ft) across, making it the tallest volcanic stack in the world.

The providence petrel is a large and heavy build gadfly petrel that nests in two locations in the Tasman Sea: Lord Howe Island and Philip Island.

The Lord Howe woodhen also known as the Lord Howe Island woodhen or Lord Howe (Island) rail, is a flightless bird of the rail family, (Rallidae). It is endemic to Lord Howe Island off the Australian coast. It is currently classified as endangered by the IUCN.

UTC+11:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +11:00. This time is used in:
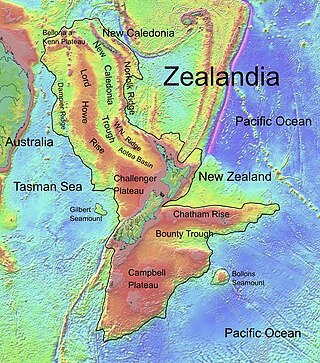
The Lord Howe Rise is a deep sea plateau which extends from south west of New Caledonia to the Challenger Plateau, west of New Zealand in the south west of the Pacific Ocean. To its west is the Tasman Basin and to the east is the New Caledonia Basin. Lord Howe Rise has a total area of about 1,500,000 km2 (580,000 sq mi), and generally lies about 750 to 1,200 metres under water. It is part of Zealandia, a much larger continent that is now mostly submerged, and so is composed of continental crust. Some have included the 3,500 m (11,500 ft) deep New Caledonia Basin as within the rise, given its continental crust origin, and this would give a larger total area of 1,950,000 km2 (750,000 sq mi).

Lord Howe Island Marine Park (Commonwealth waters) is a former marine protected area managed by the Commonwealth Department of the Environment, protecting the waters surrounding Lord Howe Island. It was adjacent to the 465.45 km2 Lord Howe Island Marine Park managed by the Marine Parks Authority New South Wales. On 8 November 2012, it was replaced by a new protected area known as the Lord Howe Commonwealth Marine Reserve.

Lord Howe Island Airport is an airport providing air transportation to Lord Howe Island. It is operated by the Lord Howe Island Board. Prior to its opening in September 1974, Lord Howe Island was served by flying boats from Rose Bay Water Airport.
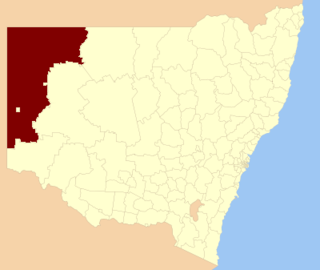
The Unincorporated Far West Region is an unincorporated area in the Far West region of New South Wales, Australia. The area is one of only two areas in New South Wales that are not part of any local government area. The region includes several small towns including Tibooburra, Milparinka and Silverton. Silverton and Tibooburra have village councils. The region includes some parts of Broken Hill, but not the city centre, which is in the separate City of Broken Hill local government area. The current administrator is Mr John McManus. It is the only local government area in Australia to have two time zones.
The large forest bat is a common vesper bat found in southeast Australia, Tasmania, and Lord Howe Island.
The Lord Howe Island skink is a part of the native Australian reptiles’ classification. The Lord Howe Island Skink is a species of skink in the family Scincidae, located on Australia's Norfolk Island and Lord Howe Island. The Lord Howe Island skink population is uncommon to be found on Lord Howe island, however the majority of their population is located on the Norfolk Island complex.This skink is metallic bronze in colour and has flecks for defining features. It can grow up to 8cm in length, making them medium in size. Its taxonomy is diverse, the skink is a part of the Scincidae family, Oligosoma genus. This skink population is protected and considered vulnerable under the Environment Protection and biodiversity conservation act 1999.

The Lord Howe silvereye, also known as the Lord Howe white-eye, Lord Howe Island white-eye or, locally, as the "Little Grinnell", is a small bird in the white-eye family, Zosteropidae. It is a subspecies of the silvereye, though sometimes considered a full species. It is endemic to Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea, part of New South Wales, Australia.

Passiflora herbertiana, or native passionfruit, is a widespread climbing twiner native to moist forests on the coast and ranges of eastern Australia. The subspecies P. h. insulae-howeiP.S.Green is endemic to Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea.

SS Makambo was a steamship first owned by Burns Philp & Co. Ltd. She was built in Port Glasgow in Scotland and named after an island in the Solomon Islands. She carried both passengers and cargo and was principally used on routes between eastern Australia and islands in Melanesia and the Tasman Sea. In November 1908 Jack and Charmian London travelled from Guadalcanal to Sydney on the Makambo after abandoning their ill-fated circumnavigation of the world on the Snark, a 45' sailing yawl.

The Lord Howe golden whistler, also known as the Lord Howe whistler or Lord Howe Island golden whistler, and locally as the “robin” or “yellow robin”, is a small bird in the whistler family, Pachycephalidae. It is a subspecies of the Australian golden whistler that is endemic to Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea, part of New South Wales, Australia.

Mount Gower, is the highest mountain on Australia's subtropical Lord Howe Island in the Tasman Sea. With a height of 875 metres (2,871 ft) above sea level, and a relatively flat 27-hectare (67-acre) summit plateau, it stands at the southern end of Lord Howe, just south of the island's second highest peak, the 777-metre (2,549 ft) high Mount Lidgbird, from which it is separated by the saddle at the head of Erskine Valley.
The Lord Howe Marine Park is an Australian marine park located about 550 km (340 mi) offshore of New South Wales, near Lord Howe Island. The marine park covers an area of 110,126 km2 (42,520 sq mi), encompassing the smaller Lord Howe Island Marine Park, and is assigned IUCN category IV. It is one of 8 parks managed under the Temperate East Marine Parks Network.

 The unofficial flag of Lord Howe Island.
The unofficial flag of Lord Howe Island.















