Related Research Articles

The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest and west of England, the West Midlands and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran its first trains in 1838. It was engineered by Isambard Kingdom Brunel, who chose a broad gauge of 7 ft —later slightly widened to 7 ft 1⁄4 in —but, from 1854, a series of amalgamations saw it also operate 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in standard-gauge trains; the last broad-gauge services were operated in 1892.
The Armagh rail disaster happened on 12 June 1889 near Armagh, County Armagh, in Ireland, when a crowded Sunday school excursion train had to negotiate a steep incline; the steam locomotive was unable to complete the climb and the train stalled. The train crew decided to divide the train and take forward the front portion, leaving the rear portion on the running line. The rear portion was inadequately braked and ran back down the gradient, colliding with a following train.

The vacuum brake is a braking system employed on trains and introduced in the mid-1860s. A variant, the automatic vacuum brake system, became almost universal in British train equipment and in countries influenced by British practice. Vacuum brakes also enjoyed a brief period of adoption in the United States, primarily on narrow-gauge railroads. Their limitations caused them to be progressively superseded by compressed air systems starting in the United Kingdom from the 1970s onward. The vacuum brake system is now obsolete; it is not in large-scale usage anywhere in the world, other than in South Africa, largely supplanted by air brakes.

Brake van and guard's van are terms used mainly in the UK, Ireland, Australia and India for a railway vehicle equipped with a hand brake which can be applied by the guard. The equivalent North American term is caboose, but a British brake van and a caboose are very different in appearance, because the former usually has only four wheels, while the latter usually has bogies. German railways employed Brakeman's cabins combined into other cars.

A coupling is a mechanism used to connect rolling stock together in a train.
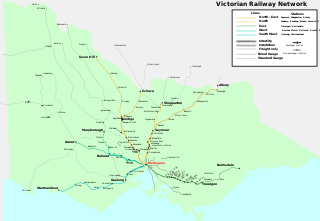
Rail transport in Victoria, Australia, is provided by a number of railway operators who operate over the government-owned railway lines. The network consists of 2,357 km of Victorian broad gauge lines, and 1,912 km of standard gauge freight and interstate lines; the latter increasing with gauge conversion of the former. Historically, a few experimental 762 mm gauge lines were built, along with various private logging, mining and industrial railways. The rail network radiates from the state capital, Melbourne, with main interstate links to Sydney and to Adelaide, as well as major lines running to regional centres, upgraded as part of the Regional Fast Rail project.

London Underground battery-electric locomotives are battery locomotives used for hauling engineers' trains on the London Underground network where they can operate when the electric traction current is switched off. The first two locomotives were built in 1905 for the construction of the Great Northern, Piccadilly and Brompton Railway, and their success prompted the District Railway to buy two more in 1909, which were the only ones built to the loading gauge of the subsurface lines. Following this, a number of battery vehicles were built by converting redundant motor cars, with the batteries placed in the unused passenger compartment. One exception to this was made by the City and South London Railway, who used a trailer car to hold the batteries, and wired them to a separate locomotive.
The African Union of Railways is an organisation under the auspices of the new African Union dealing with railways. It is similar to the International Union of Railways (UIC).

A telegraphic address or cable address was a unique identifier code for a recipient of telegraph messages. Operators of telegraph services regulated the use of telegraphic addresses to prevent duplication. Rather like a uniform resource locator (URL), the telegraphic address did not contain any routing information, but instead could be looked up by telegraph office personnel, who would then manually direct the message to the office nearest the destination or to an intermediate office. Since the destination address of a telegram counted as part of the message, using a short registered address code saved the expense of sending a complete street address. Telegraphic addresses were chosen either as versions of a company's name or as a memorable short word somehow associated with the recipient. Occasionally, an organization would come to be best known by its telegraphic address, for example Interflora, Interpol and Oxfam. A telegraphic address was a valuable part of a company's corporate identity, and disputes sometimes arose when a competitor registered a telegraphic address similar to a trade name or identifier used by a rival.

SA3 couplers or Willison coupler and Russian coupler are railway couplings used primarily in Russia and states influenced by the former Soviet Union, such as Finland, Poland, and Mongolia.

The Victorian Railways E class was a class of electric locomotive that ran on the Victorian Railways from 1923 until 1984. Introduced shortly after the electrification of the suburban rail system in Melbourne, Australia, and based on the same electrical and traction equipment as Melbourne's early suburban electric multiple unit fleet, they provided power for suburban goods services and shunting for six decades.

Great Western Railway telegraphic codes were a commercial telegraph code used to shorten the telegraphic messages sent between the stations and offices of the railway.

The passenger coaches of the Great Western Railway (GWR) were many and varied, ranging from four and six-wheeled vehicles for the original broad gauge line of 1838, through to bogie coaches up to 70 feet (21 m) long which were in service through to 1947. Vacuum brakes, bogies and through-corridors all came into use during the nineteenth century, and in 1900 the first electrically lit coaches were put into service. The 1920s saw some vehicles fitted with automatic couplings and steel bodies.

The fleet of Great Western Railway wagons was both large and varied as it carried the wide variety of goods traffic on the Great Western Railway (GWR) in the United Kingdom. This was the railway company that operated for the longest period of time in the country and covered a large geographical area that included big cities such as London, industrialised areas including the West Midlands, areas of coal and mineral mining such as South Wales, and Somerset and other important agricultural districts. In 1902 the company owned 59,036 wagons, and by 1926 this had risen to 88,580.

The Round Oak railway accident happened on 23 August 1858 between Brettell Lane and Round Oak railway stations, on the Oxford, Worcester and Wolverhampton Railway. The breakage of a defective coupling caused seventeen coaches and one brake van, containing about 450 passengers, of an excursion train to run backwards down the steep gradient between the stations, colliding with a following second portion of the excursion. 14 passengers were killed and 50 injured in the disaster. In the words of the Board of Trade accident inspector, Captain H. W. Tyler, it was at the time "decidedly the worst railway accident that has ever occurred in this country".

In telecommunication, a commercial code is a code once used to save on cablegram costs. Telegraph charged per word sent, so companies which sent large volumes of telegrams developed codes to save money on tolls. Elaborate commercial codes which encoded complete phrases into single words were developed and published as codebooks of thousands of phrases and sentences with corresponding codewords. Commercial codes were not generally intended to keep telegrams private, as codes were widely published; they were usually cost-saving measures only.

Janney couplers are a semi-automatic form of railway coupling that allow rail cars and locomotives to be securely linked together without rail workers having to get between the vehicles. They are also known as American, AAR, APT, ARA, MCB, knuckle, buckeye, tightlock, Henricot or center-buffer couplers.
Buffers and chain couplers are the de facto UIC standard railway stock coupling used in the EU and UK, and on some surviving colonial railways, such as in South America and India on older coaches. These couplers are an assembly of several devices: buffers, hooks and links or screws.
This article outlines the history and types of passenger rolling stock and guards vans on the narrow-gauge lines of the Victorian Railways in Australia. The types were constructed in parallel with very similar designs.
The Victorian Railways used a variety of former traffic wagons around depots and for specific construction, maintenance and similar tasks. Very few of these vehicles were specially constructed from scratch, often instead recycling components or whole wagon bodies and frames from old vehicles that had been withdrawn from normal service as life-expired or superseded by a better design.
References
- ↑ "Telegraphic Code Addresses". The West Australian . Perth: National Library of Australia. 5 August 1948. p. 10. Retrieved 14 April 2013.
- ↑ The Morse electric telegraph : a handbook for telegraphists, Victorian Railways, 1916, retrieved 14 April 2013
- ↑ Telegraph code book, Victorian Railways, 1937, retrieved 14 April 2013
- ↑ "Victorian Railways' Telegraph Code Book". Archived from the original on 4 May 2012. Retrieved 21 April 2012.
- ↑ Western Australian Government Railways Commission (1967), Uniform and supplementary telegraph code from 1st July, 1967, The Railways, retrieved 14 April 2013