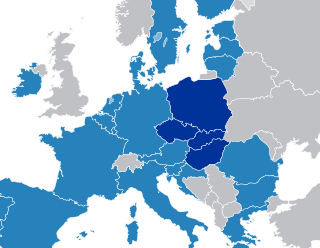
The Visegrád Group is a cultural and political alliance of four Central European countries: the Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland, and Slovakia. The alliance aims to advance co-operation in military, economic, cultural and energy affairs, and to further their integration with the EU. All four states are also members of the European Union (EU), the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), and the Bucharest Nine (B9).
European integration is the process of industrial, economic, political, legal, social, and cultural integration of states wholly or partially in Europe, or nearby. European integration has primarily but not exclusively come about through the European Union and its policies.

The Austrian Research Promotion Agency is an organization for the promotion of research and innovation in the field of applied and industrial research in Austria and is 100% owned by the Republic of Austria. The aim is to strengthen the business location Austria through targeted programs, especially in research and development. The ownership is represented by the federal government through the Federal Ministry for Transport, Innovation and Technology and the Federal Ministry of Economics and Labour.

The European Structural and Investment Funds are financial tools governed by a common rulebook, set up to implement the regional policy of the European Union, as well as the structural policy pillars of the Common Agricultural Policy and the Common Fisheries Policy. They aim to reduce regional disparities in income, wealth and opportunities. Europe's poorer regions receive most of the support, but all European regions are eligible for funding under the policy's various funds and programmes. The current framework is set for a period of seven years, from 2021 to 2027.

The Southeast European Cooperative Initiative (SECI) is a multilateral regional initiative that has been initiated by the European Union, the United States of America and the countries of Southeast Europe within the framework of the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) as a support to the implementation of the Dayton Accords in December 1996 at the inaugural session at Geneva on the basis of Final Points of Common EU-USA Understanding.

The California Department of Consumer Affairs (DCA) is a department within the California Business, Consumer Services, and Housing Agency. DCA's stated mission is to serve the interests of California's consumers by ensuring a standard of professionalism in key industries and promoting informed consumer practices. The DCA provides the public with information on safe consumer practices, in an effort to protect the public from unscrupulous or unqualified people who promote deceptive products or services.

Health policy can be defined as the "decisions, plans, and actions that are undertaken to achieve specific healthcare goals within a society". According to the World Health Organization, an explicit health policy can achieve several things: it defines a vision for the future; it outlines priorities and the expected roles of different groups; and it builds consensus and informs people.

The Ministry of Foreign Affairs is the government ministry of Austria responsible for diplomatic missions and immigration, the administration of foreign policy, and the maintenance of the country's relations with international organisations, especially the European Union. It oversees the Austrian embassies, consular representatives and other emissaries, and administers the naturalisation process and handles citizenship questions along with the Interior Ministry.

The Belgian Federal Police is the national police force of the Kingdom of Belgium. It carries out specialized and supra-local administrative and judicial police operations, and supports local police services when needed. Additionally, the Federal Police is responsible for patrolling and ensuring the safety of the country's highways. The Federal Police has approximately 12,300 officers and civilian personnel.

Austria–Kosovo relations refer to the bilateral relations of Austria and Kosovo. Kosovo has an embassy in Vienna and Austria has an embassy in Pristina.

The George C. Marshall European Center for Security Studies is a bi-national United States Department of Defense and Federal Ministry of Defence (Germany) security and defense studies institute. When the Marshall Center was founded in 1993, its mission was to create a more stable security environment by advancing democratic institutions and relationships, especially in the field of defense; promoting active, peaceful, security cooperation; and enhancing enduring partnerships among the nations of North America, Europe, and Eurasia. As of Oct. 1, 2014, the Marshall Center's regional mission changed to a transnational one based on an Office of the Secretary of Defense directive to change from a European to a global participants' base.

United States foreign aid, also known as US foreign assistance consists of a variety of tangible and intangible forms of assistance the United States gives to other countries. Foreign aid is used to support American national security and commercial interests and can also be distributed for humanitarian reasons. Aid is financed from US taxpayers and other revenue sources that Congress appropriates annually through the United States budget process. It is dispersed through "over 20 U.S. government agencies that manage foreign assistance programs," although about half of all economic assistance is channeled through the United States Agency for International Development (USAID).
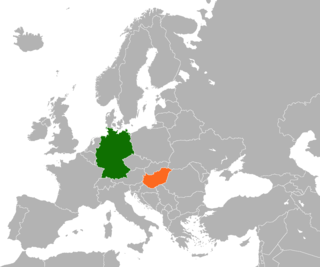
Germany and Hungary are both member states of the European Union, NATO, OECD, OSCE, Council of Europe and the World Trade Organization. Germany has an embassy in Budapest. Hungary has an embassy in Berlin, two general consulates and nine honorary consulates. The Agreement between the Federal Republic of Germany and the Republic of Hungary on 'Friendly Cooperation and Partnership in Europe' concluded on 6 February 1992 is one of the principal cornerstones of today's bilateral relations.

Cambodia–Denmark relations refers to the historical and current relationship of Cambodia and Denmark.

The nation of Austria has a two-tier health care system in which virtually all individuals receive publicly funded care, but they also have the option to purchase supplementary private health insurance. Care involving private insurance plans can include more flexible visiting hours and private rooms and doctors. Some individuals choose to completely pay for their care privately.

The International Centre for Migration Policy Development (ICMPD) is an international organisation which makes policy recommendations on migration-related issues to governments and intergovernmental agencies. Founded by Austria and Switzerland as a think tank in 1993, and headquartered in Vienna. As of May 2023 ICMPD was composed of 20 member states.

The Civil Aviation Authority of Malaysia, previously known as the Department of Civil Aviation, is a Malaysian government agency under the Ministry of Transport Malaysia. Established in 1969, it entrusted to oversee the technical issues related to the civil aviation sector in Malaysia. Effectively on 19 February 2018, DCA was incorporated into a statutory body known as CAAM.
The Austrian Development Agency GmbH (ADA) is the operational unit of the Austrian Development Cooperation. The ADA is a public-benefit, non-profit, limited liability company headquartered in Vienna. It is owned by the Republic of Austria, and represented by the Federal Ministry for Europe, Integration and Foreign Affairs. On behalf of the federal government of Austria, ADA plans, finances, and supports development programs and projects in Africa, Asia, South-Eastern and Eastern Europe, and the Caribbean. The goal of ADA is to improve conditions of life in developing countries and assist partner countries in their sustainable development. It also promotes projects in development communication and education in Austria to advance discussion on development cooperation.

The 2015 Western Balkans Summit was the second annual summit of heads of states and governments of Western Balkans. It took place in the Vienna, Austria, following the 2014 Conference of Western Balkan States that took place in Berlin, Germany. This summit forms part of the Berlin Process, a five-year process marked by yearly summits in order to underline the commitment to Future enlargement of the European Union towards the Western Balkans region. Official date of summit is 27 of August 2015. After 2014 conference Günther Oettinger confirmed that the event will be organised annually with Vienna as a host city in 2015 and Paris in 2016.

















