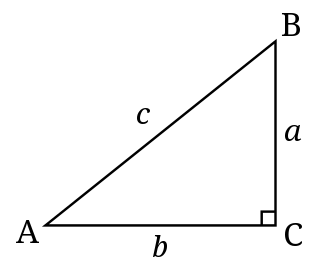
Explicit functions
Liouville's transcendence criterion
Because of the naming convention mentioned above, auxiliary functions can be dated back to their source simply by looking at the earliest results in transcendence theory. One of these first results was Liouville's proof that transcendental numbers exist when he showed that the so called Liouville numbers were transcendental. [2] He did this by discovering a transcendence criterion which these numbers satisfied. To derive this criterion he started with a general algebraic number α and found some property that this number would necessarily satisfy. The auxiliary function he used in the course of proving this criterion was simply the minimal polynomial of α, which is the irreducible polynomial f with integer coefficients such that f(α) = 0. This function can be used to estimate how well the algebraic number α can be estimated by rational numbers p/q. Specifically if α has degree d at least two then he showed that
and also, using the mean value theorem, that there is some constant depending on α, say c(α), such that
Combining these results gives a property that the algebraic number must satisfy; therefore any number not satisfying this criterion must be transcendental.
The auxiliary function in Liouville's work is very simple, merely a polynomial that vanishes at a given algebraic number. This kind of property is usually the one that auxiliary functions satisfy. They either vanish or become very small at particular points, which is usually combined with the assumption that they do not vanish or can't be too small to derive a result.
Fourier's proof of the irrationality of e
Another simple, early occurrence is in Fourier's proof of the irrationality of e, [3] though the notation used usually disguises this fact. Fourier's proof used the power series of the exponential function:
By truncating this power series after, say, N + 1 terms we get a polynomial with rational coefficients of degree N which is in some sense "close" to the function ex. Specifically if we look at the auxiliary function defined by the remainder:
then this function—an exponential polynomial—should take small values for x close to zero. If e is a rational number then by letting x = 1 in the above formula we see that R(1) is also a rational number. However, Fourier proved that R(1) could not be rational by eliminating every possible denominator. Thus e cannot be rational.
Hermite's proof of the irrationality of er
Hermite extended the work of Fourier by approximating the function ex not with a polynomial but with a rational function, that is a quotient of two polynomials. In particular he chose polynomials A(x) and B(x) such that the auxiliary function R defined by
could be made as small as he wanted around x = 0. But if er were rational then R(r) would have to be rational with a particular denominator, yet Hermite could make R(r) too small to have such a denominator, hence a contradiction.
Hermite's proof of the transcendence of e
To prove that e was in fact transcendental, Hermite took his work one step further by approximating not just the function ex, but also the functions ekx for integers k = 1,...,m, where he assumed e was algebraic with degree m. By approximating ekx by rational functions with integer coefficients and with the same denominator, say Ak(x) / B(x), he could define auxiliary functions Rk(x) by
For his contradiction Hermite supposed that e satisfied the polynomial equation with integer coefficients a0 + a1e + ... + amem = 0. Multiplying this expression through by B(1) he noticed that it implied
The right hand side is an integer and so, by estimating the auxiliary functions and proving that 0 < |R| < 1 he derived the necessary contradiction.