Related Research Articles

Sikhs are an ethnoreligious group who adhere to Sikhism, a religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Guru Nanak. The term Sikh has its origin in the Sanskrit word śiṣya, meaning 'seeker', 'disciple' or 'student'.

The Khalistan movement is a separatist movement seeking to create a homeland for Sikhs by establishing an ethno‐religious sovereign state called Khalistan in the Punjab region. The proposed boundaries of Khalistan vary between different groups; some suggest the entirety of the Sikh-majority Indian state of Punjab, while larger claims include Pakistani Punjab and other parts of North India such as Chandigarh, Haryana, and Himachal Pradesh. Shimla and Lahore have been proposed as the capital of Khalistan.

Babbar Khalsa also known as Babbar Khalsa International, is a Sikh militant organisation that aims to create an independent nation-state of Khalistan in the Punjab region of South Asia. It has used armed attacks, assassinations and bombings in aid of that goal, and is deemed to be a terrorist entity by various governments. Besides India, it operates in North America and Europe, including Scandinavia.

Talwinder Singh Parmar was an Indian militant, Sikh separatist, and the mastermind of the 1985 Air India Flight 182 bombing, which killed 329 people. It was the worst single incident of aviation terrorism in history until the September 11 attacks in the United States. In addition, another bomb was meant to explode aboard Air India Flight 301 in Japan the same day, but it exploded while the plane was still grounded, killing two people. Parmar was also the founder, leader, and Jathedar of Babbar Khalsa International (BKI), better known as Babbar Khalsa, a Sikh militant group involved in the Khalistan movement.

Dal Khalsa is a radical Sikh organisation, based in the city of Amritsar. The outfit was formed in 1978 by Gajinder Singh, the hijacker of Indian Airlines Flight 423. It came to prominence during Insurgency in Punjab along with Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale in 1981. Members of the Dal Khalsa have also been accused of the assassination of Lala Jagat Narain. The primary aim of Dal Khalsa is to form a Punjabi Sikh nation state called Khalistan.

The Sikh Empire was a regional power based in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent. It existed from 1799, when Maharaja Ranjit Singh captured Lahore, to 1849, when it was defeated and conquered by the British East India Company in the Second Anglo-Sikh War. It was forged on the foundations of the Khalsa from a collection of autonomous misls. At its peak in the 19th century, the empire extended from Gilgit and Tibet in the north to the deserts of Sindh in the south and from the Khyber Pass in the west to the Sutlej in the east as far as Oudh. It was divided into four provinces: Lahore, which became the Sikh capital; Multan; Peshawar; and Kashmir from 1799 to 1849. Religiously diverse, with an estimated population of 4.5 million in 1831, it was the last major region of the Indian subcontinent to be annexed by the British Empire.
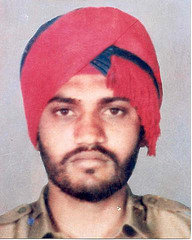
Dilawar Singh Babbar, now known as Dilavar Singh Jaisinghvala was the assassin of Beant Singh, the chief minister of Punjab, India. He was a serving Punjab Police officer and became a suicide bomber to assassinate the Chief Minister of Punjab.

Sikhism in Pakistan has an extensive heritage and history, although Sikhs form a small community in Pakistan today. Most Sikhs live in the province of Punjab, a part of the larger Punjab region where the religion originated in the Middle Ages, with some also residing in Peshawar in the Khyber-Pakhtunkhwa province. Nankana Sahib, the birthplace of Guru Nanak, the founder of Sikhism, is located in Pakistan's Punjab province. Moreover, the place where Guru Nanak died, the Gurudwara Kartarpur Sahib is also located in the same province.

Jathedar Sukhdev Singh Babbar was a was an Indian militant, Sikh separatist, and co-leader of Babbar Khalsa (BK), a Sikh militant organisation involved in the pursuit of creating a Sikh nation named as "Khalistan" and generally believed responsible for the 1985 bombing of Air India Flight 182, although Sukhdev was never named as being involved. BK was founded by Talwinder Singh Parmar, himself, and Amarjit Kaur. He commanded BK continuously for 14 years until he was killed in 1992. He was a member of the AKJ.
Guru Nanak founded the Sikh religion in the Punjab region of the northern part of the Indian subcontinent in the 15th century and opposed many traditional practices like fasting, Upanayana, idolatry, caste system, ascetism, azan, economic materialism, and gender discrimination.
The Sikhs are adherents to Sikhism, the fifth largest organized religion in the world, with around 25 million adherents. Sikh History is around 500 years and in that time the Sikhs have developed unique expressions of art and culture which are influenced by their faith and synthesize traditions from many other cultures depending on the locality of the adherents of the religion. Sikhism is the only religion that originated in the Punjab region with all other religions coming from outside Punjab. All the Sikh gurus, many saints, and many of the martyrs in Sikh history were from Punjab and from the Punjabi people. Punjabi culture and Sikhism are mistakenly considered inseparably intertwined. "Sikh" properly refers to adherents of Sikhism as a religion, strictly not an ethnic group. However, because Sikhism has seldom sought converts, most Sikhs share strong ethno-religious ties, therefore it is a common stereotype that all Sikhs share the same ethnicity. Many countries, such as the U.K., therefore misconcievingly recognize Sikh as a designated ethnicity on their censuses. The American non-profit organization United Sikhs has fought to have Sikhs included on the U.S. census as well, arguing that Sikhs "self-identify as an 'ethnic minority'" and believe "that they are more than just a religion".

Sikhism inAfghanistan in the contemporary era is limited to small populations, primarily in major cities, with the largest numbers of Afghan Sikhs living in Jalalabad, Ghazni, Kabul, and to a lesser extent in Kandahar and Khost. Sikhs have been the most prevalent non-Muslim minority in Afghanistan, and despite the many political changes in recent Afghan history, governments and political groups have generally not indulged in openly discriminating against the Sikh minority; however, their status have been severely impacted amid the country's conflict since 1978.

The Shiromani Akali Dal (SAD) is a centre-right Sikh-centric state political party in Punjab, India. The party is the second-oldest in India, after Congress, being founded in 1920. Although there are many parties with the description Akali Dal, the party that is recognized as "Shiromani Akali Dal" by the Election Commission of India is the one led by Sukhbir Singh Badal. The party has a moderate Punjabi agenda. On 26 September 2020, it left the National Democratic Alliance over the farm bills.
Punjabis in Afghanistan were residents of Afghanistan who were of Punjabi ancestry. There was historically a small Punjabi community in the country, mainly consisting of Afghan Sikhs and Hindus.
Events in the year 2018 in Afghanistan.
On 1 July 2018, a suicide bomber detonated in the center of the eastern Afghan city of Jalalabad, killing 20 people, mainly Sikhs and Hindus, and injuring 20 others.

The Islamic State–Taliban conflict is an ongoing insurgency by the Islamic State Khorasan Province (IS-KP) against the Taliban regime in Afghanistan. The conflict initially began when both operated as rival insurgent groups in Nangarhar; since the formation of the Taliban's state in 2021, IS-KP members have enacted a campaign of terrorism targeting both civilians and assassinating Taliban members using hit-and-run tactics. The group have also caused incidents and attacks across the border in Pakistan.

On 25 March 2020, ISIS gunmen and suicide bombers attacked the Gurdwara Har Rai Sahib in Kabul, Afghanistan.
Narendra Singh Khalsa is a Sikh Afghan politician. In January 2019, he secured a seat in the Lower House of the Parliament in the 2018 Afghan parliamentary election, on behalf of the Sikh and Hindu communities.
References
- ↑ Afghanistan, Unveiling (27 March 2014). "Awtar Singh Khalsa: 'They Gave the Hindus and Sikhs a place for rubbish disposal as a Place to Live'". huffingtonpost.com. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ↑ "Afghan Hindus, Sikhs see hope". The Tribune (Chandigarh) . 10 June 2002. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ↑ "Awtar Singh Khalsa: "They gave the Hindus and Sikhs a place for rubbish disposal as a place to live"". FIDH . 27 March 2014. Retrieved 23 January 2023.
- ↑ "Afghanistan blast: Sikhs among 19 dead in Jalalabad suicide attack". BBC News. 1 July 2018. Retrieved 1 July 2018.
- ↑ "Avtar Singh Khalsa, Sikh candidate for October polls among 20 killed in Afghanistan blast". Indian Express. 2 July 2018. Retrieved 2 July 2018.
- ↑ Bhaumik, Anirban (22 August 2021). "Sikh Afghan lawmaker Narender Khalsa among evacuees". Deccan Herald. Retrieved 23 January 2023.