Related Research Articles

The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa. It has historically been considered the longest river in the world, though this has been contested by research suggesting that the Amazon River is slightly longer. Of the world's major rivers, the Nile is one of the smallest, as measured by annual flow in cubic metres of water. About 6,650 km (4,130 mi) long, its drainage basin covers eleven countries: the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, Uganda, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt, Sudan and South Sudan. The Nile is an important economic driver supporting agriculture and fishing.

A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern.
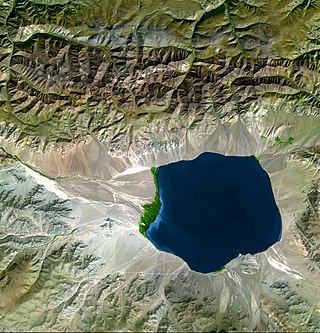
An endorheic basin is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water ; instead, the water drainage flows into permanent and seasonal lakes and swamps that equilibrate through evaporation. Endorheic basins are also called closed basins, terminal basins, and internal drainage systems.

The Awash River is a major river of Ethiopia. Its course is entirely contained within the boundaries of Ethiopia and empties into a chain of interconnected lakes that begin with Lake Gargori and end with Lake Abbe on the border with Djibouti, some 100 kilometres from the head of the Gulf of Tadjoura. The Awash River is the principal stream of an endorheic drainage basin covering parts of the Amhara, Oromia and Somali Regions, as well as the southern half of the Afar Region. The Awash River basin, spanning 23 administrative zones, covers 10% of Ethiopia's area.

The Ministry of Water Resources of the People's Republic of China is an executive department of the State Council of the People's Republic of China responsible for managing water resources in China. It is the 18th-ranking department of the State Council.

As a body of water that crosses numerous international political borders, the Nile river is subject to multiple political interactions. Traditionally it is seen as the world's longest river flowing 6,700 kilometres (4,200 mi) through ten countries in northeastern Africa – Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), Tanzania, Kenya, Uganda, Ethiopia, South Sudan, Sudan and Egypt with varying climates.
While Peru accounts for about four per cent of the world's annual renewable water resources, over 98% of its water is available east of the Andes, in the Amazon region. The coastal area of Peru, with most of economic activities and more than half of the population, receives only 1.8% of the national freshwater renewable water resources. Economic and population growth are taking an increasing toll on water resources quantity and quality, especially in the coastal area of Peru.
Water resources management is a key element of Brazil's strategy to promote sustainable growth and a more equitable and inclusive society. Brazil's achievements over the past 70 years have been closely linked to the development of hydraulic infrastructure for hydroelectric power generation and just recently to the development of irrigation infrastructure, especially in the Northeast region.

The Nile Basin Initiative (NBI) is a partnership among the Nile riparian states that “seeks to develop the river in a cooperative manner, share substantial socioeconomic benefits, and promote regional peace and security”. The NBI began with a dialogue among the riparian states that resulted in a shared vision objective “to achieve sustainable socioeconomic development through the equitable utilization of, and benefit from, the common Nile Basin water resources." It was formally launched in February 1999 by the water ministers of nine countries that share the river: Egypt, Sudan, Ethiopia, Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, Burundi, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC), as well as Eritrea as an observer. From its beginning the Nile Basin Initiative has been supported by the World Bank and by other external partners. The World Bank has a mandate to support the work of the NBI, as lead development partner and as administrator of the multi-donor Nile Basin Trust Fund. One of the partners is the "Nile Basin Discourse", which describes itself as "a civil society network of organisations seeking to achieve positive influence over the development of projects and programmes under the Nile Basin Initiative".

In geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins. This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available.
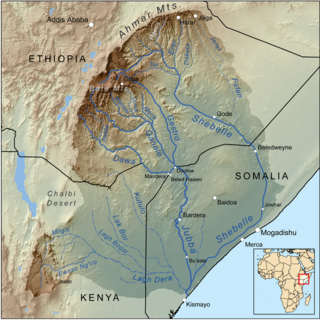
The Ganale Doria River is a perennial river in southeastern Ethiopia. Rising in the mountains east of Aleta Wendo, the Ganale flows south and east to join with the Dawa at the border with Somalia to become the Jubba. The river's tributaries include the Welmel, Weyib, and Mena. The Del Verme Falls is a notable feature of its middle course.
Water resources management in modern Egypt is a complex process that involves multiple stakeholders who use water for irrigation, municipal and industrial water supply, hydropower generation and navigation. In addition, the waters of the Nile support aquatic ecosystems that are threatened by abstraction and pollution. Egypt also has substantial fossil groundwater resources in the Western Desert.
Costa Rica is divided into three major drainage basins encompassing 34 watersheds with numerous rivers and tributaries, one major lake used for hydroelectric generation, and two major aquifers that serve to store 90% of the municipal, industrial, and agricultural water supply needs of Costa Rica. Agriculture is the largest water user demanding around 53% of total supplies while the sector contributes 6.5% to the Costa Rica GDP. About a fifth of land under cultivation is being irrigated by surface water. Hydroelectric power generation makes up a significant portion of electricity usage in Costa Rica and much of this comes from the Arenal dam.

Egypt's environmental problems include, but are not limited to, water scarcity, air pollution, damage to historic monuments, animal welfare issues and deficiencies in its waste management system.
Water resources management in El Salvador is characterized by difficulties in addressing severe water pollution throughout much of the country's surface waters due to untreated discharges of agricultural, domestic and industrial run off. The river that drains the capital city of San Salvador is considered to be polluted beyond the capability of most treatment procedures.
Guatemala faces substantial resource and institutional challenges in successfully managing its national water resources. Deforestation is increasing as the global demand for timber exerts pressure on the forests of Guatemala. Soil erosion, runoff, and sedimentation of surface water is a result of deforestation from development of urban centers, agriculture needs, and conflicting land and water use planning. Sectors within industry are also growing and the prevalence of untreated effluents entering waterways and aquifers has grown alongside.

The Nile Basin is the part of Africa drained by the Nile River and its tributaries.
The Ministry of Irrigation is the cabinet ministry of the Government of Sri Lanka responsible for:
The North Jiangsu Main Irrigation Canal is located in the lower reaches of the Huai River, one of the major rivers in the north of Jiangsu Province, China. It originates at Gaoliangjian on Hongze Lake and runs through Hongze, Qingpu, Huai'an, Funing, Sheyang and Binghai county(or district) and joins the artificial estuary of Biandan Harbour. The canal is 168 km in length and can irrigate 1,720,000 hectares of farmland. The construction program was organized and directed by the headquarters of the Jiangsu Huai River management program between October 1951 and May 1952.
References
- ↑ "Table 4.1. Important Physical Characteristics of the Ethiopian Basins, Nature and features of the Ethiopian river basins" Archived 2011-07-20 at the Wayback Machine , Ministry of Water Resources website (accessed 14 July 2009)