
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its capital city is Tepic.

Sinaloa, officially the Estado Libre y Soberano de Sinaloa, is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided into 18 municipalities and its capital city is Culiacán Rosales.

Kaminaljuyu is a Pre-Columbian site of the Maya civilization located in Guatemala City. Primarily occupied from 1500 BC to 1200 AD, it has been described as one of the greatest archaeological sites in the New World, although the extant remains are distinctly unimpressive. Debate continues about its size, integration, and role in the surrounding Valley of Guatemala and the Southern Maya area.

Mesoamerican chronology divides the history of prehispanic Mesoamerica into several periods: the Paleo-Indian ; the Archaic, the Preclassic or Formative (2500 BCE – 250 CE), the Classic (250–900 CE), and the Postclassic (900–1521 CE); as well as the post European contact Colonial Period (1521–1821), and Postcolonial, or the period after independence from Spain (1821–present).

Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area that begins in the southern part of North America and extends to most of Central America, thus comprising the lands of central Mexico, Belize, and Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, and Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. In the pre-Columbian era, many societies flourished in Mesoamerica for more than 3,000 years before the Spanish colonization of the Americas begun at Hispaniola island in 1493. In world history, Mesoamerica was the site of two historical transformations: (i) primary urban generation, and (ii) the formation of New World cultures from the mixtures of the indigenous Mesoamerican peoples with the European, African, and Asian peoples who were introduced by the Spanish colonization of the Americas.

Oasisamerica is a term that was coined by Paul Kirchhoff and published in a 1954 article, and is used by some scholars, primarily Mexican anthropologists, for the broad cultural area defining pre-Columbian southwestern North America. It extends from modern-day Utah down to southern Chihuahua, and from the coast on the Gulf of California eastward to the Río Bravo river valley. Its name comes from its position in relationship with the similar regions of Mesoamerica and mostly nomadic Aridoamerica. The term Greater Southwest is often used to describe this region by American anthropologists.

Mesoamerican architecture is the set of architectural traditions produced by pre-Columbian cultures and civilizations of Mesoamerica, traditions which are best known in the form of public, ceremonial and urban monumental buildings and structures. The distinctive features of Mesoamerican architecture encompass a number of different regional and historical styles, which however are significantly interrelated. These styles developed throughout the different phases of Mesoamerican history as a result of the intensive cultural exchange between the different cultures of the Mesoamerican culture area through thousands of years. Mesoamerican architecture is mostly noted for its pyramids, which are the largest such structures outside of Ancient Egypt.

The history of chocolate began in Mesoamerica. Fermented beverages made from chocolate date back to at least 1900 BC to 1500 BC. The Mexica believed that cacao seeds were the gift of Quetzalcoatl, the god of wisdom, and the seeds once had so much value that they were used as a form of currency. Originally prepared only as a drink, chocolate was served as a bitter liquid, mixed with spices or corn puree. It was believed to be an aphrodisiac and to give the drinker strength. Today, such drinks are also known as "Chilate" and are made by locals in the south of Mexico and the north triangle of Central America. After its arrival to Europe in the sixteenth century, sugar was added to it and it became popular throughout society, first among the ruling classes and then among the common people. In the 20th century, chocolate was considered essential in the rations of United States soldiers during war.

Trade in Maya civilization was a crucial factor in maintaining Maya cities.

Río Azul is an archaeological site of the Pre-Columbian Maya civilization. It is the most important site in the Río Azul National Park in the Petén Department of northern Guatemala, close to the borders of Mexico and Belize. Río Azul is situated to the southeast of the Azul river and its apogee dates to the Early Classic period.

Chocolá is a Preclassic Southern Maya site whose developmental emphasis was from c. 1000 BC to AD 200. The site lies within the Southern Maya area.

Like other Mesoamerican peoples, the traditional Maya recognize in their staple crop, maize, a vital force with which they strongly identify. This is clearly shown by their mythological traditions. According to the 16th-century Popol Vuh, the Hero Twins have maize plants for alter egos and man himself is created from maize. The discovery and opening of the Maize Mountain – the place where the corn seeds are hidden – is still one of the most popular of Maya tales. In the Classic period, the maize deity shows aspects of a culture hero.
The causes and degree of Olmec influences on Mesoamerican cultures has been a subject of debate over many decades. Although the Olmecs are considered to be perhaps the earliest Mesoamerican civilization, there are questions concerning how and how much the Olmecs influenced cultures outside the Olmec heartland. This debate is succinctly, if simplistically, framed by the title of a 2005 The New York Times article: “Mother Culture, or Only a Sister?”.

The Southern Maya Area is a region of Pre-Columbian sites in Mesoamerica. It is long believed important to the rise of Maya civilization, during the period that is known as Preclassic. It lies within a broad arc going southeast from Chiapa de Corzo in Mexico to Copán and Chalchuapa, in Central America.

Balberta is a major Mesoamerican archaeological site on the Pacific coastal plain of southern Guatemala, belonging to the Maya civilization. It has been dated to the Early Classic period and is the only known major site on the Guatemalan Pacific coastal plain to have exposed Early Classic architecture that has not been buried under posterior Late Classic construction. The site was related to the nearby site of San Antonio, which lies 6 kilometres (3.7 mi) to the west.

Chupícuaro is an important prehispanic archeological site from the late preclassical or formative period. The culture that takes its name from the site dates to 400 BC to 200 AD, or alternatively 500 BC to 300 AD., although some academics suggest an origin as early as 800 BC.
El Opeño is a Mesoamerican archaeological site located in the municipality of Jacona in the state of Michoacán, Mexico. It is home to a prehispanic site, mainly known from the ceramic material found in the funerary complexes of the site, which have been dated to the Late Preclassic period. The importance of this site in mesoamerican archaeology is due to its antiquity and the ample diffusion of its style, contemporary to other native culture developments such as the Capacha culture and earlier than the Chupicuaro. El Opeño tombs, the oldest in Mesoamerica, have been dated to around 1600 BCE - a similar period as Olmec culture development.
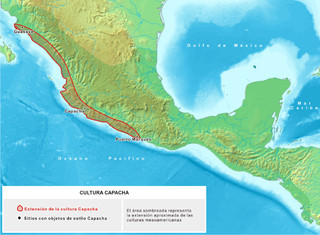
Capacha is an archaeological site located about 6 kilometers northeast of the Colima Municipality, in Colima State, Mexico. This site is the heart of the ancient Mesoamerican Capacha Culture.

Ixtlán del Rio is an archaeological site located in the Ixtlán del Rio municipality, on the south west region of the Nayarit State, Mexico. It is also known as "Los Toriles" and contains the only vestiges of the western cultures in Nayarit.
La Pintada is an archaeological site located some 60 kilometers south of the city of Hermosillo, Sonora, Mexico, within the “La Pintada” canyon, part of the “Sierra Libre”, a small mountain massif of the coastal plains that extends throughout the Sonoran Desert.














