
Beta-galactoside alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ST6GAL1 gene.

Glucosidase 2 subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCSH gene.

Galectin-8 is a protein of the galectin family that in humans is encoded by the LGALS8 gene.

Alpha-(1,3)-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FUT7 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT3 gene.

Beta-1,3-galactosyl-O-glycosyl-glycoprotein beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GCNT1 gene.

Alpha-N-acetylneuraminide alpha-2,8-sialyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ST8SIA1 gene.

Alpha-(1,3)-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FUT6 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT1 gene.

N-acetyllactosaminide beta-1,6-N-acetylglucosaminyl-transferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GCNT2 gene.
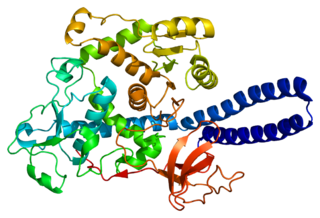
Alpha-(1,6)-fucosyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FUT8 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHST4 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT2 gene.

Beta-1,4 N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALNT1 gene.

Carbohydrate sulfotransferase 5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHST5 gene.

Polypeptide N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 13 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GALNT13 gene.

Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ST6GALNAC1 gene. This enzyme adds a N-Acetylneuraminic acid to an O-linked N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) on a peptide/proteins with an α2-6 linkage to produce the sialyl-Tn antigen. It has been shown that the enzyme prefers Thr over Ser containing GalNAc residues.
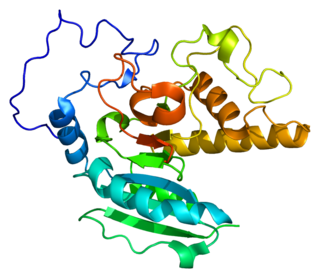
Histo-blood group ABO system transferase is an enzyme with glycosyltransferase activity, which is encoded by the ABO gene in humans. It is ubiquitously expressed in many tissues and cell types. ABO determines the ABO blood group of an individual by modifying the oligosaccharides on cell surface glycoproteins. Variations in the sequence of the protein between individuals determine the type of modification and the blood group. The ABO gene also contains one of 27 SNPs associated with increased risk of coronary artery disease.

Alpha-N-acetylgalactosaminide alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase 6 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ST6GALNAC6 gene.
The Sid blood group system is a human blood group defined by the presence or absence of the Sd(a) antigen on a person's red blood cells. About 96% of people are positive for the Sd(a) antigen, which is inherited as a dominant trait. Among Sd(a) positive individuals, the expression of the antigen ranges from extremely weak to extremely strong. Very strong expression of the antigen is referred to as a Sd(a++) phenotype. In addition to being expressed on red blood cells, Sd(a) is secreted in bodily fluids such as saliva and breast milk, and is found in the highest concentrations in urine. Urine testing is considered the most reliable method for determining a person's Sid blood type.

















