In molecular biology, housekeeping genes are typically constitutive genes that are required for the maintenance of basic cellular function, and are expressed in all cells of an organism under normal and patho-physiological conditions. Although some housekeeping genes are expressed at relatively constant rates in most non-pathological situations, the expression of other housekeeping genes may vary depending on experimental conditions.
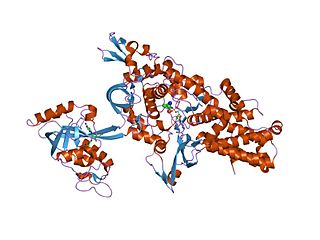
An aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, also called tRNA-ligase, is an enzyme that attaches the appropriate amino acid onto its corresponding tRNA. It does so by catalyzing the transesterification of a specific cognate amino acid or its precursor to one of all its compatible cognate tRNAs to form an aminoacyl-tRNA. In humans, the 20 different types of aa-tRNA are made by the 20 different aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, one for each amino acid of the genetic code.
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.

The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds specifically to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene promoters.
Chromosome 8 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 8 spans about 145 million base pairs and represents between 4.5 and 5.0% of the total DNA in cells.

In molecular biology, LSm proteins are a family of RNA-binding proteins found in virtually every cellular organism. LSm is a contraction of 'like Sm', because the first identified members of the LSm protein family were the Sm proteins. LSm proteins are defined by a characteristic three-dimensional structure and their assembly into rings of six or seven individual LSm protein molecules, and play a large number of various roles in mRNA processing and regulation.
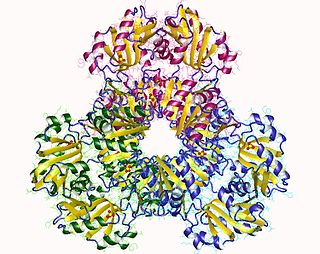
Ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase is an enzyme that converts ribose 5-phosphate into phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP). It is classified under EC 2.7.6.1.
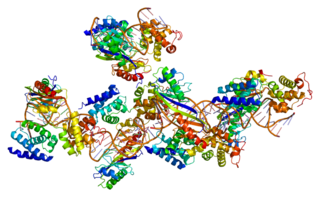
Transcription factor II B (TFIIB) is a general transcription factor that is involved in the formation of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex (PIC) and aids in stimulating transcription initiation. TFIIB is localised to the nucleus and provides a platform for PIC formation by binding and stabilising the DNA-TBP complex and by recruiting RNA polymerase II and other transcription factors. It is encoded by the TFIIB gene, and is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and analogous to bacterial sigma factors.

60S ribosomal protein L5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL5 gene.

In enzymology, a phenylalanine-tRNA ligase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
Tyrosine—tRNA ligase, also known as tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase is an enzyme that is encoded by the gene YARS. Tyrosine—tRNA ligase catalyzes the chemical reaction

Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 2 (eIF2β) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EIF2S2 gene.

Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYC gene.

Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase beta chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FARSB gene.

Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase alpha chain is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FARSA gene.
Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial (FARS2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FARS2 gene. This protein encoded by FARS2 localizes to the mitochondrion and plays a role in mitochondrial protein translation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 14, also known as Alpers encephalopathy, as well as spastic paraplegia 77 and infantile-onset epilepsy and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency.

S-Adenosylmethionine synthetase, also known as methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT), is an enzyme that creates S-adenosylmethionine by reacting methionine and ATP.

The FPG IleRS zinc finger domain represents a zinc finger domain found at the C-terminal in both DNA glycosylase/AP lyase enzymes and in isoleucyl tRNA synthetase. In these two types of enzymes, the C-terminal domain forms a zinc finger.

The B3/B4 domain, is found in tRNA synthetase beta subunits, as well as in some non-tRNA synthetase proteins.
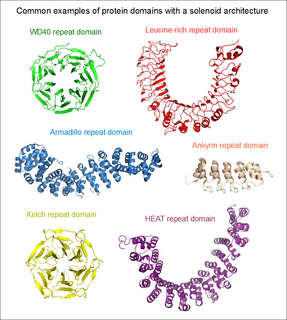
Solenoid protein domains are a highly modular type of protein domain. They consist of a chain of nearly identical folds, often simply called tandem repeats. They are extremely common among all types of proteins, though exact figures are unknown.

















