Electric power transmission is the bulk movement of electrical energy from a generating site, such as a power plant, to an electrical substation. The interconnected lines that facilitate this movement form a transmission network. This is distinct from the local wiring between high-voltage substations and customers, which is typically referred to as electric power distribution. The combined transmission and distribution network is part of electricity delivery, known as the electrical grid.

The Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) is the independent agency of the United States government that regulates the transmission and wholesale sale of electricity and natural gas in interstate commerce and regulates the transportation of oil by pipeline in interstate commerce. FERC also reviews proposals to build interstate natural gas pipelines, natural gas storage projects, and liquefied natural gas (LNG) terminals, in addition to licensing non-federal hydropower projects.

The electric power industry covers the generation, transmission, distribution and sale of electric power to the general public and industry. The commercial distribution of electric power started in 1882 when electricity was produced for electric lighting. In the 1880s and 1890s, growing economic and safety concerns lead to the regulation of the industry. What was once an expensive novelty limited to the most densely populated areas, reliable and economical electric power has become an essential aspect for normal operation of all elements of developed economies.
Eversource Energy is a publicly traded, Fortune 500 energy company headquartered in Hartford, Connecticut, and Boston, Massachusetts, with several regulated subsidiaries offering retail electricity, natural gas service and water service to approximately 4 million customers in Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Hampshire.

John Wright Hickenlooper Jr. is an American politician, geologist, and businessman serving as the junior United States senator from Colorado since 2021. A member of the Democratic Party, he served as the 42nd governor of Colorado from 2011 to 2019 and as the 43rd mayor of Denver from 2003 to 2011.

As one of the four power marketing administrations within the U.S. Department of Energy, the Western Area Power Administration (WAPA)'s role is to market wholesale hydropower generated at 57 hydroelectric federal dams operated by the Bureau of Reclamation, United States Army Corps of Engineers and the International Boundary and Water Commission. WAPA delivers this power through a more than 17,000-circuit-mile, high-voltage power transmission system to more than 700 preference power customers across the West. Those customers, in turn, provide retail electric service to more than 40 million consumers. WAPA is headquartered in the Denver, Colorado suburb of Lakewood, Colorado.

A regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States is an electric power transmission system operator (TSO) that coordinates, controls, and monitors a multi-state electric grid. The transfer of electricity between states is considered interstate commerce, and electric grids spanning multiple states are therefore regulated by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC). The voluntary creation of RTOs was initiated by FERC Order No. 2000, issued on December 20, 1999. The purpose of the RTO is to promote economic efficiency, reliability, and non-discriminatory practices while reducing government oversight.

The Electricity Act, 2003 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to transform the power sector in India.
Power Grid Corporation of India Limited is an Indian central public sector undertaking under the ownership of the Ministry of Power, Government of India. It is engaged mainly in transmission of bulk power across different states of India. It is headquartered in Gurugram. Power Grid transmits about 50% of the total power generated in India on its transmission network.

Demand response is a change in the power consumption of an electric utility customer to better match the demand for power with the supply. Until the 21st century decrease in the cost of pumped storage and batteries, electric energy could not be easily stored, so utilities have traditionally matched demand and supply by throttling the production rate of their power plants, taking generating units on or off line, or importing power from other utilities. There are limits to what can be achieved on the supply side, because some generating units can take a long time to come up to full power, some units may be very expensive to operate, and demand can at times be greater than the capacity of all the available power plants put together. Demand response, a type of energy demand management, seeks to adjust in real-time the demand for power instead of adjusting the supply.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.

Scott Harvey Peters is an American lawyer and politician serving as the U.S. representative from California's 50th congressional district since 2023, previously representing the 52nd congressional district from 2013 to 2023. His district includes both coastal and central portions of San Diego, as well as the suburbs of Poway and Coronado.

ISO New England Inc. (ISO-NE) is an independent, non-profit Regional Transmission Organization (RTO), headquartered in Holyoke, Massachusetts, serving Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont.

PJM Interconnection LLC (PJM) is a regional transmission organization (RTO) in the United States. It is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia.

An electrical grid is an interconnected network for electricity delivery from producers to consumers. Electrical grids consist of power stations, electrical substations to step voltage up or down, electric power transmission to carry power long distances, and lastly electric power distribution to individual customers, where voltage is stepped down again to the required service voltage(s). Electrical grids vary in size and can cover whole countries or continents. From small to large there are microgrids, wide area synchronous grids, and super grids.

A wide area synchronous grid is a three-phase electric power grid that has regional scale or greater that operates at a synchronized utility frequency and is electrically tied together during normal system conditions. Also known as synchronous zones, the most powerful is the Northern Chinese State Grid with 1,700 gigawatts (GW) of generation capacity, while the widest region served is that of the IPS/UPS system serving most countries of the former Soviet Union. Synchronous grids with ample capacity facilitate electricity trading across wide areas. In the ENTSO-E in 2008, over 350,000 megawatt hours were sold per day on the European Energy Exchange (EEX).

A National Interest Electric Transmission Corridor (NIETC) corridor is a geographic region designated by the United States Department of Energy where electricity transmission limitations are adversely affecting American citizens. The Energy Policy Act of 2005 granted the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) the authority to create these regions to increase transmission capacity within a short timeframe. If state and local governments fail to issue permits to increase transmission capacity in these areas, FERC can issue federal permits empowering project directors to use eminent domain to purchase property needed to complete projects.
Smart grid policy in the United States refers to legislation and other governmental orders influencing the development of smart grids in the United States.

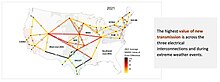
The electrical power grid that powers Northern America is not a single grid, but is instead divided into multiple wide area synchronous grids. The Eastern Interconnection and the Western Interconnection are the largest. Three other regions include the Texas Interconnection, the Quebec Interconnection, and the Alaska Interconnection. Each region delivers power at a nominal 60 Hz frequency. The regions are not usually directly connected or synchronized to each other, but there exist some HVDC interconnectors. The Eastern and Western grids are connected via seven links that allow 1.32 GW to flow between them. A study by the National Renewable Energy Laboratory found that increasing these interconnections would save energy costs.

The Mountain Valley Pipeline (MVP) is a natural gas pipeline being constructed from northwestern West Virginia to southern Virginia. The MVP will be 304 miles (489 km) long, and there is also a proposed Southgate Extension which will run 75 miles (121 km) from Virginia into North Carolina. The completed pipeline will have a capacity of 2 million dekatherms (Dts) of natural gas per day, with a large quantity of that gas being produced from the Marcellus and Utica shale formations.