This article's use of external links may not follow Wikipedia's policies or guidelines.(January 2025) |
| 118th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
117th ← → 119th | |
 United States Capitol (2023) | |
January 3, 2023 – January 3, 2025 | |
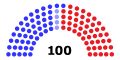
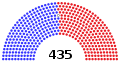
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives 6 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Democratic (through caucus) |
| Senate President | Kamala Harris (D) |
| House majority | Republican |
| House Speaker |
|
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 3, 2023 – January 3, 2024 2nd: January 3, 2024 – January 3, 2025 | |

The 118th United States Congress was a meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the United States Senate and the United States House of Representatives. It convened in Washington, D.C., on January 3, 2023, and ended on January 3, 2025, during the final two years of Joe Biden's presidency.
Contents
- Major events
- Major legislation
- Enacted
- Proposed (but not enacted)
- Major resolutions
- Adopted
- Proposed
- Vetoed
- Party summary
- Senate
- House of Representatives
- Leadership
- Senate 2
- House of Representatives 2
- Members
- Senate 3
- House of Representatives 3
- Changes in membership
- Senate changes
- House of Representatives changes
- Committees
- Senate committees
- House of Representatives committees
- Joint committees
- Officers and officials
- Congressional officers
- Senate officers
- House of Representatives officers
- See also
- Notes
- References
- External links
In the 2022 midterm elections, the Republican Party won control of the House 222–213, taking the majority for the first time since the 115th Congress, while the Democratic Party gained one seat in the Senate, where they already had effective control, and giving them a 51–49-seat majority (with a caucus of 48 Democrats and three Independents). [b] With Republicans winning the House, the 118th Congress ended the federal government trifecta Democrats held in the 117th. [1]
This congress also featured the first female Senate president pro tempore (Patty Murray), the first black party leader (Hakeem Jeffries) in congressional history, and the longest-serving Senate party leaders (Mitch McConnell and Dick Durbin). [c] The Senate had the highest number of Independent members in a single Congress since the ratification of the 17th Amendment after Joe Manchin left the Democratic Party to become an Independent. [2]
The 118th Congress was characterized as a uniquely ineffectual Congress, with its most notable events pointing towards political dysfunction. [3] The intense gridlock, particularly in the Republican-controlled House, where the Republican Conference's majority was often undercut by internal disputes among its members, [4] resulted in it passing the lowest number of laws for the first year of session since the Richard Nixon administration, and possibly ever. [5] By August 2024, the Congress has passed only 78 laws, less than a third of the next lowest laws per Congress in the 112th Congress, which also featured a Republican House opposing the Democratic Senate and White House. [6] This resulted in the need for a legislative coalition to pass key legislation, allowing the minority to exercise powers usually reserved for the majority. The fractious session demotivated many veteran legislators, with five committee chairs among the dozens who declared their resignation or retirement before the end of the session, three of whom were eligible to reprise their positions if the Republican Party retained their majority for 2025. [7] A higher-than-average number of retiring lawmakers were those attempting to pass bipartisan and collaborative legislation. [8] Two complete discharge petitions were filed in late 2024, both Republican-led with majority Democratic support, demonstrating a trend towards bucking leadership and lack of party discipline; [9] such a gambit was last successful in 2015 to support the Export–Import Bank. The second of these, a bill to remove certain Social Security restrictions, was subject to an unusual legislative procedure when a chair pro forma called forth a motion to table on a bill while the chamber was empty, flouting House convention and agreements. [10]
The Congress began with a multi-ballot election for Speaker of the House, which had not happened since the 68th Congress in 1923. Kevin McCarthy was eventually elected speaker on the 15th ballot. After relying on bipartisan votes to get out of a debt ceiling crisis and government shutdown threats, McCarthy became the first speaker ever to be removed from the role during a legislative session on October 3, 2023. [11] Following three failed attempts by various representatives to fill the post, on October 25, Mike Johnson was elected as speaker. Johnson would advance four more bipartisan continuing resolutions from November into March to avoid shutdowns. [12] [13] Congress finalized the 2024 United States federal budget on March 23, 2024, through two separate minibus packages. [14] Following a contentious foreign-aid vote, a motion to remove Johnson from the speakership was defeated in a bipartisan vote. [15]
Partisan disciplinary actions also increased. With the expulsion of New York representative George Santos from the House in December 2023, over the opposition of the speaker, this was the first congress since the 107th in which a member was expelled, and the first ever in which a Republican was. There was also an increase of censures passed in the House, [16] being the first congress with multiple censures since the 1983 congressional page sex scandal and the most in one year since 1870. In December 2023, House Republicans authorized an impeachment inquiry into Joe Biden, [17] followed by the impeachment of Alejandro Mayorkas in February 2024, the first time a cabinet secretary has been the target of impeachment proceedings since William W. Belknap in 1876, and only the second such cabinet impeachment in history. [18] [19] The charges were dismissed by the Senate, the first time the Senate dismissed impeachment articles without trial after the reading. [20]
This is the most recent Congress with Democratic senators from the states of Montana (Jon Tester) and Ohio (Sherrod Brown), both of whom lost re-election in 2024.