The Armstrong RBL 7-inch gun, also known as the 110-pounder, was an early attempt to use William Armstrong's new and innovative rifled breechloading mechanism for heavy rifled guns.

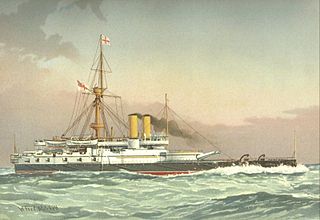
HMS Collingwood was the lead ship of her class of ironclad battleships built for the Royal Navy during the 1880s. The ship's essential design became the standard for most of the following British battleships. Completed in 1887, she spent the next two years in reserve before she was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet for the next eight years. After returning home in 1897, the ship spent the next six years as a guardship in Ireland. Collingwood was not significantly damaged during an accidental collision in 1899 and was paid off four years later. The ship was sold for scrap in 1909 and subsequently broken up.

The 100-ton gun was a 17.72 inches (450 mm) rifled muzzle-loading (RML) gun made by Elswick Ordnance Company, the armaments division of the British manufacturing company Armstrong Whitworth, owned by William Armstrong. The 15 guns Armstrong made armed two Italian battleships and, to counter these, British fortifications at Malta and Gibraltar.

The QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun (Quick-Firing) was used by many United Kingdom-built warships around the end of the 19th century and the start of the 20th century.

The QF 12-pounder 12-cwt gun was a common, versatile 3-inch (76.2 mm) calibre naval gun introduced in 1894 and used until the middle of the 20th century. It was produced by Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick and used on Royal Navy warships, exported to allied countries, and used for land service. In British service "12-pounder" was the rounded value of the projectile weight, and "12 cwt (hundredweight)" was the weight of the barrel and breech, to differentiate it from other "12-pounder" guns.

The Armstrong Whitworth 12-inch naval gun of 40 calibres length was designed by and manufactured mainly by Armstrong's ordnance branch, Elswick Ordnance Company. It was intended for the Royal Navy's Royal Sovereign-class battleships, but budgetary constraints delayed their introduction. The first units were instead supplied to Japan. As the Type 41 12-inch (305 mm) 40-calibre naval gun it was the standard main battery on several early United Kingdom-built pre-dreadnought battleships of the Imperial Japanese Navy.

The BL 12 inch naval gun Mk I was a British rifled breech-loading naval gun of the early 1880s intended for the largest warships such as battleships and also coastal defence. It was Britain's first attempt to match the large guns being installed in rival European navies, particularly France, after Britain transitioned from rifled muzzle-loading guns to the modern rifled breech-loaders somewhat later than the European powers. Mks I - VII all had a barrel of approximately 303 inches in length and similar performance.

The BL 13.5 inch naval gun Mk I was Britain's first successful large breechloading naval gun, initially designed in the early 1880s and eventually deployed in the late 1880s. Mks I - IV were all of 30 calibres length and of similar construction and performance.

The BL 12-inch Mark VIII naval gun was one of the first large British rifled breech-loading naval guns designed for the higher pressures generated by the new cordite propellant of the 1890s, and Britain's first large wire-wound gun. It represented a major advance compared to previous British guns.

The BL 9.2-inch Mk VIII naval gun was designed for the new cordite propellants and was the first British wire-wound gun of this calibre.
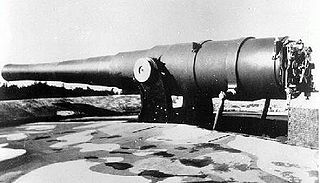
The BL 9.2-inch Mk I–VII guns were a family of early British heavy breechloading naval and coast defence guns in service from 1881 to the end of World War I. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.

The BL 10 inch guns Mks I, II, III, IV were British rifled breechloading 32-calibre naval and coast defence guns in service from 1885.

The BL 8 inch guns Mark I to Mark VII were the first generations of British rifled breechloaders of medium-heavy calibre. They were initially designed for gunpowder propellants and were of both 25.5 and 30 calibres lengths.

The BL 4-inch gun Mk I – Mk VI were a family of early British breech-loading 4-inch naval guns.

The BL 6 inch gun Mk V was an early Elswick Ordnance Company breech-loading naval gun originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants. They were used for coast defence around the British Empire.

The BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun Mk I was the first generation of British 6-inch breechloading naval gun after it switched from muzzle-loaders in 1880. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

RML 16-inch 80-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns intended to give the largest British battleships parity with the large guns being mounted by Italian and French ships in the Mediterranean Sea in the 1870s.

The RML 12-inch 25-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns of mid-late 1800s used as primary armament on British ironclad turret battleships and coastal monitors, and also ashore for coast defence. They were the shorter and less powerful of the two 12-inch (305-mm) British RML guns, the other being the 35-ton gun.

The RML 7-inch guns were various designs of medium-sized rifled muzzle-loading guns used to arm small to medium-sized British warships in the late 19th century, and some were used ashore for coast defence.