
A carronade is a short, smoothbore, cast-iron cannon which was used by the Royal Navy. It was first produced by the Carron Company, an ironworks in Falkirk, Scotland, and was used from the mid-18th century to the mid-19th century. Its main function was to serve as a powerful, short-range, anti-ship and anti-crew weapon. The technology behind the carronade was greater dimensional precision, with the shot fitting more closely in the barrel thus transmitting more of the propellant charge's energy to the projectile, allowing a lighter gun using less gunpowder to be effective. Carronades were initially found to be very successful, but they eventually disappeared as naval artillery advanced, with the introduction of rifling and consequent change in the shape of the projectile, exploding shells replacing solid shot, and naval engagements being fought at longer ranges.

The seventh HMS Enterprise of the Royal Navy was an armoured sloop launched in 1864 at Deptford Dockyard. Originally laid down as a wooden screw sloop of the Camelion class, she was redesigned by Edward Reed and completed as a central battery ironclad. The ship spent the bulk of her career assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet before returning to England in 1871 where she was paid off. Enterprise was sold for scrap in 1885.

Dahlgren guns were muzzle-loading naval artillery designed by Rear Admiral John A. Dahlgren USN, mostly used in the period of the American Civil War. Dahlgren's design philosophy evolved from an accidental explosion in 1849 of a 32 lb (14.5 kg) gun being tested for accuracy, killing a gunner. He believed a safer, more powerful naval cannon could be designed using more scientific design criteria. Dahlgren guns were designed with a smooth curved shape, equalizing strain and concentrating more weight of metal in the gun breech where the greatest pressure of expanding propellant gases needed to be met to keep the gun from bursting. Because of their rounded contours, Dahlgren guns were nicknamed "soda bottles", a shape which became their most identifiable characteristic.

Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support (NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) engagements. The term generally refers to powder-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines.

The 127 mm (5")/54 caliber lightweight gun is a U.S. naval artillery gun mount consisting of a 127 mm (5 in) L54 Mark 19 gun on the Mark 45 mount. It was designed and built by United Defense, a company later acquired by BAE Systems Land & Armaments, which continued manufacture.
Naval artillery in the Age of Sail encompasses the period of roughly 1571–1862: when large, sail-powered wooden naval warships dominated the high seas, mounting a large variety of types and sizes of cannon as their main armament. By modern standards, these cannon were extremely inefficient, difficult to load, and short ranged. These characteristics, along with the handling and seamanship of the ships that mounted them, defined the environment in which the naval tactics in the Age of Sail developed.

The 100-ton gun was a 17.72 inches (450 mm) rifled muzzle-loading (RML) gun made by Elswick Ordnance Company, the armaments division of the British manufacturing company Armstrong Whitworth, owned by William Armstrong. The 15 guns Armstrong made were used to arm two Italian battleships and, to counter these, British fortifications at Malta and Gibraltar.

The QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun (Quick-Firing) was used by many United Kingdom-built warships around the end of the 19th century and the start of the 20th century.

The QF 12-pounder 12-cwt gun (Quick-Firing) was a common, versatile 3-inch (76.2 mm) calibre naval gun introduced in 1894 and used until the middle of the 20th century. It was produced by Armstrong Whitworth, Elswick and used on Royal Navy warships, exported to allied countries, and used for land service. In British service "12-pounder" was the rounded value of the projectile weight, and "12 cwt (hundredweight)" was the weight of the barrel and breech, to differentiate it from other "12-pounder" guns.

The Armstrong Whitworth 12-inch naval gun of 40 calibres length was designed by and manufactured mainly by Armstrong's ordnance branch, Elswick Ordnance Company. It was intended for the Royal Navy's Royal Sovereign-class battleships, but budgetary constraints delayed their introduction. The first units were instead supplied to Japan. As the Type 41 12-inch (305 mm) 40-calibre naval gun it was the standard main battery on several early United Kingdom-built pre-dreadnought battleships of the Imperial Japanese Navy.

The 24 cm SK L/30 "Theodor Otto" (SK - SchnelladungskanoneL - Lange was a German railroad gun used in World War I. Four were built and saw service in 1918 on the Western Front.
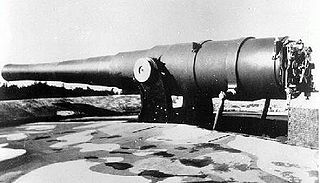
The BL 9.2-inch Mk I–VII guns were a family of early British heavy breechloading naval and coast defence guns in service from 1881 to the end of World War I. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

The BL 5-inch guns Mk I – Mk V were early British 5-inch rifled breechloading naval guns after it switched from rifled muzzle-loaders in the late 1870s. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants. The 5-inch calibre was soon discontinued in favour of QF 4.7-inch.

The RML 10-inch guns Mk I – Mk II were large rifled muzzle-loading guns designed for British battleships and monitors in the 1860s to 1880s. They were also fitted to the Bouncer and Ant-class flat-iron gunboats. They were also used for fixed coastal defences around the United Kingdom and around the British Empire until the early years of the 20th century.

The 68-pounder cannon was an artillery piece designed and used by the British Armed Forces in the mid-19th century. The cannon was a smoothbore muzzle-loading gun manufactured in several weights, the most common being 95 long cwt (4,800 kg), and fired projectiles of 68 lb (31 kg). Colonel William Dundas designed the 112 cwt version in 1841 and it was cast the following year. The most common variant, weighing 95 cwt, dates from 1846. It entered service with the Royal Artillery and the Royal Navy and saw active service with both arms during the Crimean War. Over 2,000 were made and it gained a reputation as the finest smoothbore cannon ever made.

The Canon de 155 L modèle 1918 Schneider was a French heavy artillery piece designed and produced during the First World War. A number were still on hand during the Second World War and served in French and German service.

The Canon de 155 L modèle 1877/14 Schneider was a French heavy artillery piece designed before and produced during the First World War. A number were still on hand during the Second World War and served in the French and German services.

The 15 cm Ring Kanone C/92 was a fortress and siege gun developed in the 1880s that saw service in the Italo-Turkish War, Balkan Wars, and World War I.

The Dutch naval gun 28 cm A No. 1, or 28 cm L/22, was the first of a few 28 cm Breechloader Krupp guns used by the Dutch navy. The 'A' stands for Achterlader, the Dutch word for Breechloader.

The Rupture of the Blockade of Arica was a naval battle of the War of the Pacific during the Blockade of Arica. The rupture was carried out by Manuel Villavicencio who commanded the BAP Unión of the Peruvian Navy. The Unión broke the Chilean blockade of the port twice in less than 8 hours on March 17, 1880.


















