This article explains terms used for the British Armed Forces' ordnance (weapons) and ammunition. The terms may have different meanings depending on its usage in another country's military.

The Armstrong RBL 7-inch gun, also known as the 110-pounder, was a heavy caliber Armstrong gun, an early type of rifled breechloader.

The 100-ton gun was the heaviest gun of the world for quite some time and got a lot of media attention. It was a 17.72-inch (450 mm) rifled muzzle-loading (RML) gun made by Elswick Ordnance Company, the armaments division of the British manufacturing company Armstrong Whitworth, owned by William Armstrong. The 15 guns Armstrong made were used to arm two Italian battleships and, to counter these, British fortifications at Malta and Gibraltar.
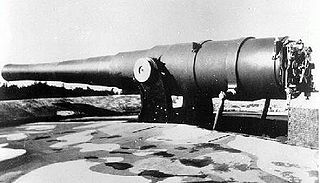
The BL 9.2-inch Mk I–VII guns were a family of early British heavy breechloading naval and coast defence guns in service from 1881 to the end of World War I. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.
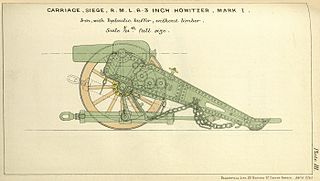
The RML 6.3-inch howitzer was a British rifled muzzle-loading "siege" or "position" howitzer/mortar proposed in 1874 and finally introduced in 1878 as a lighter version of the successful 8-inch howitzer that could be carried by the existing 40-pounder gun carriage.

The Armstrong Breech Loading 20-pounder gun, later known as RBL 20-pounder, was an early modern 3.75-inch rifled breech-loading light gun of 1859.

The RML 64-pounder 64 cwt gun is a Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) naval, field or fortification artillery gun manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately 64 pounds (29 kg). "64 cwt" refers to the gun's weight rounded up to differentiate it from other "64-pounder" guns.

The RML 10-inch guns Mk I – Mk II were large rifled muzzle-loading guns designed for British battleships and monitors in the 1860s to 1880s. They were also fitted to the Bouncer and Ant-class flat-iron gunboats. They were also used for fixed coastal defences around the United Kingdom and around the British Empire until the early years of the 20th century.

The RML 9-inch guns Mark I – Mark VI were large rifled muzzle-loading guns of the 1860s used as primary armament on smaller British ironclad battleships and secondary armament on larger battleships, and also ashore for coast defence. It should not be confused with the RML 9-inch Armstrong Gun, used by the Dutch navy, the Spanish Navy, and other navies.

The RML 12.5-inch guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns designed for British battleships and were also employed for coast defence.

The RML 12-inch 25-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns of mid-late 1800s used as primary armament on British ironclad turret battleships and coastal monitors, and also ashore for coast defence. They were the shorter and less powerful of the two 12-inch (305-mm) British RML guns, the other being the 35-ton gun.
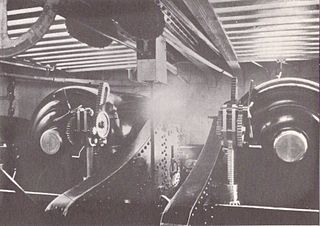
RML 12-inch 35-ton guns were large rifled muzzle-loading guns used as primary armament on British battleships of the 1870s. They were the longer and more powerful of the two 12-inch British RML guns, the other being the 25-ton gun.

The 68-pounder cannon was an artillery piece designed and used by the British Armed Forces in the mid-19th century. The cannon was a smoothbore muzzle-loading gun manufactured in several weights, the most common being 95 long cwt (4,800 kg), and fired projectiles of 68 lb (31 kg). Colonel William Dundas designed the 112 cwt version in 1841 and it was cast the following year. The most common variant, weighing 95 cwt, dates from 1846. It entered service with the Royal Artillery and the Royal Navy and saw active service with both arms during the Crimean War. Over 2,000 were made and it gained a reputation as the finest smoothbore cannon ever made.

The RML 7-inch guns were various designs of medium-sized rifled muzzle-loading guns used to arm small to medium-sized British warships in the late 19th century, and some were used ashore for coast defence.

The British RML 8-inch 9-ton guns Mark I – Mark III were medium rifled muzzle-loading guns used to arm smaller ironclad warships and coast defence batteries in the later 19th century.

The RML 40-pounder gun was a British rifled muzzle-loading siege and fortification gun designed in 1871. It was intended to supersede the RBL 40-pounder Armstrong gun after the British military reverted to rifled muzzle-loading artillery until a more satisfactory breech-loading system than that of the Armstrong guns was developed.
Gas-checks were attachments to ammunition that revolutionised the performance of RML heavy guns. The first generation of RML heavy guns began entering service in about 1865. They all had Woolwich rifling and relied on studs on the projectiles for rotation. Gas-checks were first introduced in 1878 or soon after. They significantly reduced wear on the guns while also increasing their range and accuracy. Before long, studless ammunition was being manufactured for these guns, using gas-checks for projectile rotation. Gas-checks also facilitated a switch to the second generation of RML guns which used polygroove rifling and only supported studless ammunition.
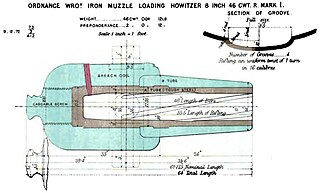
The RML 8-inch howitzer was a British Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) Howitzer manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately 180 pounds (82 kg). It was used in siege batteries and in fortifications.

The RML 6.6 inch howitzer was a British Rifled, Muzzle Loading (RML) Howitzer manufactured in England in the 19th century, which fired a projectile weighing approximately 100 pounds (45 kg). It was used in siege batteries and in fortifications.




















