
The BL 15-inch Mark I succeeded the BL 13.5-inch Mk V naval gun. It was the first British 15-inch (381 mm) gun design and the most widely used and longest lasting of any British designs, and arguably the most successful heavy gun ever developed by the Royal Navy. It was deployed on capital ships from 1915 until 1959 and was a key Royal Navy gun in both World Wars.

The BL 14-inch Mk VII naval gun was a breech loading (BL) gun designed for the battleships of the Royal Navy in the late 1930s. This gun armed the King George V-class battleships during the Second World War.

The BL 6-inch gun Mark VII was a British naval gun dating from 1899, which was mounted on a heavy travelling carriage in 1915 for British Army service to become one of the main heavy field guns in the First World War, and also served as one of the main coast defence guns throughout the British Empire until the 1950s.

The QF 6-inch 40 calibre naval gun (Quick-Firing) was used by many United Kingdom-built warships around the end of the 19th century and the start of the 20th century.

The Armstrong Whitworth 12-inch naval gun of 40 calibres length was designed by and manufactured mainly by Armstrong's ordnance branch, Elswick Ordnance Company. It was intended for the Royal Navy's Royal Sovereign-class battleships, but budgetary constraints delayed their introduction. The first units were instead supplied to Japan. As the Type 41 12-inch (305 mm) 40-calibre naval gun it was the standard main battery on several early United Kingdom-built pre-dreadnought battleships of the Imperial Japanese Navy.

The QF 12 pounder 18 cwt gun was a 3-inch high-velocity naval gun used to equip larger British warships such as battleships for defence against torpedo boats. 18 cwt referred to the weight of gun and breech, to differentiate the gun from others that also fired the "12 pound" shell.

The BL 13.5 inch naval gun Mk I was Britain's first successful large breechloading naval gun, initially designed in the early 1880s and eventually deployed in the late 1880s. Mks I - IV were all of 30 calibres length and of similar construction and performance.

The BL 9.2-inch Mk VIII naval gun was designed for the new cordite propellants and was the first British wire-wound gun of this calibre.
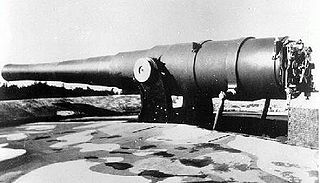
The BL 9.2-inch Mk I–VII guns were a family of early British heavy breechloading naval and coast defence guns in service from 1881 to the end of World War I. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants.

The BL 6-inch gun Marks II, III, IV and VI were the second and subsequent generations of British 6-inch rifled breechloading naval guns, designed by the Royal Gun Factory in the 1880s following the first 6-inch breechloader, the relatively unsuccessful BL 6-inch 80-pounder gun designed by Elswick Ordnance. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants but from the mid-1890s onwards were adapted to use the new cordite propellant. They were superseded on new warships by the QF 6-inch gun from 1891.

The BL 10 inch guns Mks I, II, III, IV were British rifled breechloading 32-calibre naval and coast defence guns in service from 1885.

The BL 4-inch gun Mk I – Mk VI were a family of early British breech-loading 4-inch naval guns.

The BL 4-inch gun Mk VII was a British high-velocity naval gun introduced in 1908 as an anti-torpedo boat gun in large ships, and in the main armament of smaller ships. Of the 600 produced, 482 were still available in 1939 for use as coastal artillery and as a defensive weapon on Defensively Equipped Merchant Ships (DEMS) during the Second World War.

The 14"/45 caliber gun,, whose variations were known initially as the Mark 1, 2, 3, and 5, and, when upgraded in the 1930s, were redesignated as the Mark 8, 9, 10, and 12. They were the first 14-inch (356 mm) guns to be employed with the United States Navy. The 14-inch/45 caliber guns were installed as the primary armament aboard all of the United States Navy's New York-class, Nevada-class, and Pennsylvania-class battleships. The gun also saw service in the British Royal Navy, where it was designated the BL 14 inch gun Mk II.

The BL 5-inch guns Mk I – Mk V were early British 5-inch rifled breechloading naval guns after it switched from rifled muzzle-loaders in the late 1870s. They were originally designed to use the old gunpowder propellants. The 5-inch calibre was soon discontinued in favour of QF 4.7-inch.

The BL 12 inch Gun Mark X was a British 45-calibre naval gun which was mounted as primary armament on battleships and battlecruisers from 1906. It first appeared on HMS Dreadnought.

The BL 6-inch Mark XII naval gun was a British 45 calibre naval gun which was mounted as primary armament on light cruisers and secondary armament on dreadnought battleships commissioned in the period 1914–1926, and remained in service on many warships until the end of World War II.

The BL 12-inch Mark XI and Mark XII gun were British breech loading (BL) naval guns of 50-calibres length mounted as primary armament on dreadnought battleships from 1910.
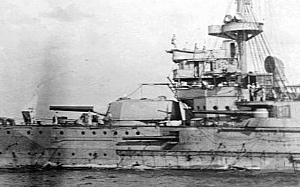
The EOC 10-inch 45 calibre gun were various similar 10-inch naval guns designed and manufactured by Elswick Ordnance Company to equip ships they built and/or armed for several countries before World War I.

The 50 calibre BL 6 inch gun Mark XXIII was the main battery gun used on the Royal Navy and British Commonwealth's conventional (non-anti-aircraft) light cruisers built from 1930 through the Second World War, and passed into service with several other navies when ships were disposed of after the end of the War.
























