| EOC 10 inch 45-calibre naval gun | |
|---|---|
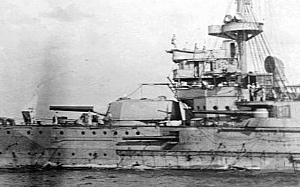 Forward 10-inch turret of HMS Swiftsure | |
| Type | Naval gun |
| Place of origin | United Kingdom |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1904–45 |
| Used by | Italy Japan United Kingdom |
| Wars | World War I World War II |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Elswick Ordnance Company |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 34.5 tons |
| Barrel length | 37 ft 6 in (11.430 m) (45 cal) |
| Shell | 500 pounds (227 kg) |
| Calibre | 10 inches (254 mm) |
| Elevation | -5° to +25° [1] |
| Muzzle velocity | UK : 2,625 ft/s (800 m/s) [2] Italy: 850 m/s (2,800 ft/s) [3] |
| Maximum firing range | UK : 18,850 yd (17,240 m) [4] Italy : 25,000 m (27,000 yd) [3] @ 25° [5] |
The EOC 10-inch 45 calibre gun were various similar 10-inch naval guns designed and manufactured by Elswick Ordnance Company to equip ships they built and/or armed for several countries before World War I.