BMP-2-inducible protein kinase is an enzyme in humans encoded by the BMP2K gene. [5]
BMP-2-inducible protein kinase is an enzyme in humans encoded by the BMP2K gene. [5]
This gene is the human homolog of mouse BMP-2-inducible kinase. Bone morphogenic proteins (BMPs) play a key role in skeletal development and patterning. Expression of the mouse gene is increased during BMP-2 induced differentiation and the gene product is a putative serine/threonine protein kinase containing a nuclear localization signal. Therefore, the protein encoded by this human homolog is thought to be a protein kinase with a putative regulatory role in attenuating the program of osteoblast differentiation. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [5]

FGF2, also known as basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF) and FGF-β, is a growth factor and signaling protein encoded by the FGF2 gene. It is synthesized primarily as a 155 amino acid polypeptide, resulting in an 18 kDa protein. However, there are four alternate start codons which provide N-terminal extensions of 41, 46, 55, or 133 amino acids, resulting in proteins of 22 kDa, 22.5 kDa, 24 kDa and 34 kDa, respectively. Generally, the 155 aa/18 kDa low molecular weight (LMW) form is considered cytoplasmic and can be secreted from the cell, whereas the high molecular weight (HMW) forms are directed to the cell's nucleus.

Bone morphogenetic protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by BMP4 gene. BMP4 is found on chromosome 14q22-q23

Bone morphogenetic protein 10 (BMP10) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP10 gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP6 gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMP5 gene.
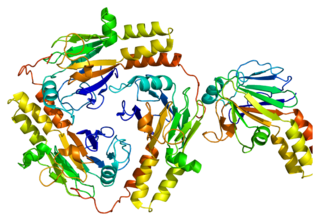
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 1 also known as SMAD family member 1 or SMAD1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD1 gene.

SMAD family member 6, also known as SMAD6, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD6 gene.

The bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type IA also known as BMPR1A is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BMPR1A gene. BMPR1A has also been designated as CD292.

Activin A receptor, type I (ACVR1) is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ACVR1 gene; also known as ALK-2. ACVR1 has been linked to the 2q23-24 region of the genome. This protein is important in the bone morphogenic protein (BMP) pathway which is responsible for the development and repair of the skeletal system. While knock-out models with this gene are in progress, the ACVR1 gene has been connected to fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva, a disease characterized by the formation of heterotopic bone throughout the body. It is a bone morphogenetic protein receptor, type 1.

Activin receptor type-2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACVR2A gene. ACVR2A is an activin type 2 receptor.

BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor homolog , also known as BAMBI, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the BAMBI gene.

Growth differentiation factor 2 (GDF2) also known as bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDF2 gene. GDF2 belongs to the transforming growth factor beta superfamily.

Growth differentiation factor 7 (GDF7) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GDF7 gene.

Bone morphogenetic protein receptor type-1B also known as CDw293 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMPR1B gene.
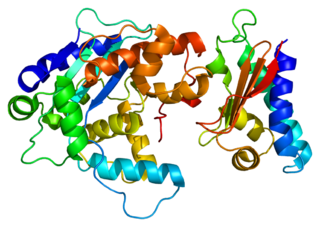
Protein Tob1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TOB1 gene.

Homeobox protein DLX-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DLX3 gene.

Krueppel-like factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF10 gene.

Protein atonal homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATOH1 gene.

Protein MRVI1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MRVI1 gene.

Tribbles homolog 1 is a protein kinase that in humans is encoded by the TRIB1 gene. Orthologs of this protein pseudokinase (pseudoenzyme) can be found almost ubiquitously throughout the animal kingdom. It exerts its biological functions through binding to signalling proteins of the MAPKK level of the MAPK pathway, therefore eliciting a regulatory role in the function of this pathway which mediates proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation in cells. Tribbles-1 is encoded by the trib1 gene, which in humans can be found on chromosome 8 at position 24.13 on the longest arm (q). Recent crystal structures show that Tribbles 1 has an unusual 3D structure, containing a 'broken' C-helix region, a binding site for ubiquitinated substrates such as C/EBPalpha and a key regulatory C-tail region. Like TRIB2 and TRIB3, TRIB1 has recently been considered as a potential allosteric drug target.
| This article on a gene on human chromosome 4 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |