The Digital Private Network Signalling System (DPNSS) is a network protocol used on digital trunk lines for connecting to PABX. It supports a defined set of inter-networking facilities.
Digital Access Signalling System 2 (DASS2) is an obsolescent protocol defined by British Telecom for digital links to PSTN based on ISDN. Although still available on request, it has been superseded by ETS 300 102 ("EuroISDN").
In telephony, ringdown is a method of signaling an operator in which telephone ringing current is sent over the line to operate a lamp or cause the operation of a self-locking relay known as a drop.

In telephony, an automated attendant allows callers to be automatically transferred to an extension without the intervention of an operator/receptionist. Many AAs will also offer a simple menu system. An auto attendant may also allow a caller to reach a live operator by dialing a number, usually "0". Typically the auto attendant is included in a business's phone system such as a PBX, but some services allow businesses to use an AA without such a system. Modern AA services can route calls to mobile phones, VoIP virtual phones, other AAs/IVRs, or other locations using traditional land-line phones.

A business telephone system is a multiline telephone system typically used in business environments, encompassing systems ranging in technology from the key telephone system (KTS) to the private branch exchange (PBX).

An intercom, talkback or doorphone is a stand-alone voice communications system for use within a building or small collection of buildings, functioning independently of the public telephone network. Intercoms are generally mounted permanently in buildings and vehicles. Intercoms can incorporate connections to public address loudspeaker systems, walkie talkies, telephones, and to other intercom systems. Some intercom systems incorporate control of devices such as signal lights and door latches.
The INI file format is an informal standard for configuration files for some computing platforms or software. INI files are simple text files with a basic structure composed of sections, properties, and values.

An attendant console is a telephone station that is generally part of a private branch exchange (PBX) or Centrex or other private telephone system. An attendant console generally is a regular PBX telephone station with one or more additional modules each bearing numerous buttons that can be programmed to be associated with particular lines in the private telephone system, or with particular specialized functions.
The BT Inspiration is a PBX telephone switchboard made by Lake Communications of Ireland. It is also sold in Scandinavia and France under the name Doro ip500pbxw and is very similar to Pathway. The systemphones for Inspiration and Pathway look identical but they are not interchangeable.
The BT Versatility is a telephone PBX switchboard sold by BT and targeted at small businesses. It is manufactured by Taratel Communications previously Lake Communications in Ireland as the OfficeLink. In South Africa it was sold by Tellumat as the Convergence 30 or C30, in Australia it was sold as the Commander Connect, in the USA it was sold by Inter-tel as the Encore CX and by Mitel as the Mitel 3000
In residential telephony, an extension telephone is an additional telephone wired to the same telephone line as another. In middle 20th century telephone jargon, the first telephone on a line was a "Main Station" and subsequent ones "Extensions". Such extension phones allow making or receiving calls in different rooms, for example in a home, but any incoming call would ring all extensions and any one extension being in use would cause the line to be busy for all users. Some telephones intended for use as extensions have built in intercom features; a key telephone system for a small business may offer two to five lines, lamps indicating lines already in use, the ability to place calls on 'hold' and an intercom on each of the multiple extensions.

The AT&T Merlin telephone system was introduced in late 1983, branded American Bell Merlin. After the breakup of AT&T in 1984, it was rebranded AT&T Merlin. It was designed at the beginning of the 1980s prior to the Bell System Divestiture as a modern electronic replacement for the dated electromechanical 1A2 Key System. Earlier Bell attempts at an electronic key system, such as the Horizon and Dimension, were not as successful as were the much larger systems, in fact the Dimension was a PBX. The Merlin was the first small electronic system, replacing the Com Key 416. The Merlin system was originally sold in two-line, six-telephone (206); four-line, 10-telephone (410); and eight-line, 20-telephone (820) configurations. Later, there was a further 10-line, 30-telephone configuration, with an expansion KSU allowing the system to accommodate up to 70 telephones available.

The 1A2 Key Telephone System is a business telephone system developed and distributed by the Western Electric Company for the Bell System.

The Kobe New Transit 2000 series (神戸新交通2000型) is an automated guideway transit (AGT) vehicle used for passenger service on the Port Island Line of the Kobe New Transit. The trains were introduced on February 2, 2006 to coincide with the extension of the Port Island Line to the newly opened Kobe Airport. The series is a successor to the 8000 series trains that has run on Port Liner since the line's opening in 1981.
IntercomPlus is the Walgreen Company's proprietary pharmacy computer system. It was founded as Intercom in 1981, and was the first large scale retail pharmacy computer system. It relies on VSAT satellite access and/or broadband connections to link the over 8,000 Walgreens retail, mail service, and specialty pharmacies. Through its usage, Intercom made Walgreens the largest private user of satellite transmission data in the world, second only to the U.S. Government. The design of the system enables seamless store-to-store prescription filling, making filling a refill at a location other than where it was filled originally essentially no different from filling it again at the original location.

Microsoft Response Point was an advanced software-based telephone system developed by Microsoft. Response Point, a PBX system targeting small businesses with less than 50 employees, was launched in March 2007, with systems available on the market in the fourth quarter of that year. Response Point is VoIP-based, and uses SIP as its signaling and call setup protocol. Response Point supports voicemail and multi-party calling in addition to two party VoIP calls. Response Point features innovative voice recognition technology to manage calls and voice mail. Voicemail messages can, optionally, be sent to e-mail where they can be retrieved and archived. Response Point voice dialing can work with the Response Point phone directory which is currently limited to 1100 contacts per user. Contacts may be imported from the Windows Address Book or Microsoft Outlook. Response Point automatically detects gateways and phones connected to the network.
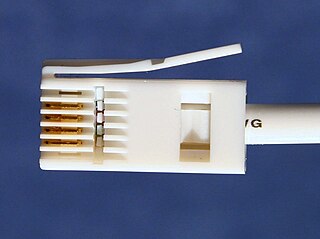
British telephone sockets were introduced in their current plug and socket form on 19 November 1981 by British Telecom to allow subscribers to connect their own telephones. The connectors are specified in British Standard BS 6312. Electrical characteristics of the telephone interface are specified by individual network operators, e.g. in British Telecom's SIN 351. Electrical characteristics required of British telephones used to be specified in BS 6305.
Ringing is a telecommunication signal that causes a bell or other device to alert a telephone subscriber to an incoming telephone call. Historically, this entailed sending a high-voltage alternating current over the telephone line to a customer station which contained an electromagnetic bell. It is therefore also commonly referred to as power ringing, to distinguish it from another signal, audible ringing, which is sent to the originating caller to indicate that the destination telephone is in fact ringing.
A trading turret or dealer board is a specialized telephony key system that is generally used by financial traders on their trading desks. Trading has progressed from floor trading through phone trading to electronic trading during the later half of the twentieth century with phone trading having dominated during the 1980s and 1990s. Although most trading volume is now done via electronic trading platforms, some phone trading persists and trading turrets are common on trading desks of investment banks.

A door phone or door bell phone is a set of electrical and electronic elements used to handle two-way communication in houses, apartments or villas. The device is connected to a secure communication system used to control the opening of the door giving access to any kind of buildings, offices, or apartment blocks. They are so widely used in the mentioned structures, that nowadays, they form part of the standard electrical installation of most buildings.











