
Bacillus thuringiensis is a Gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, commonly used as a biological pesticide. B. thuringiensis also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as Cadra calidella—in laboratory experiments working with C. calidella, many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite.

Panspermia is the hypothesis that life exists throughout the Universe, distributed by space dust, meteoroids, asteroids, comets, planetoids, and also by spacecraft carrying unintended contamination by microorganisms. Distribution may have occurred between galaxies, and so may not be restricted to the limited scale of solar systems.

An endospore is a dormant, tough, and non-reproductive structure produced by certain bacteria from the phylum Firmicutes. The name "endospore" is suggestive of a spore or seed-like form, but it is not a true spore. It is a stripped-down, dormant form to which the bacterium can reduce itself. Endospore formation is usually triggered by a lack of nutrients, and usually occurs in gram-positive bacteria. In endospore formation, the bacterium divides within its cell wall, and one side then engulfs the other. Endospores enable bacteria to lie dormant for extended periods, even centuries. There are many reports of spores remaining viable over 10,000 years, and revival of spores millions of years old has been claimed. There is one report of viable spores of Bacillus marismortui in salt crystals approximately 250 million years old. When the environment becomes more favorable, the endospore can reactivate itself to the vegetative state. Most types of bacteria cannot change to the endospore form. Examples of bacteria that can form endospores include Bacillus and Clostridium.

Prochlorococcus is a genus of very small (0.6 µm) marine cyanobacteria with an unusual pigmentation. These bacteria belong to the photosynthetic picoplankton and are probably the most abundant photosynthetic organism on Earth. Prochlorococcus microbes are among the major primary producers in the ocean, responsible for a large percentage of the photosynthetic production of oxygen. Analysis of the genome sequences of 12 Prochlorococcus strains show that 1,100 genes are common to all strains, and the average genome size is about 2,000 genes. In contrast, eukaryotic algae have over 10,000 genes.

Bacillus subtilis, known also as the hay bacillus or grass bacillus, is a Gram-positive, catalase-positive bacterium, found in soil and the gastrointestinal tract of ruminants and humans. A member of the genus Bacillus, B. subtilis is rod-shaped, and can form a tough, protective endospore, allowing it to tolerate extreme environmental conditions. B. subtilis has historically been classified as an obligate aerobe, though evidence exists that it is a facultative anaerobe. B. subtilis is considered the best studied Gram-positive bacterium and a model organism to study bacterial chromosome replication and cell differentiation. It is one of the bacterial champions in secreted enzyme production and used on an industrial scale by biotechnology companies.

Bacillus coagulans is a lactic acid-forming bacterial species. The organism was first isolated and described as Bacillus coagulans in 1915 by B.W. Hammer at the Iowa Agricultural Experiment Station as a cause of an outbreak of coagulation in evaporated milk packed by an Iowa condensary. Separately isolated in 1935 and described as Lactobacillus sporogenes in the fifth edition of Bergey's Manual, it exhibits characteristics typical of both genera Lactobacillus and Bacillus, its taxonomic position between the families Lactobacillaceae and Bacillaceae was often debated. However, in the seventh edition of Bergey's, it was finally transferred to the genus Bacillus. DNA-based technology was used in distinguishing between the two genera of bacteria which are morphologically similar and possess similar physiological and biochemical characteristics.
Bacillus safensis is a Gram-positive, spore-forming, and rod bacterium, originally isolated from a spacecraft in Florida and California. Bacillus safensis could have possibly been transported to the planet Mars on spacecraft Opportunity and Spirit in 2004. There are several known strains of this bacterium, all of which belong to the Firmicutes phylum of Bacteria. This bacterium also belongs to the large, pervasive genus Bacillus. Bacillus safensis is an aerobic chemoheterotroph and is highly resistant to salt, UV radiation, and gamma radiation. Bacillus safensis affects plant growth, since it is a powerful plant hormone producer, and it also acts as a plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria, enhancing plant growth after root colonization. Strain B. safensis JPL-MERTA-8-2 is the only bacterial strain shown to grow noticeably faster in micro-gravity environments than on the Earth surface.

Bacillus mycoides is a bacterium of the genus Bacillus. Like other Bacillus species, B. mycoides is Gram positive, rod-shaped, and forms spores. B. mycoides is distinguished from other Bacillus species by its unusual growth on agar plates, where it forms expansive hairy colonies with characteristic swirls.
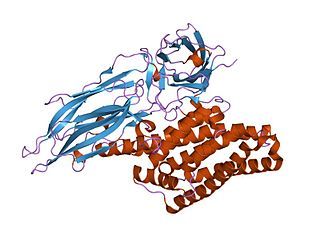
Delta endotoxins are pore-forming toxins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis species of bacteria. They are useful for their insecticidal action and are the primary toxin produced by Bt corn.

Bacillus anthracis is the etiologic agent of anthrax—a common disease of livestock and, occasionally, of humans—and the only obligate pathogen within the genus Bacillus. B. anthracis is a Gram-positive, endospore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium, with a width of 1.0–1.2 µm and a length of 3–5 µm. It can be grown in an ordinary nutrient medium under aerobic or anaerobic conditions.
Bacillus pumilus is a Gram-positive, aerobic, spore-forming bacillus commonly found in soil.
Bacillus atrophaeus is a species of black-pigmented bacteria. Its type strain is NRRL NRS-213. B. atrophaeus strains have been used extensively in biomedicine as indicator strains for heat- and chemical-based decontamination regimens. Most of the strains in use are derivatives of a lineage of B. atrophaeus that originated at Camp Detrick in the 1950s, where many modern biocontainment procedures were developed. B. atrophaeus has historically been known by several other names, including B. globigii and B. subtilis var. niger. Modern phylogenetic analyses using multiple genetic methods have placed B. atrophaeus close to B. subtilis. Its original and still most prominent use is as a surrogate organism for pathogenic B. anthracis, beginning in the U.S. bio-weapons program, as its pigmentation readily facilitated discrimination from non-pigmented background organisms in environmental samples. Subsequent genomic and phenotypic analysis of strains derived from the Camp Detrick isolates revealed that they had been deliberately selected for strains that exhibited elevated rates of sporulation.
Bacillus sporothermodurans is a species of bacteria notable for producing highly heat-resistant endospores, hence its name. It is strictly aerobic. Its type strain is M215.
Sporosarcina ureae is a type of bacteria of the genus Sporosarcina, and is closely related to the genus Bacillus. S. ureae is an aerobic, motile, spore-forming, Gram-positive coccus, originally isolated in the early 20th century from soil. S. ureae is distinguished by its ability to grow in relatively high concentrations of urea through production of at least one exourease, an enzyme that converts urea to ammonia. S. ureae has also been found to sporulate when environmental conditions become unfavorable, and can remain viable for up to a year.
Bacillus nealsonii is a species of bacteria first isolated from a spacecraft-assembly facility. Its spores are γ-radiation resistant. It is Gram-positive, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped and produces endospores. Its type strain is FO-92T.
Sporosarcina aquimarina is a rod-shaped bacterium of the genus Sporosarcina.
The exosporium is the outer surface layer of mature spores. In plant spores it is also referred to as the exine. Some bacteria also produce endospores with an exosporium, of which the most commonly studied are Bacillus species, particularly Bacillus cereus and the anthrax-causing bacterium Bacillus anthracis. The exosporium is the portion of the spore that interacts with the environment or host organism, and may contain spore antigens. Exosporium proteins, such as Cot protein, are also discovered related to strains of B. anthracis and B.cereus. This Cot protein share similar sequences with other spore coat proteins, and their putative determinants are believed to include bxpC, lunA, exsA, etc.











