Related Research Articles
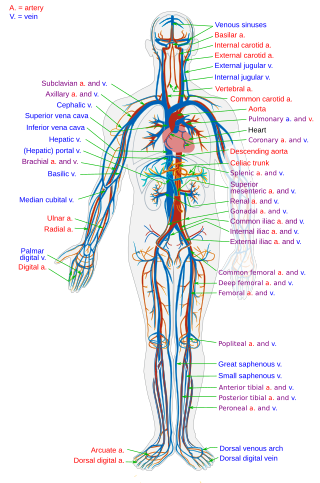
The circulatory system is a system of organs that includes the heart, blood vessels, and blood which is circulated throughout the entire body of a human or other vertebrate. It includes the cardiovascular system, or vascular system, that consists of the heart and blood vessels. The circulatory system has two divisions, a systemic circulation or circuit, and a pulmonary circulation or circuit. Some sources use the terms cardiovascular system and vascular system interchangeably with circulatory system.

dextro-Transposition of the great arteries is a potentially life-threatening birth defect in the large arteries of the heart. The primary arteries are transposed.

Atrial septal defect (ASD) is a congenital heart defect in which blood flows between the atria of the heart. Some flow is a normal condition both pre-birth and immediately post-birth via the foramen ovale; however, when this does not naturally close after birth it is referred to as a patent (open) foramen ovale (PFO). It is common in patients with a congenital atrial septal aneurysm (ASA).
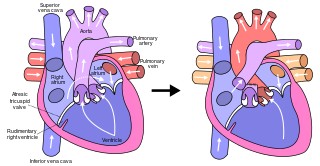
The Fontan procedure or Fontan–Kreutzer procedure is a palliative surgical procedure used in children with univentricular hearts. It involves diverting the venous blood from the inferior vena cava (IVC) and superior vena cava (SVC) to the pulmonary arteries. The procedure varies for differing congenital heart pathologies. For example in tricuspid atresia, the procedure can be done where the blood does not pass through the morphologic right ventricle; i.e., the systemic and pulmonary circulations are placed in series with the functional single ventricle. Whereas in hypoplastic left heart syndrome, the heart is more reliant on the more functional right ventricle to provide blood flow to the systemic circulation. The procedure was initially performed in 1968 by Francis Fontan and Eugene Baudet from Bordeaux, France, published in 1971, simultaneously described in July 1971 by Guillermo Kreutzer from Buenos Aires, Argentina, presented at the Argentinean National Cardilogy meeting of that year and finally published in 1973.

Cardiac catheterization is the insertion of a catheter into a chamber or vessel of the heart. This is done both for diagnostic and interventional purposes.

The atrium is one of the two upper chambers in the heart that receives blood from the circulatory system. The blood in the atria is pumped into the heart ventricles through the atrioventricular mitral and tricuspid heart valves.

Transposition of the great vessels (TGV) is a group of congenital heart defects involving an abnormal spatial arrangement of any of the great vessels: superior and/or inferior venae cavae, pulmonary artery, pulmonary veins, and aorta. Congenital heart diseases involving only the primary arteries belong to a sub-group called transposition of the great arteries (TGA), which is considered the most common congenital heart lesion that presents in neonates.

Tricuspid atresia is a form of congenital heart disease whereby there is a complete absence of the tricuspid valve. Therefore, there is an absence of right atrioventricular connection. This leads to a hypoplastic (undersized) or absent right ventricle. This defect is contracted during prenatal development, when the heart does not finish developing. It causes the systemic circulation to be filled with relatively deoxygenated blood. The causes of tricuspid atresia are unknown.

The Norwood procedure is the first of three surgeries intended to create a new functional systemic circuit in patients with hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS) and other complex heart defects with single ventricle physiology. The first successful Norwood procedure involving the use of a cardiopulmonary bypass was reported by Dr. William Imon Norwood, Jr. and colleagues in 1981.
A right-to-left shunt is a cardiac shunt which allows blood to flow from the right heart to the left heart. This terminology is used both for the abnormal state in humans and for normal physiological shunts in reptiles.
Arterial switch operation (ASO) or arterial switch, is an open heart surgical procedure used to correct dextro-transposition of the great arteries (d-TGA).
In cardiology, a cardiac shunt is a pattern of blood flow in the heart that deviates from the normal circuit of the circulatory system. It may be described as right-left, left-right or bidirectional, or as systemic-to-pulmonary or pulmonary-to-systemic. The direction may be controlled by left and/or right heart pressure, a biological or artificial heart valve or both. The presence of a shunt may also affect left and/or right heart pressure either beneficially or detrimentally.
The Mustard procedure was developed in 1963 by Dr. William Mustard at the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
Crisscross heart is a type of congenital heart defect where the right atrium is closely associated with the left ventricle in space, and the left atrium is closely associated with the right ventricle.

A double inlet left ventricle (DILV) or "single ventricle", is a congenital heart defect appearing in 5 in 100,000 newborns, where both the left atrium and the right atrium feed into the left ventricle. The right ventricle is hypoplastic or does not exist.

The bidirectional Glenn (BDG) shunt, or bidirectional cavopulmonary anastomosis, is a surgical technique used in pediatric cardiac surgery procedure used to temporarily improve blood oxygenation for patients with a congenital cardiac defect resulting in a single functional ventricle. Creation of a bidirectional shunt reduces the amount of blood volume that the heart needs to pump at the time of surgical repair with the Fontan procedure.

Hypoplastic right heart syndrome (HRHS) is a congenital heart defect in which the structures on the right side of the heart, particularly the right ventricle, are underdeveloped. This defect causes inadequate blood flow to the lungs, and thus a cyanotic infant.
The Senning procedure is an atrial switch heart operation performed to treat transposition of the great arteries. It is named after its inventor, the Swedish cardiac surgeon Åke Senning (1915–2000), also known for implanting the first permanent cardiac pacemaker in 1958.
Atrial switch is a heart operation performed to treat dextro-Transposition of the great arteries. It involves the construction of an atrial baffle which redirects the blood coming into the atria to restore the connection between systemic and pulmonary circulation.
Raghib syndrome is rare a congenital heart defect where the left superior vena cava (LSVC) is draining into the left atrium in addition to an absent coronary sinus and an atrial septal defect. This can be considered a dangerous heart condition because it puts the individual at a high risk of stroke. Other defects that are often associated with Raghib syndrome can include ventricular septal defects, enlargement of the tricuspid annulus, and pulmonary stenosis. While this is considered an extremely rare developmental complex, cases regarding a persistent left superior vena cava (PLSVC) are relatively common among congenital heart defects. It is also important to note that the PLSVC often drains into the right atrium, and only drains into the left atrium in approximately 10 to 20% of individuals with the defect.
References
- 1 2 Lu, Jimmy C.; Dorfman, Adam L.; Attili, Anil K.; Ghadimi Mahani, Maryam; Dillman, Jonathan R.; Agarwal, Prachi P. (May 2012). "Evaluation with cardiovascular MR imaging of baffles and conduits used in palliation or repair of congenital heart disease". RadioGraphics. 32 (3): E107–127. doi:10.1148/rg.323115096. ISSN 1527-1323. PMID 22582368.
- ↑ Park, In Sook; Goo, Hyun Woo (2019), Park, In Sook (ed.), "Complete Transposition of the Great Arteries (Complete TGA)", An Illustrated Guide to Congenital Heart Disease: From Diagnosis to Treatment – From Fetus to Adult, Singapore: Springer, pp. 269–308, doi:10.1007/978-981-13-6978-0_13, ISBN 978-981-13-6978-0, S2CID 199033381 , retrieved 2020-11-23
- ↑ Park, In Sook; Goo, Hyun Woo (2019), Park, In Sook (ed.), "Functional Single Ventricle (FSV)", An Illustrated Guide to Congenital Heart Disease, Singapore: Springer Singapore, pp. 531–603, doi:10.1007/978-981-13-6978-0_23, ISBN 978-981-13-6977-3, S2CID 199049116 , retrieved 2020-11-23