
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved can vary from small to covering the entire body. Dermatitis is often called eczema, and the difference between those terms is not standardized.

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by patches of abnormal skin. These areas are red, pink, or purple, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.

Tacrolimus, sold under the brand name Prograf among others, is an immunosuppressive drug. After allogenic organ transplant, the risk of organ rejection is moderate. To lower the risk of organ rejection, tacrolimus is given. The drug can also be sold as a topical medication in the treatment of T-cell-mediated diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. For example, it is prescribed for severe refractory uveitis after a bone marrow transplant, exacerbations of minimal change disease, Kimura's disease, and vitiligo. It can be used to treat dry eye syndrome in cats and dogs.

Balanitis is inflammation of the glans penis. When the foreskin is also affected, the proper term is balanoposthitis. Balanitis on boys still in diapers must be distinguished from redness caused by ammoniacal dermatitis. The word balanitis is from the Greek βάλανοςbalanos, literally meaning 'acorn', used because of the similarity in shape to the glans penis.

Seborrhoeic dermatitis, sometimes inaccurately referred to as seborrhoea, is a long-term skin disorder. Symptoms include red, scaly, greasy, itchy, and inflamed skin. Areas of the skin rich in oil-producing glands are often affected including the scalp, face, and chest. It can result in social or self-esteem problems. In babies, when the scalp is primarily involved, it is called cradle cap. Dandruff is a milder form of the condition without inflammation.

Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. This often happens in association with changes to the nails such as small depressions in the nail (pitting), thickening of the nails, and detachment of the nail from the nailbed. Skin changes consistent with psoriasis frequently occur before the onset of psoriatic arthritis but psoriatic arthritis can precede the rash in 15% of affected individuals. It is classified as a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy.

Pimecrolimus is an immunomodulating agent of the calcineurin inhibitor class used in the treatment of atopic dermatitis (eczema). It is available as a topical cream, once marketed by Novartis under the trade name Elidel.
Antipruritics, abirritants, or anti-itch drugs, are medications that inhibit the itching often associated with sunburns, allergic reactions, eczema, psoriasis, chickenpox, fungal infections, insect bites and stings like those from mosquitoes, fleas, and mites, and contact dermatitis and urticaria caused by plants such as poison ivy or stinging nettle. It can also be caused by chronic kidney disease and related conditions.

Lichen sclerosus (LS) is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease of unknown cause which can affect any body part of any person but has a strong preference for the genitals and is also known as balanitis xerotica obliterans (BXO) when it affects the penis. Lichen sclerosus is not contagious. There is a well-documented increase of skin cancer risk in LS, potentially improvable with treatment. LS in adult age women is normally incurable, but improvable with treatment, and often gets progressively worse if not treated properly. Most males with mild or intermediate disease restricted to foreskin or glans can be cured by either medical or surgical treatment.

Alopecia universalis(AU), also known as alopecia areata universalis, is a medical condition involving the loss of all body hair, including eyebrows, eyelashes, chest hair, armpit hair, and pubic hair. It is the most severe form of alopecia areata. People with the disease are usually healthy and have no other symptoms and a normal life expectancy.

Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin (dermatitis). It results in itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which can thicken over time. AD may also simply be called eczema, a term that generally refers to a larger group of skin conditions.
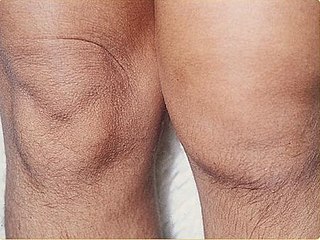
Reactive arthritis, also known as Reiter's syndrome, is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in response to an infection in another part of the body (cross-reactivity). Coming into contact with bacteria and developing an infection can trigger the disease. By the time the patient presents with symptoms, often the "trigger" infection has been cured or is in remission in chronic cases, thus making determination of the initial cause difficult.

Allergic contact dermatitis (ACD) is a form of contact dermatitis that is the manifestation of an allergic response caused by contact with a substance; the other type being irritant contact dermatitis (ICD).

Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common, sometimes chronic skin condition which presents as reddish bumps on the skin arranged in a circle or ring. It can initially occur at any age, though two-thirds of patients are under 30 years old, and it is seen most often in children and young adults. Females are two times as likely to have it as males.
Schnitzler syndrome or Schnitzler's syndrome is a rare disease characterised by onset around middle age of chronic hives (urticaria) and periodic fever, bone pain and joint pain, weight loss, malaise, fatigue, swollen lymph glands and enlarged spleen and liver.
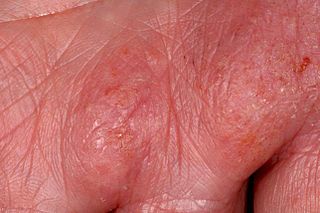
Hand eczema presents on the palms and soles, and may sometimes be difficult or impossible to differentiate from atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, and psoriasis, which also commonly involve the hands. Even a biopsy of all these conditions may not result in a definitive diagnosis, as all three conditions may demonstrate spongiosis and crusting on the hands.

Eosinophilic ulcer of the oral mucosa is a condition characterized by an ulcer with an indurated and elevated border. The lesion might be tender, fast-growing and the patient often not be aware of any trauma in the area.

Topical steroid withdrawal, also known as red burning skin and steroid dermatitis, has been reported in people who apply topical steroids for 2 weeks or longer and then discontinue use. Symptoms affect the skin and include redness, a burning sensation, and itchiness, which may then be followed by peeling.
Childhood granulomatous periorificial dermatitis (CGPD), is a rare benign granulomatous skin disease of unknown cause. The disorder was first described in 1970 by Gianotti in a case series of five children. CGPD is more common in boys than girls.

An antiarthritic is any drug used to relieve or prevent arthritic symptoms, such as joint pain or joint stiffness. Depending on the antiarthritic drug class, it is used for managing pain, reducing inflammation or acting as an immunosuppressant. These drugs are typically given orally, topically or through administration by injection. The choice of antiarthritic medication is often determined by the nature of arthritis, the severity of symptoms as well as other factors, such as the tolerability of side effects.


















