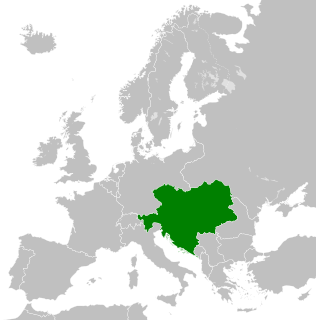
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867 in the aftermath of the Austro-Prussian War and was dissolved shortly after its defeat in the First World War.

Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning 93,030 square kilometres (35,920 sq mi) of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 10 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non-Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr.

Hungarian is a Uralic language spoken in Hungary and parts of several neighbouring countries. It is the official language of Hungary and one of the 24 official languages of the European Union. Outside Hungary, it is also spoken by Hungarian communities in southern Slovakia, western Ukraine (Subcarpathia), central and western Romania (Transylvania), northern Serbia (Vojvodina), northern Croatia, northeastern Slovenia (Prekmurje), and eastern Austria.

Transylvania is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Apuseni Mountains. Broader definitions of Transylvania also include the western and northwestern Romanian regions of Crișana and Maramureș, and occasionally Banat.

Budapest is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population of 1,752,286 over a land area of about 525 square kilometres. Budapest, which is both a city and county, forms the centre of the Budapest metropolitan area, which has an area of 7,626 square kilometres and a population of 3,303,786; it is a primate city, constituting 33% of the population of Hungary.

Franz Joseph I or Francis Joseph I was Emperor of Austria, King of Hungary, and the other states of the Habsburg monarchy from 2 December 1848 until his death on 21 November 1916. In the early part of his reign, his realms and territories were referred to as the Austrian Empire, but were reconstituted as the dual monarchy of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1867. From 1 May 1850 to 24 August 1866, Franz Joseph was also President of the German Confederation.

The Hungarian Revolution of 1956, also known as the Hungarian Uprising, was a countrywide revolution against the government of the Hungarian People's Republic (1949–1989) and the Hungarian domestic policies imposed by the Soviet Union (USSR).
The Hungary national football team represents Hungary in men's international football and is controlled by the Hungarian Football Federation. The team has made 9 appearances in the FIFA World Cup and 4 appearances in the European Championship, and plays its home matches at the Puskás Aréna, which opened in November 2019.

The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000; his family led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European middle power within the Western world.

Fejér is an administrative county in Central Hungary. It lies on the west bank of the river Danube and nearly touches the eastern shore of Lake Balaton. It shares borders with the Hungarian counties Veszprém, Komárom-Esztergom, Pest, Bács-Kiskun, Tolna and Somogy. The capital of Fejér county is Székesfehérvár.

The Habsburg monarchy, also known as the Danubian monarchy, or Habsburg Empire, was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities that were ruled by the House of Habsburg, especially the dynasty's Austrian branch.

Velké Meziříčí is a town in Žďár nad Sázavou District in the Vysočina Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 11,000 inhabitants. The historic town centre with the castle complex is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone.
Bakonycsernye is a village in Fejér county, Hungary.
Gmina Sztabin is a rural gmina in Augustów County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. Its seat is the village of Sztabin, which lies approximately 21 kilometres (13 mi) south-east of Augustów and 63 km (39 mi) north of the regional capital Białystok.

Hungarians, also known as Magyars, are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the Uralic language family. There are an estimated 15 million ethnic Hungarians and their descendants worldwide, of whom 9.6 million live in today's Hungary. About 2–3 million Hungarians live in areas that were part of the Kingdom of Hungary before the Treaty of Trianon in 1920 and are now parts of Hungary's seven neighbouring countries, Slovakia, Ukraine, Romania, Serbia, Croatia, Slovenia, and Austria. Significant groups of people with Hungarian ancestry live in various other parts of the world, most of them in the United States, Canada, Germany, France, the United Kingdom, Chile, Brazil, Australia, and Argentina.

The Křižanov Highlands is a highland and a geomorphological mesoregion of the Czech Republic. It is located mostly in the Vysočina Region.

Mór is a district in north-western part of Fejér County. Mór is also the name of the town where the district seat is found. The district is located in the Central Transdanubia Statistical Region.
Balink is a Dutch surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Pištenik is a mountain in Croatia, located southeast of Plaški and northwest of Saborsko. Its highest peak is 800 metres (2,600 ft) high. It hosts a 328 m (1,076 ft) deep karst pit called Balinka. In the 1960s, members of the local mountaineering society "HPD Željezničar" surveyed 45 speleological sites there, including a cave called Estavela Begovac with a depth of 260 m (850 ft).