
In mathematics, a projective plane is a geometric structure that extends the concept of a plane. In the ordinary Euclidean plane, two lines typically intersect at a single point, but there are some pairs of lines that do not intersect. A projective plane can be thought of as an ordinary plane equipped with additional "points at infinity" where parallel lines intersect. Thus any two distinct lines in a projective plane intersect at exactly one point.

The Sinhala script, also known as Sinhalese script, is a writing system used by the Sinhalese people and most Sri Lankans in Sri Lanka and elsewhere to write the Sinhala language as well as the liturgical languages Pali and Sanskrit. The Sinhalese Akṣara Mālāva, one of the Brahmic scripts, is a descendant of the Ancient Indian Brahmi script. It is also related to the Grantha script.

Calligraphy is a visual art related to writing. It is the design and execution of lettering with a pen, ink brush, or other writing instrument. Contemporary calligraphic practice can be defined as "the art of giving form to signs in an expressive, harmonious, and skillful manner".

In geometry, two geometric objects are perpendicular if their intersection forms right angles at the point of intersection called a foot. The condition of perpendicularity may be represented graphically using the perpendicular symbol, ⟂. Perpendicular intersections can happen between two lines, between a line and a plane, and between two planes.

Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek stenos (narrow) and graphein. It has also been called brachygraphy, from Greek brachys (short), and tachygraphy, from Greek tachys, depending on whether compression or speed of writing is the goal.

Rongorongo is a system of glyphs discovered in the 19th century on Rapa Nui that appears to be writing or proto-writing. Numerous attempts at decipherment have been made, with none being successful. Although some calendrical and what might prove to be genealogical information has been identified, none of these glyphs can actually be read. If rongorongo does prove to be writing and proves to be an independent invention, it would be one of very few independent inventions of writing in human history.
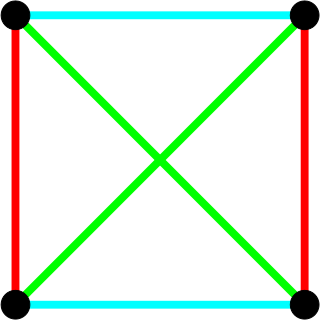
A finite geometry is any geometric system that has only a finite number of points. The familiar Euclidean geometry is not finite, because a Euclidean line contains infinitely many points. A geometry based on the graphics displayed on a computer screen, where the pixels are considered to be the points, would be a finite geometry. While there are many systems that could be called finite geometries, attention is mostly paid to the finite projective and affine spaces because of their regularity and simplicity. Other significant types of finite geometry are finite Möbius or inversive planes and Laguerre planes, which are examples of a general type called Benz planes, and their higher-dimensional analogs such as higher finite inversive geometries.

The Greek Dark Ages was the period of Greek history from the end of the Mycenaean palatial civilization, around 1100 BC, to the beginning of the Archaic age, around 750 BC, It followed the so-called Late Bronze Age collapse of civilisation in the Eastern Mediterranean world in c. 1200-1150, as the great palaces and cities of the Mycenaeans were destroyed or abandoned. At around the same time, the Hittite civilization also suffered serious disruption, with cities from Troy to Gaza being destroyed. In Egypt, the New Kingdom fell into disarray, leading to the Third Intermediate Period of Egypt. Following the collapse, there were fewer, smaller settlements, suggesting widespread famine and depopulation. In Greece, the Linear B script used by Mycenaean bureaucrats to write the Greek language ceased to be used, and the Greek alphabet did not develop until the beginning of the archaic period. The decoration on Greek pottery after about 1100 BC lacks the figurative decoration of Mycenaean ware and is restricted to simpler, generally geometric styles (1000–700 BC).

The Kufic script is a style of Arabic script that gained prominence early on as a preferred script for Quran transcription and architectural decoration, and it has since become a reference and an archetype for a number of other Arabic scripts. It developed from the Arabic alphabet in the city of Kufa, from which its name is derived. Kufic is characterized by angular, rectilinear letterforms and its horizontal orientation. There are many different versions of Kufic, such as square Kufic, floriated Kufic, knotted Kufic, and others. The artistic styling of Kufic led to its use in a non-Arabic context in Europe, as decoration on architecture, known as pseudo-Kufic.
Qashani or Kashani is a Persian decorative arts which had been popular in Iran in the 16th to 18th century, and then moved to Turkey in the time of the Ottomans with the transfer of many Persians artists to Turkey, becoming the basis for decorating the walls of mosques, palaces, shrines and tombs. It is a square-shaped ceramic tile which uses Persian-like floral-depicting 4- or 6-sided glazed tiles, decorated with blue, cyan, green and sometimes red colors. The decoration is surrounded by fine black lines that make it stand out on its white floor. The tile work had often been decorated by the inscription, floral and geometrical patterns. The inscription often provides Qur'anic verses or sentences related to historical events written in Persian script. The plant often consists of natural flowers such as lily, cloves, roses and cypress trees. Geometrical patterns consists of different geometrical shapes and polygons. In Morocco, similar artistic technique is known as zillij. Its use has been widespread in the decoration of the walls of the buildings in the Ottoman era, and this mosaical feature can also be seen in the Dome of the Rock in Jerusalem. Kashi, the abbreviated form of Qashani, was also introduced to Sindh, Kutch, and Multan where numerous examples of shrines and mosques embellished with blue, white and green tile work exist.

String art or pin and thread art, is characterized by an arrangement of colored thread strung between points to form geometric patterns or representational designs such as a ship's sails, sometimes with other artist material comprising the remainder of the work. Thread, wire, or string is wound around a grid of nails hammered into a velvet-covered wooden board. Though straight lines are formed by the string, the slightly different angles and metric positions at which strings intersect gives the appearance of Bézier curves. Quadratic Bézier curve are obtained from strings based on two intersecting segments. Other forms of string art include Spirelli, which is used for cardmaking and scrapbooking, and curve stitching, in which string is stitched through holes.
Geometric art is a phase of Greek art, characterized largely by geometric motifs in vase painting, that flourished towards the end of the Greek Dark Ages, c. 900–700 BC. Its center was in Athens, and from there the style spread among the trading cities of the Aegean. The Greek Dark Ages lasted from c. 1100 to 750 BC and include two periods, the Protogeometric period and the Geometric period, in reference to the characteristic pottery style. The vases had various uses or purposes within Greek society, including, but not limited to, funerary vases and symposium vases.
In typography, the Vox-ATypI classification makes it possible to classify typefaces into general classes. Devised by Maximilien Vox in 1954, it was adopted in 1962 by the Association Typographique Internationale (ATypI) and in 1967 as a British Standard, as British Standards Classification of Typefaces, which is a very basic interpretation and adaptation/modification of the earlier Vox-ATypI classification. On April 27, 2021, ATypI announced that they had de-adopted the system and that they were establishing a working group building towards a new, larger system incorporating the different scripts of the world.

Girih are decorative Islamic geometric patterns used in architecture and handicraft objects, consisting of angled lines that form an interlaced strapwork pattern.
In geometry, a vertex is a point where two or more curves, lines, or edges meet or intersect. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedra are vertices.
Bannai Tarao is the name of a set of Japanese mysteries, featuring a detective of the same name who could take on seven different faces, in similar fashion to the protagonists of later series 7-Color Mask, Rainbowman, and Cutie Honey. In the film series, Bannai was played by Chiezō Kataoka. He portrayed the character in eleven movies from 1946 until 1960, first for Daiei, then as a contract actor for Toei. After him, Akira Kobayashi portrayed the character in two other movies in 1978. Bannai Tarao is credited on several songs on Japanese rock pioneers Happy End's 1971 album Kazemachi Roman.

Islamic ornament is the use of decorative forms and patterns in Islamic art and Islamic architecture. Its elements can be broadly divided into the arabesque, using curving plant-based elements, geometric patterns with straight lines or regular curves, and calligraphy, consisting of religious texts with stylized appearance, used both decoratively and to convey meaning. All three often involve elaborate interlacing in various mediums.

Islamic geometric patterns are one of the major forms of Islamic ornament, which tends to avoid using figurative images, as it is forbidden to create a representation of an important Islamic figure according to many holy scriptures.

The Topkapı Scroll is a Timurid dynasty pattern scroll in the collection of the Topkapı Palace museum.

Decapoint, or raphigraphy, was a tactile form of the Latin script invented by Louis Braille as a system that could be used by both the blind and sighted. It was published in 1839. Letters retained their linear form, and so were legible without training to the sighted, but the lines were composed of embossed dots like those used in braille. Each letter contained ten dots in the height and different dots in the width to produce the graphic form of print.
















