Related Research Articles

The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, north-east of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.

Johnston Atoll is an unincorporated territory of the United States, under the jurisdiction of the United States Air Force (USAF). The island is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by letter of authorization from the USAF. A special use permit is also required from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) to access the island by boat or enter the waters surrounding the island, which are designated as a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument. The Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge extends from the shore out to 12 nautical miles, continuing as part of the National Wildlife Refuge System out to 200 nautical miles. The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument extends from the shore out to 200 nautical miles.

The Marshall Islands, officially the Republic of the Marshall Islands, is an island country west of the International Date Line and north of the equator in the Micronesia region in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. The territory consists of 29 coral atolls and five islands, divided across two island chains: Ratak in the east and Ralik in the west. 97.87% of its territory is water, the largest proportion of water to land of any sovereign state. The country shares maritime boundaries with Wake Island to the north, Kiribati to the southeast, Nauru to the south, and the Federated States of Micronesia to the west. The capital and largest city is Majuro, home to approximately half of the country's population.

Midway Atoll is a 2.4 sq mi (6.2 km2) atoll in the North Pacific Ocean. Midway Atoll is an insular area of the United States and is an unorganized and unincorporated territory. The largest island is Sand Island, which has housing and an airstrip. Immediately to the east of Sand Island across the narrow Brooks Channel is Eastern Island, which is uninhabited and no longer has any facilities. Forming a rough, incomplete circle around the two main islands and creating Midway Lagoon is Spit Island, a narrow reef.

Palmyra Atoll, also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands. It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii and American Samoa. North America is about 3,300 miles northeast and New Zealand the same distance southwest, placing the atoll at the approximate center of the Pacific Ocean. The land area is 4.6 sq mi (12 km2), with about 9 miles (14 km) of sea-facing coastline and reef. There is one boat anchorage, known as West Lagoon, accessible from the sea by a narrow artificial channel and an old airstrip; during WW2 it was turned into a Naval Air Station for several years and used for training and refueling. It was shelled by a submarine in December 1941, but was not the site of a major battle.

The United States Minor Outlying Islands is a statistical designation defined by the International Organization for Standardization's ISO 3166-1 code. The entry code is ISO 3166-2:UM. The minor outlying islands and groups of islands comprise eight United States insular areas in the Pacific Ocean and one in the Caribbean Sea.

An atoll is a ring-shaped island, including a coral rim that encircles a lagoon. There may be coral islands or cays on the rim. Atolls are located in warm tropical or subtropical parts of the oceans and seas where corals can develop. Most of the approximately 440 atolls in the world are in the Pacific Ocean.

Kwajalein Atoll is part of the Republic of the Marshall Islands (RMI). The southernmost and largest island in the atoll is named Kwajalein Island, which its majority English-speaking residents often use the shortened name, Kwaj. The total land area of the atoll amounts to just over 6 square miles (16 km2). It lies in the Ralik Chain, 2,100 nautical miles southwest of Honolulu, Hawaii.

Bikini Atoll, known as Eschscholtz Atoll between the 19th century and 1946, is a coral reef in the Marshall Islands consisting of 23 islands surrounding a 229.4-square-mile (594.1 km2) central lagoon. The atoll is at the northern end of the Ralik Chain, approximately 530 miles (850 km) northwest of the capital Majuro.

The Maldives are formed by 20 natural atolls, along with a few islands and isolated reefs today which form a pattern stretching from 7 degrees 10′ North to 0 degrees 45′ South. The largest of these atolls is Boduthiladhunmathi, while the atoll containing the most islands is Huvadhu.

The Pearl and Hermes Atoll, also known as Pearl and Hermes Reef, is part of the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands, a group of small islands and atolls that form the farthest northwest portion of the Hawaiian island chain. The atoll consists of a variable number of flat and sandy islets, typically between five and seven. More were noted in historical sources but have since been lost to erosion and rising sea levels.
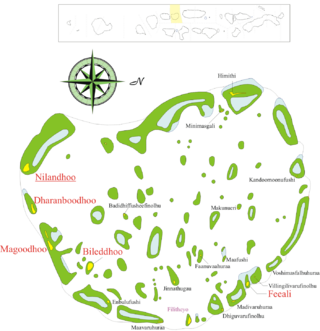
Faafu Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives. It corresponds to the natural atoll of the same name.

Baa Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives. It consists of three separate natural atolls, namely southern Maalhosmadulu Atoll, the Fasdūtherē Atoll and the smaller natural atoll known as Goifulhafehendhu Atoll.
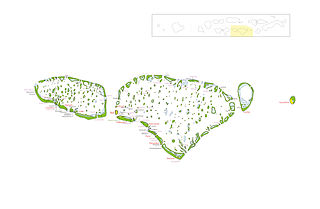
Kaafu Atoll is the code name given to an administrative division in the Republic of Maldives which consists of the geographical atolls of Kaashidhoo Island, Gaafaru, North Malé Atoll and South Malé Atoll. As the two Malé Atolls are the main islands of the administrative district, the entire Kaafu Atoll administrative division is officially named Malé Atoll or Malé Atolhu in the Dhivehi language.

Alif Alif Atoll is an administrative division of the Maldives. It was created on March 1, 1984, combining northern section of Ari Atoll, the small Rasdhukuramathi Atoll, and the isolated island of Thoddoo. Many of the islands in this atoll have been inhabited since ancient times and have archaeological remains from the Maldivian Buddhist period.
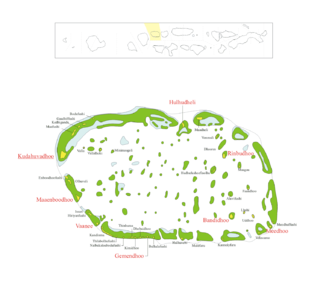
Dhaalu Atoll is one of the atolls of the Maldives. It corresponds to the natural atoll of the same name.

Gaafu Dhaalu is an administrative district of the Maldives formed by the southwestern section of Huvadhu Atoll. It was created on February 8, 1962, when Huvadhu Atoll was divided into two districts. Gaafu Dhaalu corresponds to the Southwestern section of this large natural atoll, south of the line extending between the channels of Footukandu and Vaarulu Kandu. The capital of this region is Thinadhoo (Thenadhoo). There are 153 islands in this district, 10 of which are inhabited. This district is located about 340 kilometers south of the capital Malé.
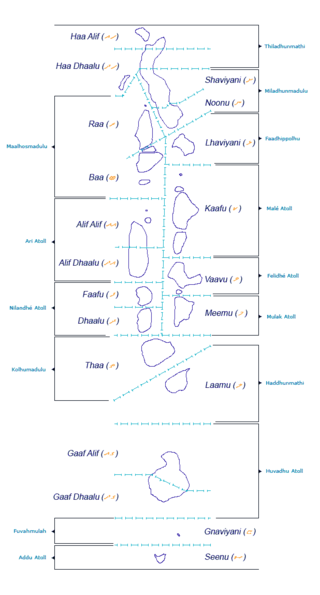
The Administrative Divisions of the Maldives refers to the various units of government that provide local government services in the Maldives. According to the Decentralization Act 2010, the administrative divisions of the Maldives would consist of atolls, islands, and cities; each administered by their own local council, under the basic terms of home rule. Geographically, the Maldives are formed by a number of natural atolls plus a few islands and isolated reefs which form a pattern from North to South. Administratively, there are currently 189 islands, 18 atolls and 4 cities in the Maldives.

Haa Alif Atoll is the code name based on the letters of the Maldivian alphabet commonly used to refer to the administrative division officially known as Northern Thiladhunmathi Atoll in the Maldives.

Nuclear testing at Bikini Atoll consisted of the detonation of 24 nuclear weapons by the United States between 1946 and 1958 on Bikini Atoll in the Marshall Islands. Tests occurred at 7 test sites on the reef itself, on the sea, in the air, and underwater. The test weapons produced a combined yield of about 75 Mt of TNT in explosive power.
References
- Divehiraajjege Jōgrafīge Vanavaru. Muhammadu Ibrahim Lutfee. G.Sōsanī.