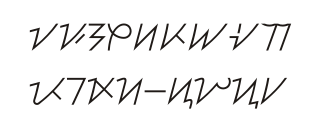An abugida – sometimes also called alphasyllabary, neosyllabary, or pseudo-alphabet – is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is secondary, similar to a diacritical mark. This contrasts with a full alphabet, in which vowels have status equal to consonants, and with an abjad, in which vowel marking is absent, partial, or optional – in less formal contexts, all three types of the script may be termed "alphabets". The terms also contrast them with a syllabary, in which a single symbol denotes the combination of one consonant and one vowel.
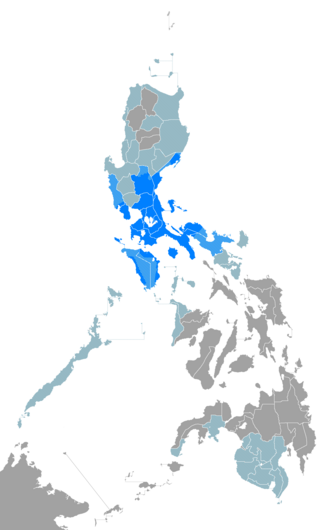
Tagalog is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named Filipino, is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages, alongside English.

The Bicol Region, designated as Region V, is an administrative region of the Philippines. It comprises six provinces, four on the Bicol Peninsula : Albay, Camarines Norte, Camarines Sur, and Sorsogon, and two off the shore: Catanduanes and Masbate.

Camarines Norte, officially the Province of Camarines Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bicol Region in Luzon. Its capital is Daet, the most populous town in the province. The province borders Quezon to the west, Camarines Sur to the south, and the Philippine Sea to the north. It has historically been a Bikol-speaking region. However, there has been a language shift in recent years to Tagalog, which is more commonly used nowadays.
Baybayin or Sulat Tagalog, also called Basahan by Bicolanos, sometimes erroneously referred to as alibata, is a Philippine script widely used primarily in Luzon during the 16th and 17th centuries and prior to write Tagalog and to a lesser extent Visayan languages, Kampampangan, Ilocano, and several other Philippine languages.
Filipinoorthography specifies the correct use of the writing system of the Filipino language, the national and co-official language of the Philippines.

Tagbanwa is one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines, used by the Tagbanwa and the Palawan people as their ethnic writing system.

Naga, officially the City of Naga, or the Pilgrim City of Naga, is a 1st class independent component city in the Bicol Region. According to the 2020 census, Naga has a population of 209,170 people. The most populous in Camarines Sur and the second most populous following Legazpi City in Albay.
Mark of Lisbon, in Portuguese Marcos de Lisboa, in Latin Marcus Ulyssiponensis, (1511-1591), was a Portuguese Franciscan, historian, and the Bishop of Porto.

Central Bikol, commonly called Bikol Naga or simply as Bikol, is an Austronesian language spoken by the Bicolanos, primarily in the Bicol Region of southern Luzon, Philippines. It is spoken in the northern and western part of Camarines Sur, second congressional district of Camarines Norte, eastern part of Albay, northeastern part of Sorsogon, San Pascual town in Masbate, and southwestern part of Catanduanes. Central Bikol speakers can be found in all provinces of Bicol and it is a majority language in Camarines Sur. The standard sprachraum form is based on the Canaman dialect.

Rinconada Bikol or simply Rinconada, spoken in the province of Camarines Sur, Philippines, is one of several languages that compose the Inland Bikol group of the Bikol macrolanguage. It belongs to the Austronesian language family that also includes most Philippine languages, the Formosan languages of Taiwanese aborigines, Malay, the Polynesian languages and Malagasy.
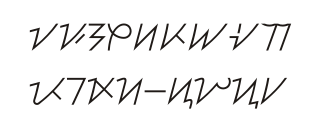
Hanunoo, also rendered Hanunó'o, is one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines and is used by the Mangyan peoples of southern Mindoro to write the Hanunó'o language.

Kulitan, also known as súlat Kapampángan and pamagkulit, is one of the various indigenous suyat writing systems in the Philippines. It was used for writing Kapampangan, a language mainly spoken in Central Luzon, until it was gradually replaced by the Latin alphabet.
Fossilized affixes abound in Austronesian languages.
Old Tagalog, also known as Old Filipino, is the earliest form of the Tagalog language during the Classical period. It is the primary language of pre-colonial Tondo, Namayan and Maynila. The language originated from the Proto-Philippine language and evolved to Classical Tagalog, which was the basis for Modern Tagalog. Old Tagalog uses the Tagalog script or Baybayin, one of the scripts indigenous to the Philippines.

The University of Santo Tomas Baybayin Documents or UST Baybayin Documents are two 17th century land deeds written in Baybayin script.

The Bikol languages or Bicolano languages are a group of Central Philippine languages spoken mostly in the Bicol Peninsula in the southeastern part of Luzon, the neighboring island-province of Catanduanes, and the island of Burias in Masbate.

Kinalas is a Bicol dish consisting of noodles (pancit) garnished by scraped meat from pork or beef's head and other parts, enhanced with a thick deep-brown sauce coming from the brains of a cow or pig. The dish is further flavored with spices and served in hot broth. Boiled egg added is optional.
Suyat is a collective name for the Brahmic scripts of Philippine ethnolinguistic groups. The term was suggested and used by cultural organizations in the Philippines to denote a unified neutral terminology for Philippine scripts.

The Vocabulario de la lengua bicol is a list of vocabulary of the Bicol language, collected by Mark of Lisbon when he was assigned to Bicol Region, Philippines.