
Excavata is a major supergroup of unicellular organisms belonging to the domain Eukaryota. It was first suggested by Simpson and Patterson in 1999 and introduced by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002 as a formal taxon. It contains a variety of free-living and symbiotic forms, and also includes some important parasites of humans, including Giardia and Trichomonas. Excavates were formerly considered to be included in the now obsolete Protista kingdom. They are classified based on their flagellar structures, and they are considered to be the most basal flagellate lineage. Phylogenomic analyses split the members of Excavata into three different and not all closely related groups: Discobids, Metamonads and Malawimonads. Except for Euglenozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic.

Discicristata is a proposed eukaryotic clade. It consists of Euglenozoa plus Percolozoa.

Retaria is a clade within the supergroup Rhizaria containing the Foraminifera and the Radiolaria. In 2019, the Retaria were recognized as a basal Rhizaria group, as sister of the Cercozoa.

The SAR supergroup, also just SAR or Harosa, is a clade of eukaryotic organisms that includes stramenopiles (heterokonts), alveolates, and Rhizaria. The name is an acronym derived from the first letters of each of these clades; it has been alternatively spelled "RAS". The term "Harosa" has also been used. The SAR supergroup is a node-based taxon.
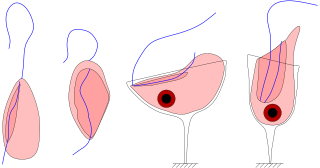
Jakobids are an order of free-living, heterotrophic, flagellar eukaryotes in the supergroup Excavata. They are small, and can be found in aerobic and anaerobic environments. The order Jakobida, believed to be monophyletic, consists of only twenty species at present, and was classified as a group in 1993. There is ongoing research into the mitochondrial genomes of jakobids, which are unusually large and bacteria-like, evidence that jakobids may be important to the evolutionary history of eukaryotes.

Diaphoretickes is a major group of eukaryotic organisms, with over 400,000 species. The majority of the earth's biomass that carries out photosynthesis belongs to Diaphoretickes.
Eopharingia is an excavata group.

Bathytoma is a genus of deep-water sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Borsoniidae.
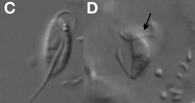
Andalucia is a genus of jakobids.

Calyptraea, commonly known as the Chinese hat snails is a genus of sea snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Calyptraeidae, a family which contains the slipper snails or slipper limpets, cup-and-saucer snails, and Chinese hat snails.

Batrachorhina is a genus of longhorn beetles of the subfamily Lamiinae, containing the following species:
Wurmiella is an extinct conodont genus.
Batrachorhina niveoscutellata is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1940.
Batrachorhina similis is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1938.
Batrachorhina approximata also known as lamiines or flat-faced longhorned beetle, is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Stephan von Breuning in 1940. It is known from Kenya.
Batrachorhina distigma is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Léon Fairmaire in 1893, originally under the genus Praonetha. It is known from Comoros.
Batrachorhina lactaria is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Léon Fairmaire in 1894. It is known from Madagascar.
Batrachorhina lateritia is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Léon Fairmaire in 1894, originally under the genus Tigrana. It is known from Madagascar, where it has existed since the Upper Pleistocene. It feeds on Hymenaea verrucosa.
Batrachorhina vulpina is a species of beetle in the family Cerambycidae. It was described by Johann Christoph Friedrich Klug in 1833, originally under the genus Saperda. It is known from Réunion and Mauritius.









