
The history of Tyrol, a historical region in the middle alpine area of Central Europe, dates back to early human settlements at the end of the last glacier period, around 12,000 BC. Sedentary settlements of farmers and herders can be traced back to 5000 BC. Many of the main and side valleys were settled during the early Bronze Age, from 1800 to 1300 BC. From these settlements, two prominent cultures emerged: the Laugen-Melaun culture in the Bronze Age, and the Fritzens-Sanzeno culture in the Iron Age.

The Battle of Oudenarde, also known as the Battle of Oudenaarde, was a major engagement of the War of the Spanish Succession, pitting a Anglo-Dutch force consisting of eighty thousand men under the command of the Duke of Marlborough, Lord Overkirk and Prince Eugene of Savoy against a French force of eighty-five thousand men under the command of the Duc de Bourgogne and the Duc de Vendôme, the battle resulting in a great victory for the Grand Alliance. The battle was fought near the city of Oudenaarde, at the time part of the Spanish Netherlands, on 11 July 1708. With this victory, the Grand Alliance ensured the fall of various French territories, giving them a significant strategic and tactical advantage during this stage of the war. The battle was fought in the later years of the war, a conflict that had come about as a result of English, Dutch and Habsburg apprehension at the possibility of a Bourbon succeeding the deceased King of Spain, Charles II, and combining their two nations and empires into one.

The Battle of Arcole or Battle of Arcola was fought between French and Austrian forces 25 kilometres (16 mi) southeast of Verona during the War of the First Coalition, a part of the French Revolutionary Wars. The battle saw a bold maneuver by Napoleon Bonaparte's French Army of Italy to outflank the Austrian army led by József Alvinczi and cut off its line of retreat. The French victory proved to be a highly significant event during the third Austrian attempt to lift the siege of Mantua. Alvinczi planned to execute a two-pronged offensive against Bonaparte's army. The Austrian commander ordered Paul Davidovich to advance south along the Adige River valley with one corps while Alvinczi led the main army in an advance from the east. The Austrians hoped to raise the siege of Mantua where Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser was trapped with a large garrison. If the two Austrian columns linked up and if Wurmser's troops were released, French prospects were grim.

The Battle of Sacile on 16 April 1809 and its companion Clash at Pordenone on 15 April saw an Austrian army commanded by Archduke John of Austria defeat a Franco-Italian army led by Eugène de Beauharnais and force it to retreat. Sacile proved to be the most notable victory of John's career. The action took place east of the Livenza River near Sacile in modern-day Italy during the War of the Fifth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.
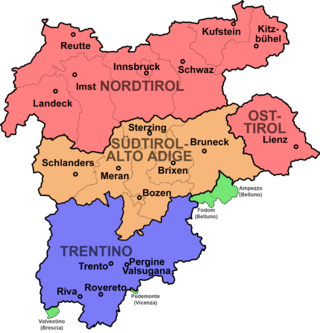
East Tyrol, occasionally East Tirol, is an exclave of the Austrian federal state of Tyrol, separated from North Tyrol by parts of Salzburg State and parts of Italian South Tyrol. It is coterminous with the administrative district (Bezirk) of Lienz.

The Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718) was fought between Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire. The 1699 Treaty of Karlowitz was not an acceptable permanent agreement for the Ottoman Empire. Twelve years after Karlowitz, it began the long-term prospect of taking revenge for its defeat at the Battle of Vienna in 1683. First, the army of Turkish Grand Vizier Baltacı Mehmet defeated Peter the Great's Russian Army in the Russo-Turkish War (1710–1711). Then, during the Ottoman–Venetian War (1714–1718), Ottoman Grand Vizier Damat Ali reconquered the Morea from the Venetians. As the guarantor of the Treaty of Karlowitz, the Austrians threatened the Ottoman Empire, which caused it to declare war in April 1716.

The Battle of Zenta, also known as the Battle of Senta, was fought on 11 September 1697, near Zenta, Kingdom of Hungary, between Ottoman and Holy League armies during the Great Turkish War. The battle was the most decisive engagement of the war, and it saw the Ottomans suffer an overwhelming defeat by an Imperial force half as large sent by Leopold I, Holy Roman Emperor.

The Prince-Bishopric of Trent was an ecclesiastical principality roughly corresponding to the present-day Northern Italian autonomous province of Trentino. It was created in 1027 and existed until 1803, when it was secularised and absorbed into the County of Tyrol held by the House of Habsburg. Trent was a Hochstift, an Imperial State under the authority of a prince-bishop at Trento.

The battle of Cadore, also known as the battle of Rio Secco or Rusecco, took place near Pieve di Cadore during the opening phase of the War of the League of Cambrai, part of the Italian Wars, on 2 March 1508, opposing the Venetian armies commanded by Bartolomeo d'Alviano and those of the Holy Roman Empire under the leadership of Sixt von Trautson. The battle resulted in a decisive Venetian victory, stopping the Habsburg invasion of Cadore and allowing the Venetians to reconquer all their lost strongholds as well as invade Habsburg-ruled lands in Friuli and the Julian March, besieging Trieste and marching on Istria. This would trigger the creation of the League of Cambrai and the beginning of the War of the League of Cambrai.

The Battle of Bassano was fought on 8 September 1796, during the French Revolutionary Wars, in the territory of the Republic of Venice, between a French army under Napoleon Bonaparte and Austrian forces led by Count Dagobert von Wurmser. The engagement occurred during the second Austrian attempt to raise the siege of Mantua. It was a French victory; however, it was the last battle in Napoleon's perfect military career as two months later he would be defeated at the Second Battle of Bassano, ending his victorious streak. The Austrians abandoned their artillery and baggage, losing supplies, cannons, and battle standards to the French. The victory led to Wurmser being trapped in Mantua, but Napoleon would find his army now badly overstretched, due to holding both Trento and Bassano, meaning he could not support either of those locations without being drawn too far away from the other, something that would nearly allow the Austrians to win during the third attempt to raise the siege of Mantua in November.

During the siege of Mantua, which lasted from 4 June 1796 to 2 February 1797 with a short break, French forces under the overall command of Napoleon Bonaparte besieged and blockaded a large Austrian garrison at Mantua for many months until it surrendered. This eventual surrender, together with the heavy losses incurred during four unsuccessful relief attempts, led indirectly to the Austrians suing for peace in 1797. The siege occurred during the War of the First Coalition, which is part of the French Revolutionary Wars. Mantua, a city in the Lombardy region of Italy, lies on the Mincio River.
The Second Battle of Bassano on 6 November 1796, saw a Habsburg army commanded by József Alvinczi fight Napoleon Bonaparte's French Army of Italy. The Austrians repulsed persistent French attacks in a struggle in which both sides suffered heavy losses. The engagement, which happened two months after the more famous Battle of Bassano, marked the first tactical defeat of Bonaparte's career and occurred near Bassano del Grappa in Northern Italy during the French Revolutionary Wars. The action was part of the third relief of the siege of Mantua during the War of the First Coalition.

The Battle of Verona was fought on 18 October 1805 between the French Army of Italy under the command of André Masséna and an Austrian army led by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. By the end of the day, Massena seized a bridgehead on the east bank of the Adige River, driving back the defending troops under Josef Philipp Vukassovich. The action took place near the city of Verona in northern Italy during the War of the Third Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.

The siege of Belgrade was a successful attempt by Habsburg forces under the command of Prince Eugene of Savoy to capture the strategically important city of Belgrade from the Ottoman Empire. It took place during the Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718), barely a year after the Habsburg victory at the Battle of Petrovaradin (Peterwardein). The Imperial Army routed the Ottoman relief army under Grand Vizier Hacı Halil Pasha on 16 August. As a consequence, the Belgrade garrison, deprived of relief, surrendered to Habsburg forces on 21 August. The Ottoman Sultan Ahmed III sued for peace, resulting in the Treaty of Passarowitz a year later, which completed the transfer of the remainder of Hungary, the Banat of Temeswar with lower Syrmia, and the city of Belgrade with central Serbia into Habsburg hands.

Tyrol is a historical region in the Alps of Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Empire and Austria-Hungary, from its formation in the 12th century until 1919. In 1919, following World War I and the dissolution of Austria-Hungary, it was divided into two modern administrative parts through the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye:

In the Battle of Caldiero or Battle of Soave or Battle of Castelcerino from 27 to 30 April 1809, an Austrian army led by Archduke John of Austria defended against a Franco-Italian army headed by Eugène de Beauharnais, the Viceroy of the Kingdom of Italy. The outnumbered Austrians successfully fended off the attacks of their enemies in actions at San Bonifacio, Soave, and Castelcerino before retreating to the east. The clash occurred during the War of the Fifth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars.

Roberto Sanseverino d'Aragona was an Italian condottiero, count of Colorno from 1458 to 1477 and count of Caiazzo from 1460 until his death in 1487. Highly esteemed man of arms, veteran of numerous battles, he was one of the greatest leaders of the Italian Renaissance.
Guido de' Rossi was an Italian condottiero.

The Expedition in Tyrol was carried out in the spring of 1797, during the final phases of the Italian campaign, when Napoleon Bonaparte decided to launch the final attack against the Holy Roman Empire.

The Italian campaign of 1796–1797, also known as the First Italian Campaign, was a series of military operations in Italy during the War of the First Coalition. Led by Napoleon Bonaparte, the First French Republic's Army of Italy fought and defeated the armies of the Kingdom of Sardinia, the Habsburg monarchy, and the Papal States, as well as various revolts, notably in the Republic of Venice.


















