
Trento, also known in English as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th century, the city was the location of the Council of Trent. Formerly part of Austria and Austria-Hungary, it was annexed by Italy in 1919. With 118,142 inhabitants, Trento is the third largest Italian city in the Alps and second largest in the historical region of Tyrol.

The province of Brescia is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. It has a population of some 1,265,964 and its capital is the city of Brescia.

Trentino is an autonomous province of Italy in the country's far north. Trentino and South Tyrol constitute the region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, an autonomous region under the constitution. The province is composed of 166 comuni. Its capital is the city of Trento (Trent). The province covers an area of more than 6,000 km2 (2,300 sq mi), with a total population of 541,098 in 2019. Trentino is renowned for its mountains, such as the Dolomites, which are part of the Alps.

The Sarca is a river springing from the Adamello-Presanella mountains in the Italian Alps and flowing into Lake Garda at Torbole. As an emissary of the lake it becomes known as the Mincio river, forming a single river system 203 kilometres (126 mi) long (Sarca-Mincio).

The Periadriatic Seam is a distinct geologic fault in Southern Europe, running S-shaped about 1,000 km (621 mi) from the Tyrrhenian Sea through the whole Southern Alps as far as Hungary. It forms the division between the Adriatic plate and the Eurasian plate.

The Sole Valley is a valley in Trentino, northern Italy.

The Valle Mesolcina, also known as the Val Mesolcina or Misox (German), is an alpine valley of the Grisons, Switzerland, stretching from the San Bernardino Pass to Grono where it joins the Calanca Valley. It is the valley formed by the river Moesa.

The Val Bregaglia is an alpine valley of Switzerland and Italy at the base of which runs the river Mera.

The Chiese, also known in the Province of Brescia as the Clisi, is a 160-kilometre (99 mi) Italian river that is the principal immisary and sole emissary of the sub-alpine lake Lago d’Idro, and is a left tributary of the Oglio.
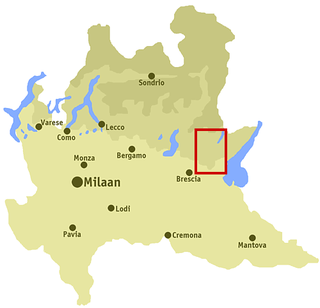
The Valle Sabbia is the second-largest of the Tre Valli Bresciane, situated in the eastern part of the province of Brescia.

Val Rendena [German:Randental] is the valley of the Sarca river in Trentino, northern Italy. The valley is part of the Giudicarie. Main towns include Spiazzo Rendena and Pinzolo.

The Rein da Medel is the longest headwater of the Rhine. It is located in the Swiss cantons of Ticino and Graubünden and flows through the valleys Val Cadlimo and Val Medel. Rein da Medel is the local Sursilvan, name in Graubünden, which is commonly used to denote the ticinese part as well.

The Brescia and Garda Prealps are a mountain range in the southern part of the Alps. They are located mainly in Lombardy but also in Trentino Alto Adige and in Veneto, in the northern part of Italy.

Alta Valsugana e Bersntol is one of the sixteen districts of Trentino in the Italian region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. Its administrative seat and major town is Pergine Valsugana.

The Garda Mountains, occasionally also the Garda Hills, are an extensive mountain range of the Southern Limestone Alps in northern Italy.

The Cismon is a mountain stream in northern Italy, the main tributary of the Brenta River. The torrent flows from the Dolomites mountains in the Trentino Alto-Adige region through the plains of Venetian territory to the bigger Brenta River, which in turn flows into the Adriatic Sea in the Gulf of Venice.

The Alpini Battalion "Val Chiese" is an inactive mountain warfare battalion of the Italian Army based last in Sterzing in South Tyrol. The battalion belongs to the Italian Army's Alpini infantry speciality and was assigned to the Alpine Brigade "Orobica". In 1915, the Royal Italian Army's 5th Alpini Regiment formed the Alpini Battalion "Val Chiese", which fought in World War I in the alpine areas of the Italian front. The battalion was disbanded in 1919.

The Italian geographic region, Italian physical region or Italian region is a geographical region of Southern Europe delimited to the north by the mountain chains of the Alps. This subregion is composed of a peninsular and continental part and an insular part. Located between the Balkan Peninsula and the Iberian Peninsula, it protrudes into the centre of the Mediterranean Sea and overlooks the Adriatic Sea, the Ionian Sea, the Ligurian Sea, the Sardinian Channel, the Sea of Corsica, the Sea of Sardinia, the Strait of Sicily, and the Tyrrhenian Sea.

The Austro-Hungarian fortifications on the Italian border were constructed in the 19th and early 20th centuries to protect against invasion from Italy. Most were built in what is today the Trentino-Alto Adige region; some built outside this territory were ceded to Italy after 1866. By the First World War many of them were obsolete, but nevertheless played a role in deterring and containing Italian assaults.

Mount Cingolo Rosso is a mountain in the Brescia and Garda Prealps belonging to the Caplone-Tombea group, a subgroup of Mount Stino, and reaches an altitude of 1,102 metres.





















