
The Battle of Blenheim fought on 13 August [O.S. 2 August] 1704, was a major battle of the War of the Spanish Succession. The overwhelming Allied victory ensured the safety of Vienna from the Franco-Bavarian army, thus preventing the collapse of the reconstituted Grand Alliance.
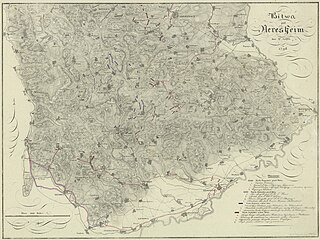
The Battle of Neresheim was fought by the Republican French army under Jean Victor Marie Moreau against the army of the Habsburg monarchy of Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. Pursued by Moreau's Army of Rhin-et-Moselle, Charles launched an attack against the French. While the Austrian left wing saw some success, the battle degenerated into a stalemate and the archduke withdrew further into the Electorate of Bavaria. Neresheim is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg in Germany a distance of 57 kilometres (35 mi) northeast of Ulm. The action took place during the War of the First Coalition, part of a larger conflict called the French Revolutionary Wars.
The Battle of Rastatt saw part of a Republican French army under Jean Victor Marie Moreau clash with elements of the Habsburg army under Maximilian Anton Karl, Count Baillet de Latour which were defending the line of the Murg River. Leading a wing of Moreau's army, Louis Desaix attacked the Austrians and drove them back to the Alb River in the War of the First Coalition action. Rastatt is a city in the state of Baden-Württemberg in Germany, located 89 kilometers (55 mi) south of Mannheim and 94 kilometres (58 mi) west of Stuttgart.

The Battle of Hastenbeck was fought as part of the Invasion of Hanover during the Seven Years' War between the allied forces of Hanover, Hesse-Kassel and Brunswick, and the French. The allies were defeated by the French army near Hamelin in the Electorate of Hanover.

The Battle of Gravelotte on 18 August 1870 was the largest battle of the Franco-Prussian War. Named after Gravelotte, a village in Lorraine, it was fought about 6 miles (9.7 km) west of Metz, where on the previous day, having intercepted the French army's retreat to the west at the Battle of Mars-la-Tour, the Prussians were now closing in to complete the destruction of the French forces.

The Battle of Mars-la-Tour was fought on 16 August 1870, during the Franco-Prussian War, near the village of Mars-La-Tour in northeast France. One Prussian corps, reinforced by two more later in the day, encountered the entire French Army of the Rhine in a meeting engagement and, following the course of battle, the Army of the Rhine retreated toward the fortress of Metz.

The Battle of Teugen-Hausen or the Battle of Thann was an engagement that occurred during the War of the Fifth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle was fought on 19 April 1809 between the French III Corps led by Marshal Louis-Nicolas Davout and the Austrian III Armeekorps commanded by Prince Friedrich Franz Xaver of Hohenzollern-Hechingen. The French won a hard-fought victory over their opponents when the Austrians withdrew that evening. The site of the battle is a wooded height approximately halfway between the villages of Teugn and Hausen in Lower Bavaria, part of modern-day Germany.

Klausen is an Ortsgemeinde – a municipality belonging to a Verbandsgemeinde, a kind of collective municipality – in the Bernkastel-Wittlich district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.

The Battle of Schleiz took place on October 9, 1806 in Schleiz, Germany between a Prussian-Saxon division under Bogislav Friedrich Emanuel von Tauentzien and a part of Jean-Baptiste Bernadotte's I Corps under the command of Jean-Baptiste Drouet, Comte d'Erlon. It was the first clash of the War of the Fourth Coalition, part of the Napoleonic Wars. As Emperor Napoleon I of France's Grande Armée advanced north through the Franconian Forest it struck the left wing of the armies belonging to the Kingdom of Prussia and the Electorate of Saxony, which were deployed on a long front. Schleiz is located 30 kilometers north of Hof and 145 kilometers southwest of Dresden at the intersection of Routes 2 and 94.

The Battle of Kaiserslautern saw a Coalition army under Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel oppose a Republican French army led by Lazare Hoche. Three days of conflict resulted in a victory by the Prussians and their Electoral Saxon allies as they turned back repeated French attacks. The War of the First Coalition combat was fought near the city of Kaiserslautern in the modern-day state of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, which is located about 60 kilometres (37 mi) west of Mannheim.
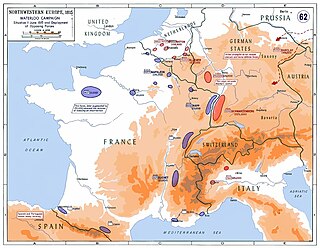
On 1 March 1815 Napoleon Bonaparte escaped from his imprisonment on the isle of Elba, and launched a bid to recover his empire. A confederation of European powers pledged to stop him. During the period known as the Hundred Days Napoleon chose to confront the armies of Prince Blücher and the Duke of Wellington in what has become known as the Waterloo Campaign. He was decisively defeated by the two allied armies at the Battle of Waterloo, which then marched on Paris forcing Napoleon to abdicate for the second time. However Russia, Austria and some of the minor German states also fielded armies against him and all of them also invaded France. Of these other armies the ones engaged in the largest campaigns and saw the most fighting were two Austrian armies: The Army of the Upper Rhine and the Army of Italy.

Karl Aloys zu Fürstenberg was an Austrian military commander. He achieved the rank of Field Marshal and died at the Battle of Stockach.

The Battle of Ettlingen or Battle of Malsch was fought during the French Revolutionary Wars between the armies of the First French Republic and Habsburg Austria near the town of Malsch, 9 kilometres (6 mi) southwest of Ettlingen. The Austrians under Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen tried to halt the northward advance of Jean Victor Marie Moreau's French Army of Rhin-et-Moselle along the east bank of the Rhine River. After a tough fight, the Austrian commander found that his left flank was turned. He conceded victory to the French and retreated east toward Stuttgart. Ettlingen is located 10 kilometres (6 mi) south of Karlsruhe.

At the Battle of Emmendingen, on 19 October 1796, the French Army of Rhin-et-Moselle under Jean Victor Marie Moreau fought the First Coalition Army of the Upper Rhine commanded by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. Emmendingen is located on the Elz River in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, 9 miles (14 km) north of Freiburg im Breisgau. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition, the first phase of the larger French Revolutionary Wars.

The Battle of Czarnowo on the night of 23–24 December 1806 saw troops of the First French Empire under the eye of Emperor Napoleon I launch an evening assault crossing of the Wkra River against Lieutenant General Alexander Ivanovich Ostermann-Tolstoy's defending Russian Empire forces. The attackers, part of Marshal Louis-Nicolas Davout's III Corps, succeeded in crossing the Wkra at its mouth and pressed eastward to the village of Czarnowo. After an all-night struggle, the Russian commander withdrew his troops to the east, ending this War of the Fourth Coalition action. Czarnowo is located on the north bank of the Narew River 33 kilometres (21 mi) north-northwest of Warsaw, Poland.

The Battle of Neuensund was a smaller battle at Neuensund of the Seven Years' War between Swedish and Prussian forces fought on September 18, 1761. The Swedish force under the command of Jacob Magnus Sprengtporten managed to rout the Prussian forces commanded by Wilhelm Sebastian von Belling.
The Battle of Kaiserslautern saw an army from the Kingdom of Prussia and Electoral Saxony led by Wichard Joachim Heinrich von Möllendorf fall upon a single French Republican division under Jean-Jacques Ambert from the Army of the Moselle. The Prussians tried to surround their outnumbered adversaries but most of the French evaded capture. Nevertheless, Möllendorf's troops inflicted casualties on the French in the ratio of nine-to-one and occupied Kaiserslautern. While the Prussians won this triumph on an unimportant front, the French armies soon began winning decisive victories in Belgium and the Netherlands. The battle occurred during the War of the First Coalition, part of the French Revolutionary Wars. In 1794 Kaiserslautern was part of the Electoral Palatinate but today the city is located in the state of Rhineland-Palatinate in Germany about 67 kilometres (42 mi) west of Mannheim.
The Battle of Haguenau saw a Republican French army commanded by Jean-Charles Pichegru mount a persistent offensive against a Coalition army under Dagobert Sigmund von Wurmser during the War of the First Coalition. In late November, Wurmser pulled back from his defenses behind the Zorn River and assumed a new position along the Moder River at Haguenau. After continuous fighting, Wurmser finally withdrew to the Lauter River after his western flank was turned in the Battle of Froeschwiller on 22 December. Haguenau is a city in Bas-Rhin department of France, located 29 kilometres (18 mi) north of Strasbourg.


The Battle of Saint-Julien saw Imperial French troops led by Jean Gabriel Marchand attack Austrian soldiers under Johann Nepomuk von Klebelsberg. In tough fighting, the Austrians managed to hold off persistent French assaults during this War of the Sixth Coalition clash. The next day, the Austrians withdrew within the defenses of Geneva, a distance of 9 kilometres (6 mi) to the northeast. The battle was part of operations in which a French army led by Marshal Pierre Augereau squared off against Austrian forces under Ferdinand, Graf Bubna von Littitz.



















