
Fort Hughes was built by the Philippine Department of the U.S. Army on Caballo Island in the Philippines in the early 1900s. The fort, which part of the Harbor Defenses of Manila and Subic Bays, was named for Major General Robert Patterson Hughes, a veteran of the American Civil War, Spanish–American War, and the Philippine–American War.

Cotabato, formerly and still commonly referred to as North Cotabato and officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan, the most populous in the province. Some of its municipalities are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

Wendell Fertig was an American civil engineer, in the American-administered Commonwealth of the Philippines, who organized and commanded an American-Filipino guerrilla force on the Japanese-occupied, southern Philippine island of Mindanao during World War II. Fertig's widely scattered guerrilla force numbered approximately 32,000. He faced about 50,000 Japanese soldiers, mostly garrison troops in towns and cities.

Malabang, officially the Municipality of Malabang, is a 3rd class municipality in the province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 49,088 people. The town is one of the two former capitals of the Sultanate of Maguindanao from 1515 until the Spanish conquered the land in 1888.

Parang, officially the Municipality of Parang, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Maguindanao del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 102,914 people.

The Battle of Mindanao was fought by the Americans and allied Filipino guerrillas against the Japanese forces on the island of Mindanao in the Philippines as part of Operation VICTOR V. It was part of the campaign to liberate the Philippines during World War II. The battle was waged to complete the recapture of the southernmost portions of the archipelago from the Imperial Japanese Army.

Ruperto Cadava Kangleón was a Filipino military officer and politician. He was a native of the municipality of Macrohon in the province now named Southern Leyte.

The 21st Infantry Regiment ("Gimlet") is a United States Army infantry regiment. The 1st Battalion currently exists as part of 2nd Infantry Brigade Combat Team, 25th Infantry Division. The regiment fought in World War II, the Korean War and the Vietnam War, as well as Operation Iraqi Freedom. Task Force Smith, the first American unit to see action in the Korean War, was derived from the regiment's 1st Battalion.

Marine Fighting Squadron 218 (VMF-218) was a reserve fighter squadron of the United States Marine Corps that was originally activated during World War II. Known as the "Hellions", they flew throughout the South Pacific but saw the majority of their fighting during the Philippines Campaign (1944–45). The squadron was credited with downing 18 enemy aircraft during the course of the war.

Russell William Volckmann was a graduate of the United States Military Academy at West Point, a U.S. Army infantry officer and a leader of the Philippine Commonwealth military and guerrilla resistance to the Japanese conquest of the Philippines during World War II. After the war, he remained in the U.S. Army and helped create the U.S. Army Special Forces. Volckmann, together with Colonels Aaron Bank and Wendell Fertig are considered the founders of the U.S. Army Special Forces. He eventually retired as a brigadier general.

Datu Salipada Khalid Pendatun was a Filipino lawyer, military officer, and politician, being the first Filipino Muslim in history to hold these offices.
Camp Iranun is a Philippine Army military base located in Barira, Maguindanao del Norte, Philippines. It is named after the Iranun people, a Moro ethnic group native to the area encompassing the boundaries of Maguindanao del Norte, Maguindanao del Sur, Lanao del Sur and North Cotabato provinces.

The 81st Infantry Division was a reserve division of the Philippine Army under the United States Army Forces in the Far East (USAFFE). It was established in the prewar period and fought 1941–1942. Its troops are from Cebu, Bohol, and Leyte but most of its troops are Americans and junior officers are Filipinos coming mostly from Luzon. The division served in defense of Mindanao but it never commanded the 4 of its maneuver regiments but was supplemented with 61st Infantry from Panay and 73rd Infantry from Negros. Also, 2nd Regular Regiment was transferred to its command in the early part of Japanese invasion of Mindanao.

Datu Ali was the Rajahmuda of Tinungkup within the Sultanate of Buayan before succeeding his cousin, Datu Uto, as Rajah of Buayan formally from Uto's death in 1902 until his death in 1905. He was the cousin of Datu Uto of Buayan and brother of Datu Djimbangan and Sultan Tambilawan of Kudarangan, and as a rising leader, Datu Ali overpowered his brothers to rule over Kudarangan.

Edward Ernest McClish (1909-1993) was an American military officer in the Philippines in World War II. During the Japanese occupation of the Philippines, Lt. Colonel McClish commanded a division of Filipino guerrillas on Mindanao island.

61st Infantry Regiment was a military unit and formation of the Philippine Army, activated in August 1941 in Panay Island. It is under the command of 61st Infantry Division. The regiment collapsed in May 1942 with its commanding officer captured by the Japanese Army in Lanao.

The 73rd Infantry Regiment of the Philippine Commonwealth Army was activated on August 25, 1941, was inducted to United States Army Forces in the Far East on September 1, 1941, by Captain Eugene B. Hicker of US Army. It was the last regiment among the three authorized to organized so it was not included when the entire 71st Infantry Division was ordered transferred to the main island of Luzon in September 1941.
Japanese Invasion of Malabang was part of the Japanese landings on the western coast of Mindanao that began on April 29, 1942. Kawaguchi Detachment landed in three important points in west coast of Mindanao including Malabang in then undivided Lanao Province. Defending forces of Filipino and American troops resisted but lacked artillery, and due to Japanese naval and air support were overwhelmed and forced to retreat.
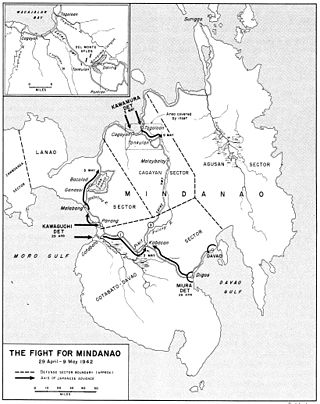
Japanese invasion of Cotabato is one of the three landings made by Japanese Army during their

84th Infantry Regiment is a provisional military unit and formation of the Philippine Army organized during WW II to bolster the defense of Lanao Sector. It fought in Lanao during Japanese landing in Malabang and moved northward to Dansalan.















