| Battle of Paso de Cuevas | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Paraguayan War | |||||||
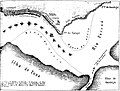
 Battle of Cuevas, 12 August 1865 (José Murature). | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
3 frigates 3 corvettes 5 gunboats 1 transport | 3,000 soldiers [1] 34 cannons | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 24 killed 42 wounded [1] | Unknown | ||||||
The Battle of Paso de Cuevas was fought on 12 August 1865 during the Paraguayan invasion of the Argentine province of Corrientes.
Contents
Following losses after the Battle of Riachuelo, and running the gauntlet set up by José María Bruguez at Bella Vista in the Battle of Paso de Mercedes the day before, the allied fleet advanced down the River Paraná, not wanting to be cut off from its supply base. [2] However, the pass at Cuevas was once again manned by 3,000 of Bruguez's men with 34 guns. Barroso suffered 24 dead and 42 wounded. [3]
This was the last operation of naval combat of the Argentine Navy at war with foreign nations prior to the Falklands War.